Conflict Resolution Tips for Scrum Masters: Keeping Teams on Track Effective conflict resolution is a critical skill for Scrum Masters, as conflicts are inevitable in dynamic, high-performing teams. Managed well, conflicts can lead to growth, better ideas, and stronger team cohesion. However, if left unresolved, they can derail progress and harm morale. In this blog, we’ll explore actionable conflict resolution tips that Scrum Masters can use to keep their teams on track and thriving. Understanding the Nature of Conflicts in Agile Teams Conflicts in Agile teams arise from various sources, including: Divergent perspectives: Team members often have different ideas on how to approach a problem or implement a solution. Role confusion: Misunderstandings about responsibilities can lead to friction. Pressure to deliver: Tight deadlines and high expectations can create stress and disagreements. Cultural differences: Teams working in distributed or multicultural environments may experience conflicts due to communication styles or cultural norms. Recognizing these sources is the first step in resolving conflicts effectively. Key Conflict Resolution Tips for Scrum Masters 1. Create a Safe Environment for Open Dialogue Teams need a safe space where they can express concerns without fear of judgment or retaliation. Scrum Masters play a pivotal role in fostering psychological safety. Actionable Steps: Encourage team members to speak up during retrospectives and daily stand-ups. Reinforce positive behaviors, such as active listening and respectful disagreement. Intervene when necessary to prevent escalation. 2. Use Active Listening Techniques Active listening is crucial for understanding the root cause of a conflict. Scrum Masters should listen not just to respond, but to understand. Tips for Active Listening: Maintain eye contact and open body language. Paraphrase what the speaker has said to confirm understanding. Avoid interrupting or jumping to conclusions. By practicing active listening, you can build trust and defuse tensions. 3. Facilitate Constructive Discussions When conflicts arise, Scrum Masters should facilitate discussions that lead to solutions rather than blame. Best Practices: Focus on the issue, not the individual. Encourage team members to propose solutions. Guide the team towards a consensus by summarizing points and identifying common ground. 4. Leverage Agile Values and Principles The Agile Manifesto emphasizes collaboration, respect, and adaptability. Scrum Masters should remind teams of these core values when conflicts arise. How to Apply Agile Values: Emphasize the importance of working together to deliver value. Encourage flexibility and openness to change. Reinforce the principle of continuous improvement. 5. Address Conflicts Early Small disagreements can escalate into major conflicts if not addressed promptly. Scrum Masters should be proactive in identifying and resolving issues early. Early Intervention Tips: Pay attention to non-verbal cues, such as body language or tone of voice, that indicate tension. Check in with team members regularly to gauge morale. Use one-on-one meetings to address sensitive issues discreetly. 6. Use Conflict Resolution Frameworks Having a structured approach to conflict resolution can help Scrum Masters navigate difficult situations more effectively. Popular Frameworks: The Interest-Based Relational Approach (IBR): Focuses on preserving relationships while addressing the underlying interests of all parties. Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Mode Instrument (TKI): Identifies different conflict-handling styles (e.g., competing, collaborating, compromising) and helps choose the best approach for the situation. 7. Promote Empathy and Understanding Empathy is key to resolving conflicts and building stronger teams. By understanding each other’s perspectives, team members can find common solutions. How to Foster Empathy: Encourage team members to share their viewpoints and feelings. Promote cross-functional collaboration to build mutual respect. Lead by example by showing empathy in your interactions. 8. Document and Reflect on Resolutions Once a conflict is resolved, it’s important to document the outcome and reflect on lessons learned. Steps for Documentation: Record key points discussed and the agreed-upon solution. Share the resolution with the team during a retrospective. Use the experience to improve team processes and avoid similar conflicts in the future. 9. Seek External Help When Necessary In some cases, conflicts may require external intervention. Scrum Masters should know when to escalate issues to HR or seek help from an Agile coach. When to Escalate: When conflicts persist despite multiple attempts at resolution. When a conflict begins to impact team performance or well-being. When personal issues or unethical behavior are involved. Common Mistakes Scrum Masters Should Avoid Ignoring conflicts: Pretending that conflicts don’t exist can lead to bigger problems later. Taking sides: Scrum Masters should remain neutral and focus on facilitating resolution. Over-controlling the process: Allow the team to take ownership of conflict resolution while providing guidance. Tools and Techniques for Conflict Resolution Retrospectives: Use retrospectives to surface and address underlying tensions. Collaboration tools: Platforms like Miro or MURAL can help visualize ideas and facilitate discussions in distributed teams. Anonymous feedback: Encourage team members to provide feedback anonymously if they are hesitant to speak up directly. Conclusion: Foster a Culture of Collaboration Effective conflict resolution is not just about managing disagreements—it’s about fostering a culture of collaboration, empathy, and continuous improvement. As a Scrum Master, your role is to guide the team through challenges and help them grow stronger together. Ready to take your conflict resolution skills to the next level? Start by implementing one or two tips from this blog and observe the difference in your team dynamics. Don’t forget to share this blog with fellow Scrum Masters and agile practitioners!
Author: Admin
The Role of a Scrum Master in Scaling Agile Frameworks
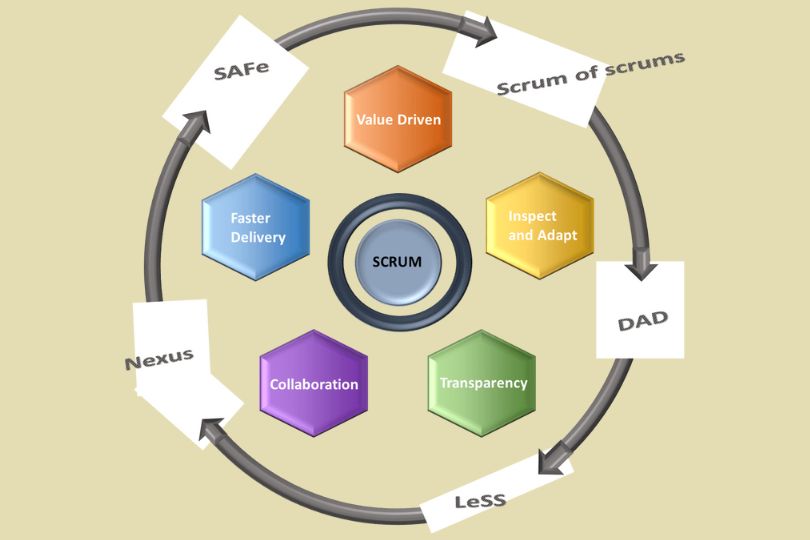
The Role of a Scrum Master in Scaling Agile Frameworks Scaling agile frameworks is becoming essential as organizations grow and seek to extend agile practices across multiple teams. In this environment, the role of a Scrum Master becomes more critical and complex. Unlike traditional Scrum implementations that focus on a single team, scaling requires Scrum Masters to collaborate across teams, manage interdependencies, and ensure the smooth flow of value. This blog will delve into the vital role of a Scrum Master in scaling agile frameworks, offering actionable insights and tips. Why Scaling Agile Frameworks is Important Organizations adopt scaling frameworks like SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework), LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum), and Nexus to coordinate multiple agile teams working on large, complex projects. Scaling enables: Alignment across teams and stakeholders. Increased efficiency by reducing bottlenecks. Consistent value delivery across all levels of the organization. However, scaling also introduces challenges in communication, coordination, and governance—which is where the Scrum Master plays a pivotal role. Key Responsibilities of a Scrum Master in Scaling Agile 1. Facilitating Cross-Team Collaboration In a scaled environment, multiple teams work towards a common goal. Ensuring effective collaboration between teams is crucial. Tips for Effective Collaboration: Conduct Scrum of Scrums: Regular cross-team meetings to discuss progress, dependencies, and impediments. Use shared tools: Platforms like Jira or Azure DevOps can help maintain transparency and track progress. Encourage open communication: Promote a culture where teams feel comfortable sharing concerns and updates. 2. Managing Dependencies and Impediments Scaling frameworks often introduce dependencies between teams. Scrum Masters must identify and manage these dependencies to prevent delays. How to Manage Dependencies: Create a dependency board: Visualize inter-team dependencies and track their resolution. Engage Product Owners: Work closely with Product Owners to prioritize backlog items based on dependencies. Escalate issues: When necessary, escalate impediments that cannot be resolved at the team level. 3. Ensuring Consistency in Scrum Practices When scaling, consistency in Scrum practices across teams ensures that everyone is aligned and working efficiently. Steps to Ensure Consistency: Standardize ceremonies: Ensure that all teams follow the same sprint cadence and conduct similar ceremonies. Provide training: Offer ongoing training and coaching to new teams and members. Monitor adherence: Use metrics to track whether teams are following Scrum principles. 4. Coaching and Mentoring Teams The Scrum Master’s role as a coach becomes more pronounced in a scaled environment. Teams may have varying levels of maturity in agile practices. Coaching Strategies: Tailor coaching to team maturity: More mature teams may need coaching on advanced topics, while newer teams may need foundational guidance. Promote self-organization: Encourage teams to take ownership of their processes and decisions. Foster a growth mindset: Help teams embrace continuous improvement. 5. Driving Continuous Improvement Continuous improvement is a core agile principle. In a scaled environment, Scrum Masters must ensure that not only individual teams but the entire organization is improving. Methods to Drive Improvement: Conduct retrospectives: Hold regular retrospectives at both the team and program level. Track improvement actions: Maintain a backlog of improvement actions and track their implementation. Leverage metrics: Use metrics like lead time, cycle time, and team velocity to identify areas for improvement. Key Challenges in Scaling Agile Frameworks 1. Communication Overhead As the number of teams increases, so does the complexity of communication. Scrum Masters must establish clear communication channels and ensure information flows efficiently. 2. Resistance to Change Scaling often involves significant organizational changes. Resistance from teams and stakeholders can hinder progress. How to Overcome Resistance: Communicate the benefits: Clearly explain how scaling will benefit the organization and the teams. Involve stakeholders early: Engage stakeholders in the scaling process from the beginning. Celebrate small wins: Recognize and celebrate milestones to build momentum. 3. Maintaining Team Autonomy While scaling requires coordination, it’s important to maintain the autonomy of individual teams. Balancing Autonomy and Alignment: Define clear boundaries: Establish what decisions teams can make independently and what requires cross-team alignment. Promote decentralized decision-making: Encourage teams to make decisions at the lowest possible level. Best Practices for Scrum Masters in Scaling Agile Adopt a servant-leader mindset: Focus on serving the teams and enabling them to deliver value. Build a community of practice: Establish a forum where Scrum Masters can share experiences and best practices. Stay updated: Continuously learn about new scaling frameworks and techniques by attending conferences and reading industry publications. Use visual management tools: Tools like Kanban boards and dashboards can help visualize progress and bottlenecks. Commonly Used Scaling Frameworks 1. Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) SAFe is one of the most popular frameworks for scaling agile. It provides detailed guidelines on roles, ceremonies, and artifacts at different levels. 2. Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS) LeSS is a simpler approach to scaling that focuses on extending Scrum principles to multiple teams. 3. Nexus Nexus, developed by Scrum.org, emphasizes integration and coordination between teams working on the same product. Conclusion Scaling agile frameworks can transform how organizations deliver value, but it comes with its share of challenges. As a Scrum Master, your role in scaling is pivotal—you facilitate collaboration, manage dependencies, and drive continuous improvement. Ready to take your Scrum Master skills to the next level? Explore advanced certifications like SAFe Scrum Master or LeSS Practitioner, and join our community of agile professionals. If you found this blog helpful, share it with your peers and leave a comment below with your thoughts and experiences!
Overcoming Challenges as a Scrum Master in Distributed Teams
Overcoming Challenges as a Scrum Master in Distributed Teams Distributed teams have become the norm in today’s workplace, driven by globalization, remote work trends, and the need to tap into diverse talent pools. While distributed teams offer numerous benefits, they also present unique challenges, especially for Scrum Masters tasked with fostering collaboration, communication, and productivity across dispersed team members. This blog explores key challenges faced by Scrum Masters in distributed teams and offers actionable strategies to overcome them. 1. Communication Barriers Challenges In distributed teams, communication is often asynchronous due to time zone differences, leading to delays and misunderstandings. The lack of face-to-face interaction can hinder the flow of information and reduce clarity. Solutions Leverage communication tools: Use platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Zoom for real-time communication and asynchronous updates. Set communication norms: Establish guidelines on response times, meeting etiquettes, and preferred communication channels. Promote transparency: Encourage team members to document decisions and share updates in a centralized platform like Confluence or Jira. By setting clear communication protocols and leveraging technology, Scrum Masters can bridge the communication gap and foster a collaborative environment. 2. Building Trust and Team Cohesion Challenges In distributed setups, team members often miss out on informal interactions that build trust and camaraderie. Without strong relationships, collaboration may suffer. Solutions Virtual team-building activities: Organize virtual games, coffee chats, or happy hours to help team members bond. Foster psychological safety: Create an environment where everyone feels safe to express their opinions without fear of judgment. Encourage knowledge sharing: Promote pair programming, code reviews, and cross-functional collaborations to build trust through shared experiences. Building trust takes time, but consistent efforts by the Scrum Master can help create a cohesive and high-performing distributed team. 3. Time Zone Differences Challenges When team members are spread across multiple time zones, scheduling meetings and synchronizing work can be difficult. Solutions Use overlapping hours effectively: Identify overlapping hours where most team members are available and schedule critical meetings during these windows. Adopt asynchronous practices: Encourage the use of recorded updates, detailed meeting notes, and asynchronous sprint reviews or retrospectives. Rotate meeting times: To ensure fairness, rotate meeting times so that no single group always bears the burden of late-night or early-morning meetings. Managing time zone differences requires flexibility and creative scheduling to ensure inclusivity and engagement. 4. Maintaining Engagement and Motivation Challenges Remote work can sometimes lead to feelings of isolation, disengagement, and reduced motivation among team members. Solutions Regular check-ins: Schedule one-on-one meetings to understand individual concerns and offer support. Celebrate achievements: Acknowledge and reward team successes, both big and small, to boost morale. Provide growth opportunities: Encourage team members to pursue certifications, attend webinars, or participate in conferences. An engaged team is more productive, and Scrum Masters play a pivotal role in keeping motivation levels high. 5. Ensuring Accountability Challenges In a distributed setup, it can be harder to track progress and ensure that everyone is accountable for their tasks. Solutions Use visual management tools: Utilize tools like Jira, Trello, or Azure DevOps to track tasks, progress, and impediments. Define clear goals: Set clear sprint goals and ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. Conduct regular stand-ups: Use daily stand-ups to provide visibility into progress and identify roadblocks early. By fostering a culture of accountability, Scrum Masters can ensure that distributed teams remain focused and productive. 6. Addressing Cultural Differences Challenges Distributed teams often consist of members from diverse cultural backgrounds, which can lead to misunderstandings and varying work styles. Solutions Promote cultural awareness: Encourage team members to share their cultural practices and holidays to foster mutual understanding. Adapt communication styles: Be mindful of cultural differences in communication, such as directness or formality. Provide diversity training: Offer training sessions to help the team appreciate and leverage cultural diversity. A culturally aware team can turn diversity into a strength, enhancing creativity and innovation. 7. Facilitating Effective Meetings Challenges Virtual meetings can often be less engaging, with distractions and technical issues reducing their effectiveness. Solutions Prepare in advance: Share agendas and required pre-reading materials ahead of time. Use interactive tools: Incorporate tools like Miro, MURAL, or Poll Everywhere to make meetings more interactive. Limit meeting durations: Keep meetings short and focused to maintain engagement. Effective meetings are crucial for collaboration, and Scrum Masters must ensure they are well-structured and productive. 8. Managing Impediments Remotely Challenges Identifying and resolving impediments can be more difficult when the team is not co-located. Solutions Create an impediment board: Use a shared digital board to track and prioritize impediments. Encourage open communication: Foster an environment where team members feel comfortable raising issues. Collaborate with stakeholders: Work closely with product owners and other stakeholders to address impediments quickly. Proactively managing impediments helps maintain the team’s velocity and ensures smooth sprint execution. 9. Balancing Work-Life Boundaries Challenges Remote work can blur the lines between personal and professional life, leading to burnout. Solutions Encourage breaks: Remind team members to take regular breaks and respect their time off. Set clear expectations: Define working hours and ensure team members aren’t expected to be online beyond those hours. Lead by example: As a Scrum Master, model healthy work-life boundaries. Maintaining a healthy work-life balance is essential for long-term team well-being and performance. Conclusion Mastering the art of leading distributed teams is a continuous journey. As a Scrum Master, your ability to overcome challenges in communication, engagement, and collaboration directly impacts your team’s success. Start by implementing the strategies discussed in this blog, and don’t hesitate to experiment with new practices. Are you currently leading a distributed team? What challenges have you faced, and how have you addressed them? Share your experiences in the comments below, and let’s learn from each other!
Scrum Master vs. Project Manager: What’s the Difference?
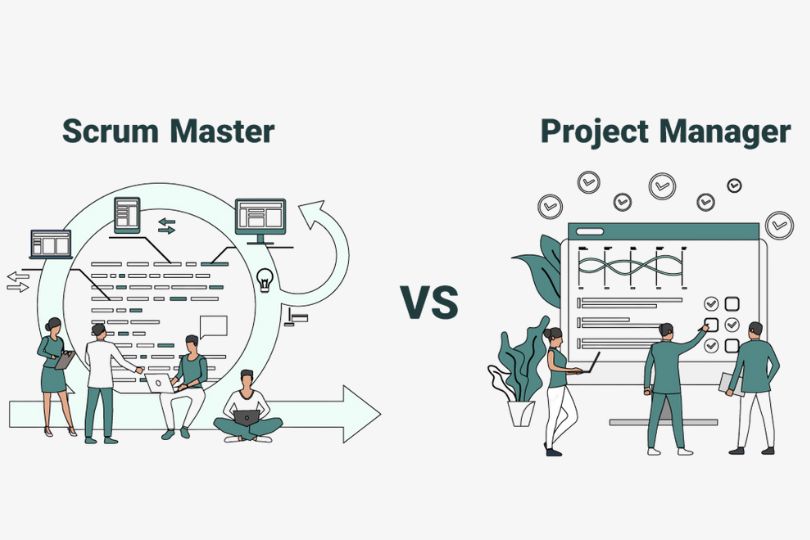
Scrum Master vs. Project Manager: What’s the Difference? The roles of Scrum Master and Project Manager often create confusion due to their overlapping responsibilities in managing projects. However, they serve distinct functions, especially in organizations adopting agile methodologies. This blog explores the key differences between a Scrum Master and a Project Manager, providing actionable insights to help professionals better understand these roles and choose the right career path. 1. Core Responsibilities Scrum Master Responsibilities A Scrum Master focuses on facilitating the Scrum framework and ensuring the team adheres to agile principles. Facilitates Scrum ceremonies: Manages daily stand-ups, sprint planning, reviews, and retrospectives. Removes impediments: Identifies and eliminates obstacles that hinder the team’s progress. Coaches the team: Guides the team in adopting agile practices and becoming self-organizing. Protects the team: Shields the team from external disruptions and distractions. Project Manager Responsibilities A Project Manager oversees the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to closure, ensuring it meets its objectives. Defines project scope: Establishes the project’s goals, deliverables, and timeline. Manages resources: Allocates and manages team members, budget, and tools. Tracks progress: Monitors project performance, timelines, and milestones. Communicates with stakeholders: Maintains regular communication with clients, sponsors, and team members. Key Takeaway: While a Scrum Master ensures the team follows agile practices, a Project Manager focuses on delivering the project within the defined constraints. 2. Approach to Work Scrum Master’s Approach Servant-leader mindset: Acts as a facilitator rather than a traditional manager. Iterative delivery: Encourages incremental progress through sprints. Team empowerment: Fosters a collaborative environment where the team makes key decisions. Project Manager’s Approach Command and control: Often takes a directive approach in managing tasks and resources. Sequential process: Uses a linear approach (Waterfall) or a hybrid model for project execution. Accountability: Holds responsibility for project outcomes, including budget and timeline adherence. Key Takeaway: A Scrum Master supports an agile, iterative approach, while a Project Manager typically follows a structured, linear methodology. 3. Focus Area Scrum Master’s Focus Team performance: Prioritizes team cohesion, communication, and productivity. Process improvement: Continuously enhances team processes through retrospectives. Project Manager’s Focus Project delivery: Concentrates on meeting project goals, timelines, and budgets. Stakeholder satisfaction: Ensures that the project meets stakeholder expectations and delivers value. Key Takeaway: Scrum Masters emphasize team dynamics and agile processes, whereas Project Managers focus on achieving project deliverables. 4. Tools and Metrics Tools Used by Scrum Masters Agile tools: Jira, Trello, and Azure DevOps for sprint management. Collaboration tools: Slack, Zoom, and Miro for team communication. Metrics: Velocity, cycle time, and sprint burndown charts to track progress. Tools Used by Project Managers Project management software: Microsoft Project, Asana, and Monday.com for project planning. Reporting tools: Gantt charts, dashboards, and earned value analysis (EVA) for performance tracking. Metrics: Budget variance, schedule variance, and resource utilization. Key Takeaway: Both roles use different sets of tools and metrics tailored to their specific responsibilities. 5. Certifications Scrum Master Certifications Certified ScrumMaster (CSM): Offered by Scrum Alliance. Professional Scrum Master (PSM): Provided by Scrum.org. SAFe Scrum Master: Focuses on scaled agile frameworks. Project Manager Certifications Project Management Professional (PMP): Offered by PMI, globally recognized. PRINCE2: A process-based approach to project management. Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM): Entry-level certification by PMI. Key Takeaway: Certifications play a crucial role in validating skills for both Scrum Masters and Project Managers. 6. Career Path and Opportunities Scrum Master’s Career Path Entry-level roles: Scrum Master, Agile Coach. Mid-level roles: Senior Scrum Master, Program Manager. Advanced roles: Enterprise Agile Coach, Head of Agile Practices. Project Manager’s Career Path Entry-level roles: Assistant Project Manager, Project Coordinator. Mid-level roles: Project Manager, Program Manager. Advanced roles: Portfolio Manager, Director of Project Management. Key Takeaway: Both career paths offer opportunities for advancement, but they cater to different interests and skill sets. 7. When to Choose Which Role? Choose Scrum Master If: You enjoy facilitating team collaboration. You are passionate about agile methodologies. You prefer a servant-leader role over a directive one. Choose Project Manager If: You excel at planning and managing complex projects. You enjoy working across different project phases. You are comfortable taking accountability for project delivery. Key Takeaway: Your choice should depend on your strengths, career goals, and interest in either team facilitation or project execution. If you’re considering a career in project management or agile coaching, understanding the differences between these roles is crucial. Whether you’re inclined toward leading agile teams as a Scrum Master or managing complex projects as a Project Manager, there are numerous growth opportunities in both fields. Ready to take the next step? Explore relevant certifications, join agile communities, and start your journey today!
Key Skills Every Scrum Master Needs in 2025
Key Skills Every Scrum Master Needs in 2025 The role of a Scrum Master has evolved significantly over the years, and 2025 brings new challenges and opportunities. As organizations increasingly adopt agile methodologies to stay competitive, Scrum Masters must enhance their skill sets to remain effective. This blog explores the key skills every Scrum Master needs in 2025, offering actionable insights to help you excel in this dynamic role. 1. Advanced Facilitation Skills In 2025, effective facilitation goes beyond running daily stand-ups or sprint retrospectives. Scrum Masters must create an environment where team members feel heard and empowered to contribute. Tips to Enhance Facilitation: Use visual aids: Tools like digital whiteboards or collaboration platforms can make meetings more engaging. Encourage participation: Use techniques such as round-robin or silent brainstorming to involve quieter team members. Handle conflicts tactfully: Develop conflict resolution techniques to keep discussions productive. By mastering advanced facilitation, you can foster better collaboration and drive meaningful outcomes. 2. Emotional Intelligence (EI) Emotional intelligence is becoming increasingly critical as Scrum Masters work with cross-functional and diverse teams. Key Aspects of EI: Empathy: Understand the perspectives and emotions of team members. Self-awareness: Recognize your own emotions and how they affect your interactions. Relationship management: Build strong, trust-based relationships with stakeholders and team members. Scrum Masters with high EI can create a psychologically safe environment that enhances team performance. 3. Technical Acumen While Scrum Masters aren’t expected to be developers, having a solid understanding of technology can improve their effectiveness. Areas to Focus On: DevOps principles: Familiarize yourself with continuous integration, continuous deployment (CI/CD), and automation. Software development lifecycle (SDLC): Understand the stages of software development to better support the team. Agile tools: Stay updated on the latest project management tools like Jira, Azure DevOps, and Confluence. A strong technical foundation enables Scrum Masters to better communicate with technical teams and remove impediments. 4. Change Management Skills Organizations are constantly evolving, and Scrum Masters play a crucial role in facilitating change. Best Practices for Change Management: Communicate clearly: Ensure all stakeholders understand the reasons for change and the expected benefits. Involve the team: Engage the team in planning and implementing changes to gain their buy-in. Monitor and adapt: Track the impact of changes and adjust as necessary. Being an effective change agent helps Scrum Masters drive successful agile transformations. 5. Coaching and Mentoring Coaching is at the heart of a Scrum Master’s role, and in 2025, it’s more important than ever to develop this skill. How to Become a Better Coach: Adopt a servant-leader mindset: Focus on serving the team rather than directing them. Ask open-ended questions: Encourage team members to think critically and find their own solutions. Provide constructive feedback: Offer feedback that is specific, actionable, and supportive. Great coaching leads to empowered, self-organizing teams that can solve their own challenges. 6. Metrics-Driven Decision Making Data-driven decision-making is crucial for Scrum Masters to improve team performance and deliver value consistently. Key Metrics to Track: Velocity: Measure how much work the team completes each sprint. Cycle time: Track the time it takes to complete a task from start to finish. Burndown and burnup charts: Visualize progress toward sprint or release goals. Using metrics effectively helps Scrum Masters identify patterns, anticipate risks, and drive continuous improvement. 7. Stakeholder Management Stakeholder expectations can make or break a project. Scrum Masters must excel at managing these relationships. Stakeholder Management Tips: Set clear expectations: Ensure stakeholders understand agile principles and what to expect from the team. Provide regular updates: Share progress reports and involve stakeholders in sprint reviews. Manage conflicts: Address disagreements early and find common ground. Effective stakeholder management ensures alignment and enhances trust. 8. Remote and Hybrid Team Management With remote and hybrid work becoming the norm, Scrum Masters must adapt their practices to support distributed teams. Tips for Managing Distributed Teams: Leverage technology: Use collaboration tools like Zoom, Slack, and Miro to keep the team connected. Promote inclusivity: Ensure all team members, regardless of location, feel equally valued and engaged. Maintain team cohesion: Organize virtual team-building activities to strengthen relationships. Successfully managing remote teams requires intentional effort and flexibility. 9. Business Acumen In 2025, Scrum Masters must understand the broader business context in which they operate. Key Areas of Focus: Value delivery: Ensure the team delivers work that aligns with business goals. Market trends: Stay informed about industry trends and how they impact the product. Cost management: Help the team balance speed and quality while staying within budget. Business-savvy Scrum Masters can bridge the gap between technical teams and business stakeholders. 10. Continuous Learning and Adaptability The agile landscape is constantly evolving, and Scrum Masters must stay ahead by continuously learning. Ways to Stay Updated: Attend conferences: Join events like Agile Alliance or Scrum Gatherings. Read industry blogs: Follow thought leaders and stay informed about new practices. Take certifications: Pursue advanced certifications like SAFe Scrum Master or ICAgile Certified Professional. By embracing a growth mindset, Scrum Masters can remain relevant and effective in a changing environment. Are you ready to enhance your Scrum Master skills for 2025? Start by focusing on one or two areas from this list and gradually expand your expertise. Don’t forget to share this blog with fellow Scrum Masters or aspiring agile leaders, and leave a comment below to join the discussion. Continuous improvement begins with small, consistent steps—so start today!
Future-Proofing Your Project Management Skills: Training and Development Trends
Future-Proofing Your Project Management Skills: Training and Development Trends In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving business environment, project managers need to continually develop their skills to stay competitive. With emerging technologies, changing work cultures, and evolving methodologies, future-proofing your project management skills has never been more important. This blog explores the top training and development trends that will help project managers adapt, grow, and lead successful projects in the future. 1. The Rise of Agile Methodologies As businesses strive for faster and more flexible project delivery, agile methodologies have become essential. Agile allows teams to adapt to changing requirements and deliver results more efficiently. The global shift towards agile practices is expected to continue, making it critical for project managers to master agile frameworks. Why Agile is Here to Stay: Flexibility and Adaptability: Agile methodologies allow for continuous improvement and rapid response to change. Customer-Centric Focus: Agile puts an emphasis on delivering value to customers through frequent iterations. Team Collaboration: Agile fosters collaboration and improves communication within project teams. Key Agile Training Areas: Scrum Master Certification: Scrum is one of the most popular agile frameworks, and obtaining a Scrum Master certification can boost your credibility and skill set. Kanban: A visual tool for managing workflows that focuses on limiting work-in-progress to improve efficiency. Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe): A set of principles that helps large organizations implement agile at scale. Investing in agile training will equip you with the tools and knowledge to effectively lead teams and manage projects in an increasingly agile environment. 2. Embracing Digital Project Management Tools Technology is rapidly transforming the project management landscape. The adoption of digital tools and platforms has become crucial for managing complex projects efficiently. From task management and resource allocation to real-time collaboration, project managers now have access to a wide range of digital tools that can streamline workflows and improve decision-making. Popular Project Management Tools to Consider: Trello: A simple, visual tool that helps you organize tasks and manage workflows. Asana: A comprehensive project management platform that allows teams to plan, track, and collaborate on projects. Microsoft Project: A traditional project management tool that offers extensive features for resource management and scheduling. Monday.com: A customizable platform for project management that integrates with various other tools and offers real-time collaboration. Slack: Although primarily a communication tool, Slack is essential for team collaboration in real-time and can be integrated with project management tools. Training Areas for Digital Tools: Tool-Specific Training: Learn the ins and outs of popular project management software. Automation Skills: Understanding how to automate repetitive tasks using digital tools can save time and improve efficiency. Cloud Collaboration: Mastering cloud-based platforms that allow real-time access to project data from anywhere. Familiarizing yourself with these tools will help you stay competitive and ensure you can manage projects more efficiently in the digital age. 3. Focus on Soft Skills and Leadership Development While technical expertise is important, soft skills such as leadership, communication, and emotional intelligence are just as crucial for successful project management. As teams become more diverse and remote work continues to rise, strong leadership and interpersonal skills are essential for managing and motivating teams. Key Soft Skills to Develop: Communication: The ability to clearly communicate project goals, progress, and challenges to both internal and external stakeholders. Conflict Resolution: The skill to mediate and resolve conflicts within teams to maintain a positive work environment. Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and managing your emotions, as well as those of others, to build stronger relationships with team members. Time Management: Prioritizing tasks and managing time effectively to ensure projects stay on track. Decision-Making: Being able to make quick, informed decisions that benefit the project and the team. Leadership Training Areas: Situational Leadership: Learning how to adapt your leadership style based on the situation and the team’s needs. Team Motivation: Developing strategies to inspire and engage your team to achieve optimal performance. Coaching and Mentoring: Building the skills to develop the next generation of project managers within your team. Developing these soft skills will enable you to lead your project teams more effectively and manage interpersonal dynamics in an increasingly complex workplace. 4. The Shift Toward Remote and Hybrid Work Models The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the trend toward remote and hybrid work models, and this shift is likely to remain in the future. As a project manager, it’s essential to adapt to the challenges and opportunities that come with managing teams that may be distributed across different locations and time zones. Remote and Hybrid Work Trends: Global Teams: Project teams may include members from all over the world, requiring you to manage diverse cultural perspectives and communication styles. Flexible Work Hours: With remote work, project managers must navigate flexible work hours and ensure that teams remain productive without traditional 9-to-5 structures. Virtual Collaboration: Remote teams rely on digital communication and collaboration tools, making proficiency with these tools essential. Training for Remote Project Management: Virtual Team Management: Learning how to manage virtual teams, build trust remotely, and foster collaboration without in-person meetings. Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding the dynamics of working with people from different cultural backgrounds and ensuring inclusivity in the team. Remote Communication Skills: Enhancing your ability to communicate effectively through video conferencing, messaging, and other virtual platforms. By honing these skills, you can ensure that your remote or hybrid project teams are efficient, engaged, and productive, no matter where they are located. 5. Staying Current with Industry Trends and Certifications As the project management field continues to evolve, staying updated on the latest trends, methodologies, and certifications is essential for future-proofing your career. Certification programs provide formal recognition of your expertise and commitment to professional growth. Key Certifications to Consider: Project Management Professional (PMP): Offered by the Project Management Institute (PMI), this certification remains one of the most recognized credentials for project managers worldwide. Certified ScrumMaster (CSM): A certification that focuses on agile practices and is highly valued in industries that rely on agile project management. PRINCE2 Certification: A process-driven project management methodology widely used in
How to Handle Conflict Resolution in Project Teams
How to Handle Conflict Resolution in Project Teams Conflict within project teams is inevitable. With diverse personalities, different perspectives, and varying priorities, disagreements can arise, potentially hindering project progress. However, when handled effectively, conflict can be a powerful tool for growth, leading to better decision-making, increased creativity, and stronger team dynamics. This blog will provide actionable insights into managing and resolving conflicts within project teams, ensuring that conflicts do not derail progress but instead create opportunities for improvement. 1. Understanding Conflict in Project Teams Before diving into conflict resolution strategies, it’s important to understand why conflict arises in project teams. Here are the common causes of conflict: Common Causes of Conflict: Different Work Styles: Team members may have different approaches to work, leading to misunderstandings. Poor Communication: Lack of clear communication can result in confusion, missed expectations, and frustrations. Resource Scarcity: Limited resources can create competition or tension over who gets what. Clashing Goals: If team members have different priorities or understandings of the project’s objectives, conflict can arise. Personality Clashes: Sometimes, personality differences can cause friction, especially when individuals are working closely together. 2. The Impact of Conflict on Project Teams When left unresolved, conflict can have several negative impacts on project teams, such as: Reduced Productivity: Team members may become distracted by ongoing issues, affecting their performance. Low Morale: Continuous conflict can lead to dissatisfaction, disengagement, and high turnover rates. Decreased Collaboration: When team members are at odds, it becomes harder to share ideas and work together efficiently. Project Delays: Disagreements can lead to delays as time is spent resolving issues instead of focusing on project tasks. However, conflict, if managed well, can lead to: Improved Communication: Open discussions can foster clearer communication, leading to better understanding. Innovative Solutions: Different perspectives can drive creativity and lead to innovative solutions. Stronger Team Bonds: Successfully resolving conflict can strengthen relationships and enhance trust among team members. 3. Steps for Effective Conflict Resolution The key to handling conflict in project teams lies in addressing the issue promptly, calmly, and constructively. Here are steps you can take to resolve conflicts effectively: 1. Acknowledge the Conflict Ignoring conflict or pretending it doesn’t exist can lead to bigger issues down the road. The first step in conflict resolution is acknowledging that there is a problem. Why Acknowledge It: Prevents the issue from escalating. Demonstrates to team members that their concerns are valid. Encourages open communication. 2. Identify the Root Cause Conflict is often a symptom of a deeper issue. To resolve it effectively, you must understand what’s causing the disagreement. Steps to Identify the Root Cause: Hold a meeting with the involved parties. Ask open-ended questions to understand their perspectives. Listen actively and empathetically to all sides. 3. Foster Open Communication Effective communication is the backbone of conflict resolution. Encourage team members to express their concerns and feelings openly but respectfully. Communication Tips: Use “I” statements (e.g., “I feel frustrated when…” instead of “You always…”). Practice active listening by repeating what the other person has said to ensure understanding. Avoid interrupting and let each person speak without judgment. 4. Encourage Collaboration Instead of positioning individuals as opponents, foster a collaborative mindset where both parties work together to find a mutually beneficial solution. Collaborative Techniques: Brainstorm possible solutions together. Identify common goals and emphasize shared objectives. Work toward a compromise or consensus that satisfies both sides. 5. Mediate if Necessary As a project leader, it’s important to step in as a neutral mediator if the conflict escalates. Your role is to facilitate communication and guide the team toward a resolution. How to Mediate: Set a neutral tone by staying calm and objective. Ensure everyone’s voice is heard, but prevent arguments from becoming personal or aggressive. Help the team members focus on the issue at hand, not on personalities. 6. Define Clear Solutions and Action Plans Once a resolution is reached, define clear steps for how the issue will be addressed moving forward. This can prevent future conflicts and ensure that the resolution is effective. Action Plan Guidelines: Clearly outline what will change or improve as a result of the resolution. Assign specific tasks or responsibilities to prevent misunderstandings. Set a timeline for implementing the changes. 7. Monitor and Follow Up Conflict resolution doesn’t end once the discussion is over. Regular follow-up is crucial to ensure that the solution is working and that the issue doesn’t resurface. Follow-Up Tips: Schedule check-ins with the team to assess the situation. Be open to further discussions if necessary. Ensure that the team remains aligned and any lingering issues are addressed promptly. 4. Conflict Resolution Styles Understanding different conflict resolution styles can help you choose the best approach for your team. The five primary styles are: 1. Avoiding In this style, individuals avoid engaging in the conflict. While this may seem like an easy way out, it can often lead to unresolved issues. 2. Accommodating This style involves one person yielding to the other’s perspective. While it resolves conflict quickly, it may lead to resentment if the other party is always giving in. 3. Competing A competitive style is more about “winning” the conflict, rather than finding a mutually beneficial solution. It’s useful in urgent situations but can create long-term issues. 4. Compromising This style involves finding a middle ground. Both parties give something up to reach a solution that is acceptable to both. 5. Collaborating Collaboration is the most effective style, where both parties work together to find a solution that satisfies everyone’s needs. This approach builds stronger relationships and addresses the root causes of conflict. 5. Tools and Techniques for Managing Conflict Here are a few additional tools and techniques that can help prevent or resolve conflicts in project teams: 1. Conflict Resolution Training Provide your team with conflict resolution training to ensure they have the skills to manage disagreements constructively. 2. Team Building Activities Regular team-building exercises can help improve communication and trust, reducing the likelihood of conflicts. 3. Use of Technology Collaboration tools like Slack,
The Importance of Documentation in Remote Project Management
The Importance of Documentation in Remote Project Management Remote project management presents unique challenges that require a mix of strong communication, collaboration, and well-defined processes. Among these, one of the most essential yet often overlooked aspects is documentation. Proper documentation is vital to ensure smooth project execution, efficient workflows, and a transparent working environment, especially when teams are dispersed across various locations. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of documentation in remote project management and provide actionable insights on how to create and maintain effective documentation to support your team’s success. 1. Why Documentation is Crucial in Remote Projects In traditional office settings, team members can easily communicate face-to-face, resolve misunderstandings quickly, and rely on verbal instructions. In a remote setup, however, communication is primarily done via digital means, making clear and structured documentation even more critical. Benefits of Documentation in Remote Project Management: Clarity and Consistency: Documentation ensures that everyone has access to the same information, minimizing misunderstandings and maintaining consistency. Collaboration Efficiency: Clear documents allow team members to collaborate effectively without the need for constant back-and-forth communication. Accountability: Written records clarify who is responsible for what tasks and ensure that nothing falls through the cracks. Onboarding and Training: Well-organized documentation helps new team members get up to speed quickly, improving onboarding efficiency. Knowledge Retention: In a remote environment, where employees may come and go, documentation preserves vital knowledge and project details. 2. Types of Documentation in Remote Project Management Different types of documentation are required at various stages of a project to maintain clarity and organization. Here are the key types that every remote team should focus on: 1. Project Plans and Roadmaps A comprehensive project plan is the foundation of any project. It outlines the goals, timelines, resources, and milestones, providing a clear direction for the team. Key Elements to Include: Project objectives Deliverables and timelines Roles and responsibilities Resources and tools needed Why It’s Important: A well-documented project plan ensures that everyone knows the scope, deadlines, and expectations, even when working from different locations. 2. Communication Guidelines Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful remote project management. Clear documentation of communication guidelines helps teams stay on the same page. Key Elements to Include: Preferred tools (e.g., Slack for quick chats, Zoom for meetings) Response times for emails and messages Frequency of team meetings and check-ins Expectations for meeting agendas and follow-up actions Why It’s Important: Without face-to-face interactions, remote teams need clear communication protocols to avoid confusion and delays. This ensures that all team members can access relevant information promptly. 3. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) SOPs document the processes and workflows that the team follows for different tasks. These documents help streamline operations and provide guidance on how to complete recurring tasks. Key Elements to Include: Step-by-step instructions for common tasks Tools and software to be used Roles responsible for different steps Deadlines and quality standards Why It’s Important: SOPs ensure consistency and efficiency across the team. They make sure that even when team members are working independently, the same procedures are followed. 4. Meeting Notes and Action Items Documenting meeting discussions, decisions, and action items is essential in remote project management. This ensures that no important points are missed, and all team members are aligned. Key Elements to Include: Date and time of the meeting Attendees and absent members Key discussion points Action items, assigned owners, and deadlines Why It’s Important: With remote teams, it’s easy to forget or misinterpret discussions. Meeting notes provide a clear reference for what was agreed upon and help team members stay accountable for their tasks. 5. Progress Reports and Updates Regularly documented progress reports help stakeholders stay informed about project status and any roadblocks the team may be facing. These reports should be updated consistently. Key Elements to Include: Task progress (completed, in progress, pending) Milestones achieved Potential challenges or delays Upcoming tasks or deadlines Why It’s Important: Progress reports provide transparency, help identify risks early on, and ensure that everyone is aligned with the project’s goals. 3. Best Practices for Remote Project Documentation While documentation is crucial, how you implement it can make a significant difference. Here are some best practices to ensure your project documentation is effective and accessible: 1. Keep Documentation Organized Clear organization is key to ensuring that everyone can easily find the information they need. Use folders, tags, and naming conventions to categorize documents. Tips for Organization: Use cloud-based tools like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive for easy access. Create a consistent folder structure (e.g., “Project Plan,” “Meeting Notes,” “SOPs”). Use clear file names (e.g., “Q1 Project Plan” or “Meeting Notes – 2025-01-18”). 2. Update Documents Regularly Documentation should never be static. Keep your documents updated to reflect any changes, such as shifting project timelines, updated task statuses, or new team members. Tips for Updates: Assign someone to oversee documentation updates. Set reminders to review and revise documents periodically. Make use of version control tools to track changes. 3. Use Collaborative Tools Leverage collaborative tools that allow team members to contribute to and comment on documents in real-time. This fosters a collaborative environment and ensures that everyone has input. Tools to Consider: Google Docs for live collaboration. Trello or Asana for task and project tracking. Confluence for creating knowledge bases and documentation. 4. Make Documents Accessible Ensure that all team members can easily access documentation, regardless of their location or time zone. Cloud-based solutions provide universal access, but it’s also important to ensure compatibility with the team’s devices. Tips for Accessibility: Use cross-platform tools that work on mobile, tablet, and desktop. Avoid using overly complex software that may create barriers for less tech-savvy team members. 5. Keep It Simple and Concise Documentation should be clear, concise, and to the point. Avoid excessive jargon, and use bullet points, headings, and simple language to ensure that everyone can easily understand and navigate the documents. 4. Tools for Remote Project Documentation Several tools can assist in maintaining effective remote project documentation. Here are some popular
Implementing Agile Metrics to Measure Project Success
Implementing Agile Metrics to Measure Project Success Agile methodologies have revolutionized the way teams approach project management. With its emphasis on flexibility, collaboration, and incremental progress, agile has become the go-to framework for many businesses. However, while agile emphasizes adaptability, it’s equally important to measure progress and success. This is where agile metrics come into play. Agile metrics are essential for tracking the effectiveness of agile processes, ensuring that teams are on track, and delivering value to stakeholders. These metrics provide insights into both the team’s productivity and the project’s success. In this blog, we’ll explore how to implement agile metrics and how they can help measure project success. 1. Why Agile Metrics Matter Before diving into specific metrics, it’s important to understand why they are necessary in an agile environment. In agile projects, teams work iteratively, often in short cycles known as sprints. This dynamic environment requires real-time insights to help teams stay aligned with project goals and stakeholders’ expectations. Key Benefits of Agile Metrics: Measure Team Performance: Metrics help teams understand their capacity, velocity, and areas of improvement. Enhance Predictability: Metrics like cycle time and burn-down charts offer insights into how long tasks will take, enabling better planning. Continuous Improvement: Agile metrics highlight inefficiencies, providing opportunities for teams to optimize their workflows. Improve Communication: Agile metrics create transparency, helping team members and stakeholders understand the project’s progress at a glance. 2. Key Agile Metrics for Measuring Project Success Agile metrics vary depending on the type of project and team, but there are several common metrics that can be used across different projects. These metrics provide a clear view of a team’s productivity and the overall project health. 1. Velocity Velocity is a measure of the amount of work a team completes during a sprint. It’s typically measured in story points, which represent the complexity of tasks. Velocity helps predict how much work a team can handle in future sprints. How to Implement: Track the total story points completed in each sprint. Compare velocity over several sprints to assess consistency or improvement. Use velocity to estimate future sprint capacity. Why It’s Important: Velocity helps with sprint planning by providing a historical measure of how much work can be realistically completed. It ensures that teams aren’t overburdened and that the project progresses at a steady pace. 2. Burn-Down Chart A burn-down chart shows how much work remains in a sprint or project. It tracks the progress of tasks from the backlog and provides a visual representation of the work left to do. How to Implement: Plot the total work (in story points) remaining at the start of the sprint. Track daily progress by updating the burn-down chart. Ensure that the line on the chart slopes downward, indicating that work is being completed. Why It’s Important: A burn-down chart provides transparency into project progress, making it easy to see if the team is on track to meet sprint goals. It also highlights potential delays or obstacles early on. 3. Cycle Time Cycle time measures the total time it takes to complete a task from the moment work begins until it’s finished. It’s an important metric for understanding how quickly the team is delivering value. How to Implement: Track the time it takes for tasks to move through each stage of the process. Measure from when the work begins to when it’s marked as done. Identify stages where work is getting delayed and investigate potential bottlenecks. Why It’s Important: Shorter cycle times generally mean faster delivery of value to customers. Monitoring cycle time helps identify areas where the team can improve efficiency. 4. Lead Time Lead time is similar to cycle time but measures the entire time from when a request is made until the task is completed. It includes waiting time in the backlog, which cycle time does not. How to Implement: Track the time from when a task is added to the backlog to when it’s completed. Identify delays in the backlog or during the task prioritization phase. Why It’s Important: Lead time is useful for understanding how long it takes to fulfill customer requests. A reduction in lead time can increase customer satisfaction by delivering solutions faster. 5. Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD) A cumulative flow diagram tracks the flow of work through different stages, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” It helps identify bottlenecks and visualizes the overall flow of the project. How to Implement: Visualize the work in each column of your Kanban board. Plot the cumulative amount of work in each stage over time. Look for spikes in any stage, indicating a bottleneck. Why It’s Important: The CFD provides insight into how smoothly the work is flowing through the system. It allows teams to identify issues before they become major blockers. 6. Work in Progress (WIP) Work in progress is the number of tasks or stories that are actively being worked on at any given time. It helps prevent overloading the team and ensures that work is completed before new tasks are started. How to Implement: Set WIP limits for each stage of the workflow. Track the number of tasks in progress at any time. Use WIP limits to avoid overburdening the team and to ensure focus on completing tasks. Why It’s Important: WIP limits ensure that the team is not stretched too thin and helps prioritize completing tasks before starting new ones. Reducing WIP can improve flow and focus. 3. Implementing Agile Metrics: Best Practices Implementing agile metrics effectively is key to driving continuous improvement and ensuring the success of agile projects. Here are some best practices for successfully using agile metrics: 1. Use Metrics to Drive Improvement Agile metrics should not just be tracked for reporting purposes. Use them to identify areas for improvement. For example, if your cycle time is increasing, this could signal inefficiencies in the process that need attention. 2. Keep Metrics Simple and Relevant Avoid tracking too many metrics. Focus on the ones that provide the most value
Best Practices for Virtual Project Team Building
Best Practices for Virtual Project Team Building In today’s world of remote work and global teams, virtual project team building is more important than ever. With teams spread across various locations and time zones, ensuring strong collaboration, trust, and productivity requires a strategic approach. Building a cohesive and high-performing virtual team can be challenging, but with the right best practices in place, you can foster an environment where your team can thrive, even from a distance. In this blog, we’ll explore the key best practices for virtual project team building, from communication strategies to fostering a positive team culture. These actionable insights will help you navigate the complexities of virtual collaboration and achieve successful project outcomes. 1. Clear Communication Is Key One of the biggest challenges in virtual project team building is maintaining effective communication. When team members are not in the same physical space, it’s easy for messages to get lost or misunderstood. Key Strategies: Use Multiple Communication Tools: Leverage a combination of tools like video calls, messaging apps, and project management software. Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom can help facilitate different types of communication depending on the need—whether for quick chats, in-depth discussions, or face-to-face meetings. Establish Communication Guidelines: Set clear expectations for communication within your team. Define how often team members should check in, what platforms they should use for different types of messages, and when to escalate issues. Over-Communicate: In virtual teams, it’s often better to over-communicate than under-communicate. Regular updates and check-ins help keep everyone aligned and avoid any confusion. 2. Foster Trust and Transparency Building trust in a virtual environment can be more difficult, as there’s less opportunity for informal interactions. However, trust is essential for a high-functioning virtual team. Key Strategies: Be Transparent: Keep team members informed about project goals, timelines, and any challenges or changes. Transparency builds trust and helps everyone feel they are working towards the same objectives. Encourage Open Feedback: Create a culture where team members feel comfortable providing feedback, both positive and constructive. Regular feedback sessions can improve performance and strengthen relationships within the team. Lead by Example: Leaders should demonstrate honesty, reliability, and accountability. Your actions will set the tone for the entire team. 3. Define Roles and Responsibilities Clearly In any team, clarity is crucial, but it becomes even more important in virtual environments where team members can’t easily check in with one another. Define each team member’s roles and responsibilities to avoid confusion and inefficiency. Key Strategies: Set Clear Expectations: Define the deliverables, timelines, and responsibilities for each team member. Use project management tools like Trello, Asana, or Jira to track tasks and ensure everyone knows what they are responsible for. Use Role Descriptions: Clearly outline each team member’s role, including their specific tasks, how they contribute to the project, and who they report to. This reduces overlap and potential conflicts. Monitor Progress: Regularly track progress and adjust workloads as necessary. This helps ensure that no one is overwhelmed and that tasks are being completed on time. 4. Leverage Technology for Collaboration Without the ability to meet in person, technology plays a key role in fostering collaboration within virtual project teams. The right tools can streamline communication, manage tasks, and track project progress. Key Strategies: Project Management Software: Tools like Asana, Basecamp, or Monday.com are perfect for organizing tasks, setting deadlines, and tracking milestones. These tools help keep everyone on the same page and ensure accountability. Collaboration Platforms: Tools like Google Drive, Dropbox, or Microsoft OneDrive allow for real-time collaboration on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations, ensuring that team members can work together even when they’re miles apart. Time Zone Management: For teams spread across multiple time zones, use scheduling tools like World Time Buddy or Time Zone Converter to find suitable meeting times. Consider rotating meeting times to accommodate everyone’s time zone. 5. Foster a Positive Team Culture Even in a virtual environment, team culture is critical to success. A positive team culture promotes collaboration, motivation, and engagement. Key Strategies: Virtual Team-Building Activities: Engage your team with regular virtual team-building activities, such as online games, virtual happy hours, or even simple ice-breaker sessions. These activities can help build rapport and trust among team members, even from afar. Recognize Achievements: Publicly acknowledge individual and team accomplishments, whether big or small. Recognition fosters a sense of belonging and boosts morale. Celebrate Milestones: Celebrate project milestones, birthdays, or work anniversaries virtually. Simple gestures of recognition help build a more cohesive team. 6. Encourage Flexibility and Work-Life Balance In virtual teams, members often face challenges in balancing work with personal life, especially when they work from home. Encouraging a healthy work-life balance can prevent burnout and increase productivity. Key Strategies: Flexible Schedules: Allow flexibility in work hours, especially if your team is located in different time zones. This flexibility can improve job satisfaction and help maintain a healthier work-life balance. Encourage Breaks: Remind your team to take regular breaks. Long hours in front of a screen can lead to burnout, so encourage team members to step away from their computers when needed. Respect Personal Time: Avoid sending messages or expecting work outside of designated hours. This respect for personal time promotes a healthier and more sustainable work environment. 7. Maintain Accountability and Motivation In a virtual environment, it’s easy for team members to feel disconnected from the project or the team’s overall goals. Maintaining accountability and motivation is essential to ensuring productivity and project success. Key Strategies: Set Clear Deadlines: Define realistic deadlines and hold team members accountable for meeting them. Use project management tools to track progress and ensure tasks are being completed on schedule. Regular Check-Ins: Hold regular one-on-one or team check-ins to monitor progress, discuss challenges, and adjust goals as necessary. This helps keep everyone motivated and on track. Encourage Ownership: Empower team members by giving them ownership of tasks or areas of the project. This responsibility can increase motivation and performance. 8. Measure and Evaluate Team Performance To continually improve your virtual team’s