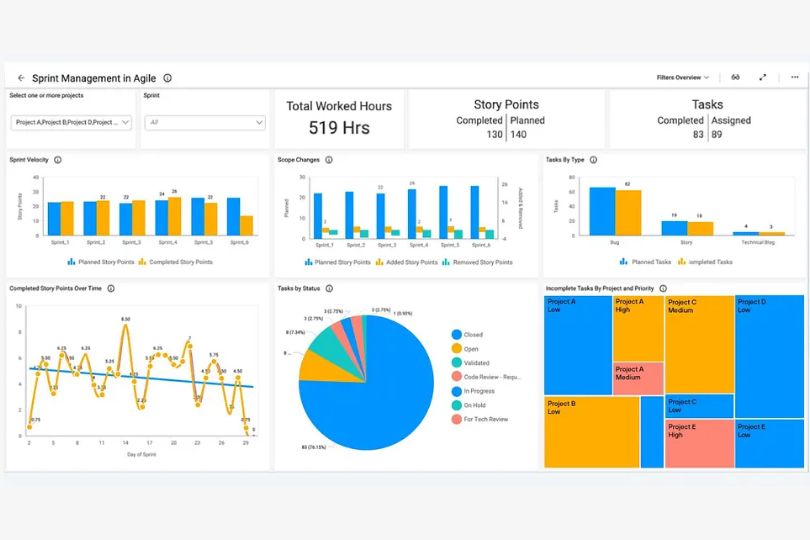
Implementing Agile Metrics to Measure Project Success
Agile methodologies have revolutionized the way teams approach project management. With its emphasis on flexibility, collaboration, and incremental progress, agile has become the go-to framework for many businesses. However, while agile emphasizes adaptability, it’s equally important to measure progress and success. This is where agile metrics come into play.
Agile metrics are essential for tracking the effectiveness of agile processes, ensuring that teams are on track, and delivering value to stakeholders. These metrics provide insights into both the team’s productivity and the project’s success. In this blog, we’ll explore how to implement agile metrics and how they can help measure project success.
1. Why Agile Metrics Matter
Before diving into specific metrics, it’s important to understand why they are necessary in an agile environment. In agile projects, teams work iteratively, often in short cycles known as sprints. This dynamic environment requires real-time insights to help teams stay aligned with project goals and stakeholders’ expectations.
Key Benefits of Agile Metrics:
- Measure Team Performance: Metrics help teams understand their capacity, velocity, and areas of improvement.
- Enhance Predictability: Metrics like cycle time and burn-down charts offer insights into how long tasks will take, enabling better planning.
- Continuous Improvement: Agile metrics highlight inefficiencies, providing opportunities for teams to optimize their workflows.
- Improve Communication: Agile metrics create transparency, helping team members and stakeholders understand the project’s progress at a glance.
2. Key Agile Metrics for Measuring Project Success
Agile metrics vary depending on the type of project and team, but there are several common metrics that can be used across different projects. These metrics provide a clear view of a team’s productivity and the overall project health.
1. Velocity
Velocity is a measure of the amount of work a team completes during a sprint. It’s typically measured in story points, which represent the complexity of tasks. Velocity helps predict how much work a team can handle in future sprints.
How to Implement:
- Track the total story points completed in each sprint.
- Compare velocity over several sprints to assess consistency or improvement.
- Use velocity to estimate future sprint capacity.
Why It’s Important:
Velocity helps with sprint planning by providing a historical measure of how much work can be realistically completed. It ensures that teams aren’t overburdened and that the project progresses at a steady pace.
2. Burn-Down Chart
A burn-down chart shows how much work remains in a sprint or project. It tracks the progress of tasks from the backlog and provides a visual representation of the work left to do.
How to Implement:
- Plot the total work (in story points) remaining at the start of the sprint.
- Track daily progress by updating the burn-down chart.
- Ensure that the line on the chart slopes downward, indicating that work is being completed.
Why It’s Important:
A burn-down chart provides transparency into project progress, making it easy to see if the team is on track to meet sprint goals. It also highlights potential delays or obstacles early on.
3. Cycle Time
Cycle time measures the total time it takes to complete a task from the moment work begins until it’s finished. It’s an important metric for understanding how quickly the team is delivering value.
How to Implement:
- Track the time it takes for tasks to move through each stage of the process.
- Measure from when the work begins to when it’s marked as done.
- Identify stages where work is getting delayed and investigate potential bottlenecks.
Why It’s Important:
Shorter cycle times generally mean faster delivery of value to customers. Monitoring cycle time helps identify areas where the team can improve efficiency.
4. Lead Time
Lead time is similar to cycle time but measures the entire time from when a request is made until the task is completed. It includes waiting time in the backlog, which cycle time does not.
How to Implement:
- Track the time from when a task is added to the backlog to when it’s completed.
- Identify delays in the backlog or during the task prioritization phase.
Why It’s Important:
Lead time is useful for understanding how long it takes to fulfill customer requests. A reduction in lead time can increase customer satisfaction by delivering solutions faster.
5. Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD)
A cumulative flow diagram tracks the flow of work through different stages, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” It helps identify bottlenecks and visualizes the overall flow of the project.
How to Implement:
- Visualize the work in each column of your Kanban board.
- Plot the cumulative amount of work in each stage over time.
- Look for spikes in any stage, indicating a bottleneck.
Why It’s Important:
The CFD provides insight into how smoothly the work is flowing through the system. It allows teams to identify issues before they become major blockers.
6. Work in Progress (WIP)
Work in progress is the number of tasks or stories that are actively being worked on at any given time. It helps prevent overloading the team and ensures that work is completed before new tasks are started.
How to Implement:
- Set WIP limits for each stage of the workflow.
- Track the number of tasks in progress at any time.
- Use WIP limits to avoid overburdening the team and to ensure focus on completing tasks.
Why It’s Important:
WIP limits ensure that the team is not stretched too thin and helps prioritize completing tasks before starting new ones. Reducing WIP can improve flow and focus.
3. Implementing Agile Metrics: Best Practices
Implementing agile metrics effectively is key to driving continuous improvement and ensuring the success of agile projects. Here are some best practices for successfully using agile metrics:
1. Use Metrics to Drive Improvement
Agile metrics should not just be tracked for reporting purposes. Use them to identify areas for improvement. For example, if your cycle time is increasing, this could signal inefficiencies in the process that need attention.
2. Keep Metrics Simple and Relevant
Avoid tracking too many metrics. Focus on the ones that provide the most value to your team. Overcomplicating metrics can lead to confusion and a lack of focus on what truly matters for project success.
3. Regularly Review and Adjust Metrics
Agile metrics should be reviewed regularly, such as during sprint reviews or retrospectives. Use the insights gathered to adjust processes, improve team efficiency, and make necessary changes.
4. Foster a Culture of Transparency
For metrics to be effective, they must be visible and understood by all team members. Create an environment where team members feel comfortable discussing metrics, sharing challenges, and brainstorming improvements.
5. Tailor Metrics to Your Team and Project
Not all teams or projects are the same. Customize metrics to fit your team’s specific needs. For instance, if you’re working on a highly complex project, focus on metrics like cycle time and lead time. For simpler projects, velocity and burn-down charts might suffice.
4. Conclusion: Enhancing Project Success with Agile Metrics
Agile metrics are powerful tools that help measure and guide project success. By implementing key metrics like velocity, burn-down charts, and cycle time, teams can gain valuable insights into their performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that projects are completed on time and within scope.
The successful implementation of agile metrics requires continuous review, a focus on simplicity, and alignment with project goals. By leveraging these metrics effectively, teams can make data-driven decisions that lead to better outcomes, improved team collaboration, and more successful projects.
Ready to take your agile project management to the next level? Subscribe to our blog for more insights on agile best practices and project success!