The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Product Management Introduction In product management, technical skills and strategic thinking are often viewed as the most critical competencies. However, one trait that significantly influences a product manager’s success is emotional intelligence (EI). Emotional intelligence is the ability to identify, understand, and manage your own emotions while also recognizing and influencing the emotions of others. In a role where collaboration, decision-making, and leadership are crucial, emotional intelligence plays an indispensable role. This blog explores why emotional intelligence is vital for product managers and how you can harness it to improve your effectiveness and relationships within your team and with stakeholders. What is Emotional Intelligence? Emotional intelligence can be broken down into five key components, as defined by psychologist Daniel Goleman: Self-Awareness: Recognizing and understanding your emotions and how they impact your behavior and decisions. Self-Regulation: The ability to control or redirect disruptive emotions and impulses in difficult situations. Motivation: A drive to achieve beyond external rewards and a passion for work that leads to success. Empathy: The ability to understand the emotional needs of others, particularly during stressful or challenging situations. Social Skills: Proficiency in managing relationships and building networks to collaborate effectively with others. Each of these components plays a significant role in how product managers lead their teams, make decisions, and interact with cross-functional stakeholders. Why Emotional Intelligence is Essential for Product Managers 1. Building Strong Relationships A product manager’s success often hinges on their ability to build and maintain strong relationships with cross-functional teams, customers, and other stakeholders. Emotional intelligence is key to understanding and managing the emotions of others, helping PMs navigate delicate situations, such as negotiating feature requests with stakeholders or resolving conflicts within the team. How EI Helps PMs Build Strong Relationships: Empathy enables product managers to relate to the concerns of different teams and prioritize customer needs effectively. Social skills help in maintaining open and productive communication across departments. Self-regulation helps PMs stay calm and positive in stressful situations, promoting collaboration even under pressure. 2. Effective Leadership and Decision-Making As a product manager, you’re often required to lead teams without direct authority, meaning you must influence others to execute your product vision. EI helps PMs motivate their teams, align people around shared goals, and resolve conflicts, all of which are essential for effective leadership. How EI Impacts Leadership: Self-awareness allows you to recognize how your emotions affect your decision-making process and interactions. Empathy enables you to understand your team members’ perspectives and offer support when needed. Self-regulation helps you make clear-headed decisions, even in high-pressure situations, ensuring that you lead with composure. 3. Managing Stress and Pressure Product management is a high-stakes, fast-paced job with plenty of room for stress and uncertainty. Whether dealing with tight deadlines, changing market demands, or conflicting stakeholder priorities, emotional intelligence can help you manage these pressures without compromising your decision-making abilities. How EI Helps with Stress Management: Self-regulation allows you to manage your emotions, even in challenging situations, preventing them from negatively affecting your work or relationships. Motivation keeps you focused on long-term goals, helping you push through obstacles while maintaining a positive outlook. Social skills enable you to delegate effectively and lean on your team, reducing individual stress. 4. Enhancing Communication and Collaboration Effective communication is at the heart of product management. Whether you’re discussing technical details with engineers or presenting product strategies to executives, emotional intelligence allows you to tailor your message appropriately to the audience and ensure that your communication fosters collaboration. How EI Supports Effective Communication: Empathy helps you understand the emotions and perspectives of others, making your communication more relevant and persuasive. Social skills allow you to adapt your communication style to different personalities and cultures within your team. Self-regulation ensures that you communicate calmly and professionally, even in emotionally charged discussions. 5. Navigating Conflict and Negotiation In product management, conflicts are inevitable, whether it’s disagreements over product features or timelines. Emotional intelligence helps PMs navigate these conflicts effectively by managing their emotions and understanding the emotional dynamics at play. How EI Enhances Conflict Resolution: Empathy helps you understand where others are coming from, even if you disagree with their views. Social skills enable you to negotiate and mediate in a way that fosters cooperation rather than animosity. Self-regulation allows you to maintain objectivity during emotionally charged situations, helping to resolve conflicts without escalating tensions. How to Develop Emotional Intelligence as a Product Manager While some people may naturally possess higher emotional intelligence, the good news is that EI can be developed over time with practice and awareness. Here are a few tips for product managers who want to strengthen their emotional intelligence: 1. Practice Active Listening One of the most effective ways to develop empathy is to practice active listening. Give your full attention to the speaker, make eye contact, and avoid interrupting. Show that you understand their perspective by reflecting back what you’ve heard. 2. Seek Feedback Requesting feedback from colleagues, team members, and stakeholders is crucial for self-awareness. It helps you identify blind spots in your behavior or communication style. Be open to constructive criticism, and use it to grow and improve. 3. Focus on Stress-Relief Techniques In high-pressure situations, practicing mindfulness, breathing exercises, or taking short breaks can help you maintain composure. Regular stress-relief techniques can help you regulate your emotions and maintain clear-headed decision-making. 4. Build Empathy through Perspective-Taking Empathy can be improved by regularly putting yourself in others’ shoes. Try to understand how different stakeholders feel in various situations. This helps you better manage relationships and communicate more effectively with team members from different disciplines. 5. Improve Conflict Resolution Skills Work on your ability to manage and resolve conflicts calmly and effectively. Focus on finding win-win solutions, listen to all parties involved, and try to reach a consensus that aligns with the overall product vision. Conclusion Emotional intelligence is not just a “nice-to-have” skill in product management; it is essential for driving collaboration, making sound decisions, and leading successful
Author: Admin
Product Manager Interview Questions: What to Expect and How to Prepare
Product Manager Interview Questions: What to Expect and How to Prepare Introduction Landing a product manager (PM) role can be a transformative step in your career, but the interview process can feel daunting. It’s not just about demonstrating your technical knowledge; it’s also about showing how well you can collaborate, think strategically, and manage complex projects. This blog will guide you through the common product manager interview questions, provide insights into what interviewers are looking for, and offer tips on how to prepare effectively. Key Skills Interviewers Look For in Product Managers Before diving into specific interview questions, it’s essential to understand the key skills that product managers are expected to demonstrate: Strategic Thinking: The ability to develop a vision and roadmap for the product. Technical Understanding: A grasp of the technical aspects of the product development process, even if you aren’t an engineer. Cross-Functional Collaboration: The ability to work with teams from engineering, design, marketing, sales, and customer support. Customer-Centric Mindset: The ability to prioritize customer needs and make data-driven decisions. Leadership and Decision-Making: Leading without authority and making tough decisions that balance stakeholder interests. Common Product Manager Interview Questions 1. Tell Me About Yourself This is typically the first question you’ll encounter. While it may seem like a simple question, it’s an opportunity to summarize your career path, highlight your key experiences, and align them with the role you’re applying for. How to Answer: Start with a brief overview of your career history. Focus on your product management experience, highlighting key achievements and projects. Tailor your answer to emphasize how your background aligns with the company’s needs. Example Answer: “I’ve been working in product management for over three years, primarily focusing on developing SaaS products. In my previous role at XYZ Company, I led a cross-functional team that successfully launched a product used by over 10,000 customers within six months. I’m excited about the opportunity to leverage my skills in data analysis, strategic planning, and team leadership to help your company achieve its product goals.” 2. How Do You Prioritize Features in a Product? As a PM, prioritizing features is a core part of your job. Interviewers want to know how you balance customer needs, technical constraints, and business goals. How to Answer: Explain your process for prioritization, such as using frameworks like RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort) or MoSCoW (Must Have, Should Have, Could Have, Won’t Have). Mention how you consider both short-term needs and long-term product vision. Talk about how you collaborate with stakeholders to understand their needs and make data-driven decisions. Example Answer: “When prioritizing features, I use the RICE framework. I start by evaluating the reach of a feature (how many users it will impact), followed by its impact on user satisfaction or business goals. I also assess the confidence in my estimates and the effort required to implement the feature. I ensure that decisions align with both the immediate needs of the user and the long-term vision of the product.” 3. Describe a Time You Had to Manage Conflicting Stakeholder Opinions Stakeholder management is a key part of a PM’s role. Companies want to know how well you navigate conflicts between teams, such as sales wanting more features vs. engineering saying it’s too complex. How to Answer: Highlight a specific example where you balanced different perspectives. Focus on how you handled the conflict, whether through negotiation, data analysis, or aligning with the broader product vision. Conclude with the outcome of the situation and how you ensured the product stayed on track. Example Answer: “In one project, the sales team wanted a feature that would add significant complexity to our product, while engineering raised concerns about its feasibility. I organized a meeting where both teams could share their concerns. I then presented data on how the feature would impact our target audience and business goals. After further discussion, we reached a compromise where we released a simpler version of the feature that met both teams’ needs.” 4. How Do You Measure the Success of a Product? Product managers need to track the success of their products to inform future decisions. Interviewers will want to know how you measure success and whether you use metrics effectively. How to Answer: Mention specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like user adoption, revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and retention rates. Explain how you align product success with business goals and how data helps you monitor progress. If possible, share examples of how you’ve used metrics to iterate on a product. Example Answer: “I measure product success by focusing on a few key metrics. For example, user engagement and retention rates are important for tracking how well our product solves customer pain points. Additionally, I monitor revenue growth and customer feedback to ensure our product is meeting the business’s financial objectives. In a recent project, we increased monthly active users by 20% by making data-driven improvements based on user feedback.” 5. Can You Explain a Complex Product Feature to a Non-Technical Audience? This question evaluates your communication skills and your ability to simplify complex concepts, which is vital when dealing with stakeholders who aren’t familiar with technical jargon. How to Answer: Choose a specific feature and break it down step by step, avoiding technical terms. Relate the feature to its benefits for users or the business. Focus on making the concept clear and relatable. Example Answer: “Let’s take our new recommendation engine feature. It’s designed to suggest products based on customer preferences. Think of it as a personal shopping assistant that remembers your choices and recommends products you might like. The more you use it, the better it gets at predicting your preferences, increasing your likelihood of finding something you love.” 6. How Do You Handle Product Launches? A product launch involves various teams and stakeholders, and your approach can determine the success of the launch. Interviewers want to see how you manage the planning, coordination, and execution of a launch. How to Answer: Describe the steps you take when
Cross-Functional Collaboration: How Product Managers Bring Teams Together
Cross-Functional Collaboration: How Product Managers Bring Teams Together Introduction In today’s fast-paced business world, the success of a product is no longer just about building a great product; it’s about building a product through collaboration. Product managers (PMs) play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between various teams—engineering, marketing, sales, customer support, and design—to ensure the product meets its goals. Cross-functional collaboration, the process of multiple departments working together to achieve a common objective, is essential for product success. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of cross-functional collaboration, its challenges, and how product managers can facilitate teamwork between diverse teams to deliver superior results. Why Cross-Functional Collaboration Matters Product managers are the glue that binds all aspects of a product’s lifecycle together. The role involves working with various teams, each having its own expertise and focus, to ensure the product is designed, built, launched, and maintained successfully. Without effective collaboration, teams might pull in different directions, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and misalignment of product goals. Here’s why cross-functional collaboration is crucial: Holistic Product Development: Product success requires input from different departments. Design ensures the product is user-friendly, engineering guarantees technical feasibility, and marketing ensures it resonates with the target audience. Better Decision-Making: By bringing together diverse perspectives, product managers can make more informed decisions, avoiding blind spots and fostering innovation. Streamlined Processes: Effective collaboration leads to clearer communication, fewer misunderstandings, and smoother product development workflows. Customer-Centric Products: Cross-functional teams can respond to customer feedback faster and more accurately, ensuring the product remains relevant and competitive. Challenges of Cross-Functional Collaboration Although cross-functional collaboration is essential, it comes with its own set of challenges. Product managers need to be prepared to address these obstacles to ensure effective teamwork: Different Goals and Priorities: Each department may have its own KPIs and objectives, which can sometimes conflict with the overall product goals. Communication Barriers: Technical jargon, misinterpretation of objectives, and different working styles can hinder effective communication. Resource Allocation: Different teams might have competing demands for resources, which can create tension and delays. Decision-Making Bottlenecks: Having multiple decision-makers can slow down the process, especially if the roles and responsibilities are not clearly defined. Despite these challenges, product managers can play a crucial role in aligning teams and navigating conflicts. How Product Managers Facilitate Cross-Functional Collaboration 1. Establish Clear Objectives and Shared Goals One of the first steps in fostering effective collaboration is setting clear, shared goals. Product managers must ensure that all teams are aligned with the product vision, mission, and roadmap. Align Team Goals with Product Vision: Ensure that every team understands how their work contributes to the larger product vision. Set SMART Goals: Ensure goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This clarity helps prevent misalignment between teams. Keep Communication Open: Product managers should regularly communicate the product’s progress and share updates with all teams. Actionable Tip: Hold a cross-functional kickoff meeting to discuss the product’s vision, goals, and KPIs. This ensures everyone is on the same page from the beginning. 2. Foster a Culture of Transparency and Open Communication Clear and open communication is vital for seamless collaboration. Product managers should create an environment where teams can freely exchange ideas and concerns. Use Collaboration Tools: Tools like Slack, Trello, and Jira can facilitate communication, task management, and real-time updates. These platforms ensure everyone has access to important information and deadlines. Regular Check-ins: Hold weekly or bi-weekly stand-up meetings to keep teams updated on each other’s progress, bottlenecks, and milestones. This promotes transparency and keeps everyone engaged. Encourage Feedback: Create an environment where teams feel comfortable providing constructive feedback and asking questions without fear of conflict. Actionable Tip: Implement a centralized communication platform (e.g., Confluence or Notion) for sharing documents, updates, and feedback in real time. 3. Define Roles and Responsibilities Clearly Confusion around roles and responsibilities can hinder collaboration. Product managers need to clearly define who is responsible for what at each stage of the product lifecycle. Create Clear Job Descriptions: Outline the roles and responsibilities of each team in relation to the product development process. RACI Matrix: A RACI Matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) is a useful tool to clarify who is involved in each task and decision-making process. This ensures that no one team or individual feels overwhelmed or left out. Empower Teams: Allow teams to make decisions in their areas of expertise, but ensure product managers are the final decision-makers when cross-departmental coordination is needed. Actionable Tip: Use the RACI framework for clarity around who owns and who needs to be consulted on each task. 4. Facilitate Problem-Solving and Conflict Resolution Conflicts are inevitable, especially when different teams have varying opinions. Product managers should be skilled in resolving conflicts constructively. Encourage Collaborative Problem-Solving: When disagreements arise, encourage teams to come together to discuss their points of view and find mutually beneficial solutions. Focus on the End Goal: Emphasize the product’s success as the common objective. This can help align teams and keep discussions focused on finding solutions. Be a Mediator: Product managers should remain neutral and guide conversations towards a resolution without taking sides. Actionable Tip: When conflicts arise, organize a problem-solving session with representatives from each team. Let everyone voice their concerns and collaboratively find solutions. 5. Celebrate Success and Learn from Failures Acknowledge the efforts of cross-functional teams, celebrate wins, and learn from failures. This encourages further collaboration and improves morale. Celebrate Milestones: When teams meet goals or hit product milestones, celebrate these achievements together. This fosters a sense of teamwork and accomplishment. Post-Mortem Analysis: After a project is completed, conduct a retrospective to analyze what went well and what can be improved for future projects. Actionable Tip: After every major milestone or product launch, hold a celebration or team-building event to acknowledge hard work and boost team morale. Best Practices for Cross-Functional Collaboration Here are some best practices for product managers to ensure efficient and smooth cross-functional collaboration: Build Relationships Across Teams: Develop trust and rapport with key members from different
How to Manage Multiple Products as a Product Manager
How to Manage Multiple Products as a Product Manager Introduction Managing multiple products simultaneously is one of the most challenging yet rewarding tasks a product manager can undertake. Each product comes with its unique set of challenges, from varying customer needs to different market demands, and product managers must juggle their attention across multiple teams, timelines, and deliverables. Whether you are managing a portfolio of physical products, software solutions, or digital services, understanding how to effectively manage multiple products is crucial to ensuring their success. In this blog, we’ll explore the best strategies, tools, and practices that can help product managers thrive while managing multiple products. Key Challenges of Managing Multiple Products Before diving into how to manage multiple products, it’s important to understand the challenges that come with it. These include: Prioritization: Deciding which product or feature gets attention first can be overwhelming, especially when each product has different business objectives and timelines. Resource Allocation: Balancing resources, including time, budget, and personnel, across multiple product teams can lead to potential inefficiencies and missed deadlines. Stakeholder Management: Coordinating between different departments and stakeholders for each product requires careful communication and alignment. Market Trends and Competition: Keeping track of industry shifts, competitor actions, and market trends for each product can be time-consuming. Maintaining Product Quality: Ensuring consistent quality across all products while meeting different customer expectations. By identifying these challenges, product managers can put strategies in place to effectively overcome them. Strategies for Managing Multiple Products 1. Prioritize and Categorize Products Managing multiple products means dealing with different levels of urgency and strategic importance. Prioritization is key to success. Establish Clear Goals: Define the business objectives for each product. This helps in deciding which products need more attention and resources at any given time. Categorize Products by Importance: Some products may require more frequent updates or development, while others might need less attention. Use categories such as “high-priority,” “long-term,” and “low-priority” to guide decision-making. Actionable Tip: Use the Eisenhower Matrix to sort tasks into urgent vs. important categories to manage your time and attention effectively. 2. Delegate and Empower Your Teams You can’t do everything yourself, and managing multiple products requires building strong, reliable teams that you can delegate tasks to. Empower Teams: Assign product owners to each product, allowing them to take full responsibility for their product’s success. Trust your teams to execute the vision while you focus on overarching strategy. Develop a Strong Communication Structure: Regular check-ins, stand-up meetings, and clear reporting systems will help keep everything on track. Ensure that team members are aware of each other’s responsibilities and timelines to avoid overlap. Actionable Tip: Set up weekly or bi-weekly touchpoints to track the progress of each product. Tools like Trello or Asana can help in setting clear tasks and deadlines for teams. 3. Streamline Processes and Workflows When you’re handling multiple products, efficiency is vital. Streamlining processes will help you save time and effort in managing day-to-day tasks. Use Agile Methodology: Agile product management allows for iterative development and quick pivots. By adopting Agile practices, you can ensure that every product is continuously improving while minimizing delays. Create Reusable Templates: Develop templates for things like roadmaps, status reports, and sprint planning. These can be adapted to suit each product’s specific needs but will save time on repetitive tasks. Standardize Workflows: Whether it’s customer feedback collection, product testing, or product launches, standardizing key workflows helps maintain consistency and reduces the likelihood of mistakes. Actionable Tip: Create a standardized process for handling common tasks, such as product feedback gathering, and ensure it’s followed across all product teams. 4. Use Product Portfolio Management Tools Product portfolio management tools help product managers oversee all products from a centralized dashboard, allowing for easier decision-making and resource allocation. ProductRoadmap.com: Use product management tools to create a unified product roadmap across all products. This will provide visibility and help prevent product overlap and schedule clashes. Jira: This tool is particularly useful for managing tasks, sprints, and timelines across multiple products. It allows you to track progress, assign resources, and plan for future iterations. Aha!: Aha! is another great tool for building and sharing roadmaps across teams, tracking objectives, and defining product strategies. Actionable Tip: Choose a portfolio management tool that aligns with your team size, complexity, and product types. Ensure all stakeholders have access to real-time information. 5. Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Monitoring KPIs for each product ensures that you are aligned with your business objectives. Each product will have different metrics to focus on, but common KPIs for product managers include: User Acquisition & Retention Rates: Monitor how well each product attracts and retains users. Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT): Understand user sentiment by collecting feedback and analyzing satisfaction levels. Revenue Growth: Track sales performance and other monetization metrics. Product Usage: Keep an eye on how often each product is being used and identify areas for improvement. Actionable Tip: Use dashboards (via tools like Google Analytics or Tableau) to track product performance in real time. This will help you make data-driven decisions and highlight areas needing attention. 6. Stay Aligned with Stakeholders Effective communication is the backbone of product management, especially when dealing with multiple products. Ensure that all stakeholders, including senior leadership, marketing, and development teams, are aligned on the goals and progress of each product. Regular Reporting: Send out weekly or bi-weekly status reports to keep all stakeholders updated. Ensure Cross-Functional Collaboration: Align your teams around shared goals, ensuring marketing, development, sales, and support are all working towards the same outcomes for each product. Actionable Tip: Set up an internal communication platform like Slack or Microsoft Teams for quick collaboration and information sharing among all teams involved. Time Management Tips for Product Managers When managing multiple products, effective time management is critical. Here are a few tips: Block Time for Each Product: Schedule specific time blocks in your calendar for each product. This prevents you from jumping between products too frequently and helps you focus on one at a time.
The Role of Data Analytics in Modern Product Management
The Role of Data Analytics in Modern Product Management Introduction In today’s fast-paced, competitive business landscape, data analytics has become an essential tool for product managers. With the vast amount of data available, product managers need to leverage this resource to drive informed decisions and deliver products that meet customer needs while achieving business goals. Data analytics in product management goes beyond simple number crunching. It helps product managers gain deeper insights into user behavior, market trends, and performance metrics, enabling them to make decisions that drive product innovation, growth, and long-term success. In this blog, we’ll explore the role of data analytics in modern product management and how product managers can use it to enhance their decision-making process. Why Data Analytics Matters in Product Management Product management is inherently complex. From market research to product development and launch, product managers are constantly juggling various tasks, all while ensuring that the product delivers value to users and meets business objectives. Data analytics helps streamline this process by providing actionable insights that guide these decisions. Here are some key reasons why data analytics is critical in modern product management: Informed Decision-Making: Data-driven insights help product managers make decisions based on actual user behavior, rather than assumptions or intuition. Customer-Centric Approach: Analytics help product managers understand user preferences, pain points, and feedback, allowing them to develop products that better meet customer needs. Performance Monitoring: Analytics tools track how well a product is performing in the market, allowing product managers to identify opportunities for improvement. Optimizing Product Roadmaps: Data analytics helps prioritize features and improvements that will have the greatest impact, ensuring a more effective product development process. Key Areas Where Data Analytics Enhances Product Management 1. User Research and Customer Insights Understanding your users is the foundation of successful product management. Data analytics can uncover valuable insights about customer behavior, needs, and preferences, allowing product managers to make decisions that are tailored to their target audience. How it helps: Customer Segmentation: By analyzing user demographics, behaviors, and purchase patterns, product managers can create more targeted product offerings for specific customer segments. Behavioral Analytics: Tools like heatmaps, click tracking, and session recordings give product managers insights into how users interact with the product, helping them identify areas for improvement. User Feedback Analysis: Using sentiment analysis on reviews, social media mentions, and customer support tickets, product managers can gauge overall user satisfaction and spot recurring pain points. Actionable Tip: Use tools like Google Analytics, Hotjar, and Mixpanel to analyze user behavior and collect actionable insights. 2. Product Development and Design Data analytics plays a crucial role in guiding product development and design decisions. Product managers can use data to test ideas, validate hypotheses, and prioritize features that align with both customer needs and business goals. How it helps: Feature Prioritization: Product managers can use customer feedback and data-driven models to determine which features will most likely drive user engagement and satisfaction. A/B Testing: Conducting A/B tests allows product managers to test variations of features or designs to determine which version performs better based on user responses. Design Optimization: Data can reveal design flaws and areas of improvement, enabling product managers to refine the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) based on real usage patterns. Actionable Tip: Utilize A/B testing platforms like Optimizely or VWO to experiment with design and feature changes and assess the impact on user behavior. 3. Product Launch and Marketing Once the product is ready for launch, data analytics becomes essential for executing a successful go-to-market strategy. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and customer interactions, product managers can fine-tune marketing efforts and make sure the product reaches the right audience. How it helps: Market Fit Evaluation: Analytics can help product managers evaluate whether the product is resonating with the target market and whether it meets customer expectations. Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Using data to track landing page performance, email campaigns, and social media ads allows product managers to optimize conversion rates and improve customer acquisition strategies. Customer Acquisition: By analyzing the performance of different marketing channels, product managers can focus on the most effective channels for customer acquisition. Actionable Tip: Use tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, or HubSpot to track key metrics and assess the effectiveness of marketing strategies. 4. Performance Tracking and Product Iteration After the product is launched, continuous performance tracking is essential. Data analytics helps product managers measure product performance in real time and identify areas that require iteration or improvement. How it helps: Monitoring KPIs: Track metrics like user engagement, retention, and churn to understand how well the product is meeting user needs and business goals. User Retention: Data analytics can help track customer retention and identify reasons for churn, allowing product managers to address issues proactively. Continuous Improvement: With ongoing data collection, product managers can identify areas where the product can be improved, whether it’s a feature update, a bug fix, or a design tweak. Actionable Tip: Set up dashboards to track KPIs such as active users, user retention, lifetime value (LTV), and churn rate, using tools like Tableau or Power BI for visual insights. 5. Forecasting and Roadmap Planning Data analytics also plays a crucial role in long-term planning. By analyzing trends and user feedback, product managers can forecast product performance and plan roadmaps that align with both current market demands and future growth. How it helps: Demand Forecasting: Using historical data, product managers can predict future demand for features and plan resources accordingly. Trend Analysis: Data-driven trend analysis helps product managers stay ahead of the competition by identifying emerging market shifts, new technologies, and evolving customer needs. Resource Allocation: Data analytics helps optimize the allocation of resources by identifying high-priority tasks and features that will have the greatest impact. Actionable Tip: Use predictive analytics tools like Salesforce Einstein or IBM Watson Analytics to forecast future trends and adjust your roadmap accordingly. How to Get Started with Data Analytics in Product Management Invest in the Right Tools: Use analytics platforms such as
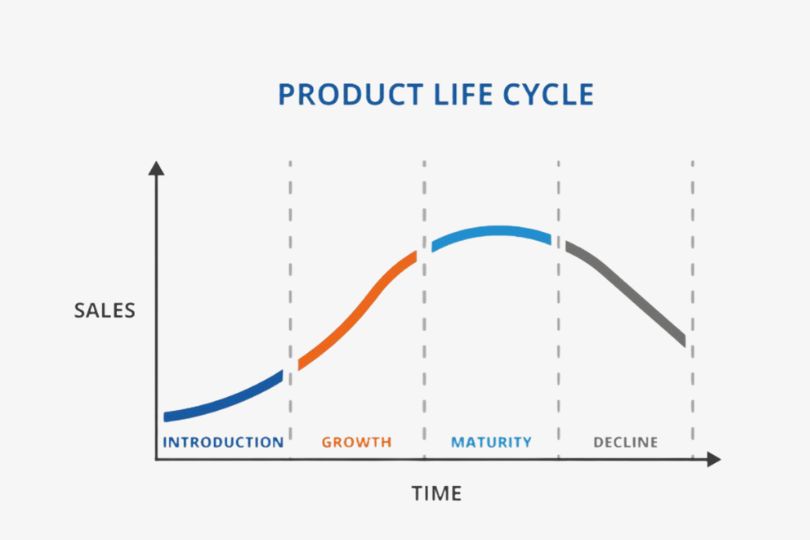
Understanding the Product Lifecycle: A Framework for Product Managers
Understanding the Product Lifecycle: A Framework for Product Managers Introduction The product lifecycle is a critical concept for product managers. It provides a structured approach for managing a product from its initial idea to its eventual phase-out. Understanding the product lifecycle helps product managers make informed decisions, prioritize resources, and optimize strategies throughout the product’s journey. In this blog, we’ll explore the stages of the product lifecycle, offering a practical framework to help product managers successfully navigate each phase and drive the product’s success. What is the Product Lifecycle? The product lifecycle refers to the series of stages a product goes through from its introduction to the market until it is discontinued. Understanding these stages allows product managers to anticipate challenges, make informed decisions, and drive product success. Typically, the product lifecycle consists of the following stages: Introduction: The product is launched. Growth: The product gains traction and begins to see rapid adoption. Maturity: The product has reached its peak, and growth slows down. Decline: The product begins to lose market interest and eventually faces obsolescence. By understanding these phases, product managers can optimize their efforts, allocate resources effectively, and adjust strategies to align with the product’s current lifecycle stage. The Stages of the Product Lifecycle 1. Introduction Phase The introduction phase is where your product is first launched into the market. This stage is often characterized by high costs and low sales, as the product has yet to gain a significant following. Key Activities: Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand your target audience, competitors, and potential demand for the product. Positioning and Branding: Define the product’s unique value proposition (UVP) and craft a messaging strategy that resonates with your target audience. Marketing and Promotion: Focus on building awareness. Use marketing tactics such as social media campaigns, influencer partnerships, and targeted ads to introduce your product. Feedback Collection: Engage early adopters and gather feedback to refine the product and identify any potential issues. Tips for Success: Focus on educating customers about the product’s benefits and features. Be prepared for limited sales initially. Patience and consistent marketing are crucial. Ensure your customer support is prepared to handle early inquiries and issues. 2. Growth Phase Once your product gains traction, it enters the growth phase. During this stage, sales increase significantly, and more customers begin to adopt your product. Competition might also increase as other players enter the market. Key Activities: Scaling Marketing Efforts: At this stage, you need to ramp up your marketing campaigns to build brand awareness and differentiate your product from competitors. Product Improvements: Based on early feedback, consider improving your product. This could involve adding features, enhancing user experience, or fixing any issues that have surfaced. Optimizing Distribution Channels: Expand your distribution networks and sales channels. Look into partnerships, retail opportunities, and international expansion. Customer Retention: Focus on customer satisfaction to turn one-time buyers into loyal customers. Implement retention strategies like loyalty programs or customer success initiatives. Tips for Success: Invest in customer support to maintain satisfaction as your customer base grows. Leverage data and analytics to monitor growth and identify trends. Keep an eye on emerging competitors and adapt your strategy to maintain a competitive edge. 3. Maturity Phase The maturity phase is when your product has reached its peak in terms of sales and market penetration. Growth slows down, and the product becomes a well-established offering in the market. While competition is at its highest, it also becomes crucial to maintain market share. Key Activities: Product Optimization: At this stage, it’s important to focus on refining and optimizing your product. Look for ways to improve performance, usability, or features that meet evolving customer needs. Differentiation: To avoid stagnation, continue differentiating your product through unique features, value propositions, and superior customer service. Cost Management: As the product becomes more standardized, focus on reducing costs. Streamline operations and production processes to maintain profitability. Market Segmentation: Revisit your target segments. Look for new opportunities in untapped markets or specific niches. Tips for Success: Regularly engage with customers to ensure they remain satisfied with the product. Focus on building long-term customer relationships and loyalty. Analyze competitor strategies and adjust your offering to stay relevant. 4. Decline Phase The decline phase occurs when your product starts to lose market interest. Sales decrease, customer demand wanes, and newer, more innovative products may have emerged to take its place. This phase doesn’t mean the end, but it requires strategic decisions on how to phase the product out or revamp it. Key Activities: Evaluate the Product’s Future: Assess whether the product is still worth maintaining or if it’s time to discontinue it. Analyze factors like profitability, market relevance, and customer demand. Cost-Cutting Measures: If you choose to keep the product on the market for a while longer, focus on reducing production and operational costs to maintain profitability. Product Transition: Consider offering customers an alternative, whether it’s a new product or an upgrade. Ensure smooth transitions for customers who may be affected by the discontinuation. Tips for Success: Be transparent with customers about the product’s phase-out process, offering support as they transition to new options. Use this phase as an opportunity to gather insights for your next product launch. How to Manage the Product Lifecycle Effectively 1. Regular Product Audits Conduct regular audits to assess the product’s performance at each lifecycle stage. This includes tracking sales, customer feedback, market trends, and competitor activity. These audits help you make data-driven decisions about the next steps. 2. Cross-Functional Collaboration Product management requires collaboration across multiple teams—marketing, sales, design, and engineering. Keep communication open between these departments to ensure that everyone is aligned and working toward the same goals. 3. Customer-Centric Approach Throughout the product lifecycle, maintain a focus on the customer. Gather feedback from your users at every stage and ensure that their needs and pain points are addressed. 4. Flexibility in Strategy The product lifecycle is not a rigid, linear process. Market conditions, customer preferences, and competition can change rapidly. Be prepared to
How to Navigate Conflict as a Product Manager: Tips for Success
How to Navigate Conflict as a Product Manager: Tips for Success Introduction Conflict is an inevitable part of any role that involves working with diverse teams, and as a product manager, you’re no stranger to it. Whether it’s a disagreement with stakeholders over feature priorities or a clash between engineering and design teams, conflicts can arise at any stage of the product development cycle. The key is not to avoid them but to manage and resolve them effectively. In this blog, we’ll dive into the common sources of conflict in product management, strategies to navigate those conflicts, and tips for turning challenging situations into opportunities for growth and collaboration. Why Conflicts Arise in Product Management Before we can address how to manage conflict, it’s essential to understand why conflicts arise in product management. Here are some common reasons: Conflicting Priorities: Stakeholders, teams, and individuals often have different goals and priorities, leading to disagreement on features, deadlines, and resources. Miscommunication: Lack of clarity around product goals, timelines, or expectations can easily lead to misunderstandings. Limited Resources: Product managers often have to make tough decisions about where to allocate limited time, budget, and personnel, which can lead to tension. Differing Perspectives: Teams like UX, engineering, and marketing may approach problems from different perspectives, creating friction when it comes to aligning on solutions. Understanding the root causes of conflict allows product managers to approach each situation with a clear strategy and mindset. Key Strategies for Navigating Conflict as a Product Manager Here are some actionable strategies to help product managers navigate and resolve conflicts effectively: 1. Foster Open and Transparent Communication The foundation of resolving any conflict is clear communication. As a product manager, you should always encourage an environment of open, transparent communication where everyone feels heard and understood. Listen Actively: When conflict arises, listen to all parties involved before jumping to conclusions or offering solutions. Active listening shows respect for differing opinions. Clarify Misunderstandings: Miscommunication can often fuel conflict. Take the time to clarify expectations, goals, and reasons behind decisions to prevent confusion from escalating into a bigger issue. Encourage Constructive Feedback: Create a safe space where team members can provide feedback without fear of backlash. This helps identify underlying issues before they grow into conflicts. 2. Align on Shared Goals One of the most effective ways to prevent and resolve conflict is to ensure that all teams are aligned on the same overall goals. When everyone understands the product vision and their role in achieving it, disagreements are less likely to occur. Establish Clear Product Objectives: Ensure that everyone, from design to engineering, understands the key business goals, user needs, and product vision. Involve Teams Early: Involve key stakeholders and team members early in the planning process to ensure their input is taken into account from the start. This helps minimize conflicts later. Revisit Goals Regularly: Keep the product vision top of mind. Regularly revisit and reinforce the product’s goals to keep teams aligned, especially during tough decision-making processes. 3. Stay Neutral and Act as a Mediator As a product manager, you must be a neutral party in conflicts between different teams. You may need to mediate discussions, ensuring all voices are heard and helping teams find common ground. Maintain Objectivity: As the mediator, avoid taking sides. Stay focused on finding a solution that benefits the product and the teams involved. Encourage Empathy: Help each party see things from the other’s perspective. Empathy fosters understanding and cooperation, which can quickly defuse tension. Facilitate Collaboration: After understanding everyone’s concerns, facilitate a collaborative problem-solving process. Guide the team toward finding a compromise that satisfies both user needs and business goals. 4. Focus on Solutions, Not Blame When conflicts arise, it’s easy to focus on who is at fault. However, this approach rarely leads to productive outcomes. Instead, focus on finding solutions that move the product forward. Shift the Focus to Outcomes: Encourage the team to think about the best solution for the product, users, and business goals rather than getting caught up in blame. Collaborate on Problem-Solving: Work with the team to brainstorm and evaluate potential solutions. This inclusive approach ensures that everyone feels involved and invested in the solution. Compromise and Prioritize: Sometimes, conflicts arise due to competing priorities. In these situations, it’s important to compromise and prioritize the most impactful features or solutions. 5. Be Transparent About Trade-Offs Product management is all about balancing trade-offs. Conflicts often arise when teams are unwilling to accept certain compromises. Be transparent about the trade-offs you’re making and the reasons behind them. Clarify the Constraints: If there are budget, time, or resource limitations, make sure all teams understand these constraints upfront. Explain the Rationale: When you make tough decisions, such as prioritizing one feature over another, communicate the reasoning behind it. Explain how the decision will benefit the product in the long run. Highlight the Bigger Picture: Help teams see how their work fits into the overall product and company strategy. This can reduce frustration and increase buy-in. 6. Learn from Past Conflicts Every conflict provides an opportunity for learning. After a conflict has been resolved, take the time to reflect on the situation to identify what worked well and what could be improved. Debrief with Teams: Hold a post-mortem meeting to discuss what caused the conflict and how it was resolved. This reflection helps prevent similar issues in the future. Use Conflict as a Learning Tool: Use past conflicts to fine-tune processes, improve communication, and ensure that future conflicts are managed more effectively. Encourage Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement, where teams learn from every challenge and become better equipped to handle future conflicts. How to Handle Specific Types of Conflicts Different types of conflicts may require different approaches. Here’s how to handle a few common ones: 1. Conflicts Over Priorities Prioritization conflicts often occur when stakeholders or teams disagree on which features should be prioritized. To resolve this: Use a Framework: Implement a prioritization framework like RICE (Reach, Impact,
The Product Manager’s Guide to Working with UX Teams
The Product Manager’s Guide to Working with UX Teams Introduction In the world of product development, collaboration is key. As a product manager, one of the most crucial partnerships you will have is with the UX team. The synergy between product management and UX design can lead to innovative products that delight customers and meet business goals. However, building a seamless working relationship requires clear communication, shared goals, and a mutual understanding of each team’s role. In this guide, we’ll explore how product managers (PMs) can effectively collaborate with UX teams to drive product success. From fostering open communication to aligning on objectives, we will dive into actionable strategies that can improve your product development process. Why Collaboration Between Product Managers and UX Teams is Crucial Before we get into the specifics of working with UX teams, it’s important to understand why this collaboration matters. The relationship between product managers and UX teams is pivotal because: User-Centered Focus: UX teams bring a deep understanding of user behavior, needs, and pain points. Product managers, on the other hand, focus on business goals and product-market fit. Together, they ensure that the product meets user needs while achieving business objectives. Enhanced Decision Making: By working closely with UX, PMs can make informed decisions based on user research and design feedback, leading to products that resonate with their audience. Streamlined Development: Effective collaboration between the teams helps avoid misunderstandings, reduces redesigns, and ensures a smoother, more efficient development process. Key Principles for Product Managers When Working with UX Teams As a product manager, working with a UX team means aligning your goals, setting clear expectations, and fostering a collaborative environment. Here are some key principles for working effectively with UX teams: 1. Start with a Shared Vision Both the product manager and the UX team should be aligned on the vision for the product. This vision should be user-centered and based on business objectives. Here’s how to establish that shared vision: Collaborate on Product Goals: Define clear product goals together. Discuss how these goals will impact users and the product’s market position. Create a Unified Vision Statement: A clear and concise product vision statement will help guide both the product and design teams in the right direction. 2. Communicate Openly and Frequently Effective communication is vital in any relationship, especially between product managers and UX teams. Regular communication helps ensure both teams are on the same page and fosters a collaborative environment. Set Regular Meetings: Schedule recurring check-ins to review progress, discuss challenges, and align on next steps. Use Collaborative Tools: Tools like Slack, Trello, or Jira can help facilitate ongoing communication, track tasks, and share updates in real time. 3. Be Involved in the Design Process As a product manager, your role is to ensure the product meets user needs while aligning with business goals. Actively participating in the UX design process helps you guide the design team and make informed decisions. Provide Context: Share user insights, market research, and customer feedback with the UX team to provide context for design decisions. Review Prototypes Together: Regularly review wireframes and prototypes to ensure they align with the product’s goals. 4. Prioritize User Research User research is at the heart of UX design, and it’s equally important for product managers. The insights derived from user testing and research help inform product decisions. Collaborate on User Testing: Work together to conduct user research, usability tests, and user interviews. This helps validate assumptions and uncover new insights. Use Data to Make Decisions: Ensure decisions are backed by data, whether it’s qualitative insights from users or quantitative data from product analytics. 5. Foster a Culture of Feedback Feedback is essential to the iterative nature of product development. Both the PM and UX teams should be open to giving and receiving feedback to improve the product. Encourage Honest Feedback: Create an environment where constructive feedback is welcomed. Be open to revising the product based on the feedback from both users and team members. Use Feedback Loops: Establish regular feedback loops to ensure the product continues to evolve based on user input and market changes. Best Practices for Product Managers to Support UX Teams To enhance collaboration and improve outcomes, product managers should consider these best practices when working with UX teams: 1. Align on Success Metrics Agreeing on success metrics upfront ensures that both the PM and UX team are working toward the same outcomes. Success metrics could include user engagement, satisfaction, retention, or business outcomes like revenue or customer acquisition. Define Clear KPIs: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the product’s user experience and overall performance. Track Metrics Together: Monitor user behavior, analyze feedback, and review data together to make data-driven decisions. 2. Stay Focused on the End-User While business goals are important, the product’s success hinges on user satisfaction. Always keep the end-user in mind when working with UX teams. Empathy Mapping: Use empathy maps to better understand users’ emotional states, challenges, and motivations. This tool helps both the PM and UX teams align on user needs. Customer Journey Mapping: Create detailed customer journey maps to visualize user experiences at every touchpoint. This can help identify pain points and opportunities for improvement. 3. Manage Constraints and Expectations Product development often involves navigating constraints like timelines, budgets, and resources. It’s essential to manage these constraints while still maintaining a high-quality user experience. Set Realistic Deadlines: Work with the UX team to establish achievable timelines. Balance the urgency of product launches with the need for thoughtful design and testing. Prioritize Features Based on Value: Use frameworks like MoSCoW (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have) to prioritize features based on their importance to both users and the business. 4. Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration UX design doesn’t happen in isolation. Encourage collaboration with other teams, including engineering, marketing, and sales. Cross-functional collaboration helps ensure that everyone is aligned on the product vision and goals. Involve Engineering Early: Engaging the engineering team early in the design
Key Metrics Every Product Manager Should Track
Key Metrics Every Product Manager Should Track Introduction Product managers play a crucial role in guiding products through every stage of development. One of the key responsibilities is tracking performance and success. Metrics are essential for making informed decisions, understanding user behavior, and aligning with business goals. In this blog, we will explore the key metrics that every product manager should track. By understanding these metrics, you can measure the success of your product, improve decision-making, and drive better outcomes for your product and business. Why Metrics Matter for Product Managers Tracking the right metrics is fundamental to managing a product effectively. These metrics provide insights into the performance of the product, user satisfaction, and areas for improvement. Without proper measurement, product managers might make decisions based on intuition rather than data, leading to inefficiencies or missed opportunities. Metrics also help PMs align product development efforts with business objectives, communicate progress to stakeholders, and adjust strategies as necessary. Essential Product Metrics Every Product Manager Should Track There are several categories of metrics that product managers should monitor to assess the health of their products. Below are the most critical metrics in each category: 1. Product Usage Metrics Understanding how users interact with your product is crucial to improving its features and functionality. The following product usage metrics are vital: Active Users (Daily Active Users – DAU / Monthly Active Users – MAU): These metrics track the number of users who interact with your product on a daily or monthly basis. A high DAU/MAU ratio indicates high user engagement and retention. Retention Rate: This measures how many users continue using your product over time, typically on a weekly, monthly, or quarterly basis. Higher retention rates indicate that users find value in the product. Session Length: This metric tracks how long users spend interacting with your product during each session. Longer session lengths can indicate that users are engaging more deeply with your product. Feature Usage: Tracking the adoption rate of specific features allows you to understand which parts of the product are most valuable to users. This helps prioritize future updates or improvements. 2. Customer Satisfaction Metrics Product managers need to gauge customer satisfaction to ensure the product is meeting user needs. The following metrics help track this: Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty by asking users how likely they are to recommend your product to others. A high NPS indicates that your customers are satisfied and willing to act as advocates for your brand. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): This metric is typically collected after a user interaction, such as a support request or after product usage. It helps gauge the satisfaction level of users with a specific experience. Customer Effort Score (CES): CES measures how easy or difficult it was for customers to achieve their goal with your product. A lower effort score is better, indicating that your product is user-friendly and easy to navigate. 3. Financial Metrics Financial metrics are crucial for ensuring that your product aligns with business objectives and generates a return on investment. Some key financial metrics include: Revenue: Tracking overall revenue generated by the product helps you determine whether the product is meeting financial goals. Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): CLTV measures the total revenue you can expect from a customer over their entire relationship with your product. It’s a key indicator of product profitability. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC calculates the cost of acquiring a new customer. If the CAC is too high compared to CLTV, it may indicate inefficiencies in the customer acquisition process. Churn Rate: Churn refers to the percentage of customers who stop using your product over a specific period. A high churn rate is a red flag and suggests that improvements are needed to retain customers. 4. Conversion Metrics Conversion metrics are vital for understanding how well your product is turning potential customers into paying customers, or achieving other business goals. Conversion Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of users who complete a desired action (such as signing up for a trial, making a purchase, etc.) compared to the total number of visitors. Funnel Metrics: Tracking users through the various stages of the sales or onboarding funnel allows you to identify bottlenecks where users drop off. Improving these stages can boost conversions. Onboarding Completion Rate: For products with an onboarding process, tracking how many users complete it is essential. A high completion rate indicates that users are successfully learning how to use your product. 5. Growth Metrics Growth metrics provide insight into how your product is scaling and reaching new users. Customer Acquisition Rate (CAR): This metric tracks how quickly new customers are being acquired. It helps you understand the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and the product’s overall growth trajectory. Market Penetration: Market penetration measures the product’s reach within its target market. Tracking this metric helps identify whether your product is gaining traction within the desired customer base. Viral Coefficient: This measures how many new users each existing user brings to the product. A viral coefficient greater than 1 indicates that your product has a viral nature, meaning existing users help bring in new ones. How to Use These Metrics Effectively Tracking metrics alone is not enough; product managers must know how to use the data to drive decisions. Here are some tips on how to leverage these metrics effectively: 1. Set Clear Goals and KPIs Before diving into metrics, it’s essential to set clear business and product goals. Define the KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that align with those goals, and use them as a guide to measure success. For example, if your goal is to improve user engagement, you should focus on metrics like DAU/MAU ratio, session length, and feature usage. 2. Segment Your Data Data segmentation allows you to dive deeper into specific user groups and behaviors. Segment your users by factors like geography, user type, or behavior. This will help you identify patterns that may be hidden in aggregate data and allow for more
The Role of a Product Manager in an Agile Environment
The Role of a Product Manager in an Agile Environment Introduction Agile methodologies have revolutionized the way companies approach product development, allowing teams to deliver value to customers more quickly and efficiently. In this fast-paced environment, the role of the product manager has become increasingly vital. A product manager (PM) must work closely with agile teams, ensuring that the product meets customer needs while maintaining alignment with business goals. In this blog, we’ll dive into the role of a product manager in an agile environment, exploring key responsibilities, challenges, and best practices that can help PMs succeed in agile teams. Understanding Agile Methodology Before diving into the role of a product manager in an agile environment, it’s essential to understand what agile is and how it works. Agile is an iterative approach to software development and project management. The methodology focuses on delivering small, incremental improvements through collaboration, flexibility, and customer feedback. Teams work in short cycles, or sprints, allowing them to adapt quickly to changing requirements and priorities. Core Agile Principles Include: Collaboration over Contract Negotiation: Emphasizing teamwork and collaboration with stakeholders. Responding to Change over Following a Plan: Embracing flexibility in project planning. Customer Collaboration over Contract Negotiation: Focusing on customer satisfaction and feedback. In agile environments, product managers serve as the bridge between the customer, business stakeholders, and development teams. They play a crucial role in ensuring that products are developed according to user needs while aligning with business objectives. Key Responsibilities of a Product Manager in Agile Product managers in agile environments are tasked with a wide range of responsibilities. Here are the key functions that define their role: 1. Defining and Prioritizing Product Backlog One of the primary duties of a product manager is managing the product backlog—a prioritized list of features, enhancements, and bug fixes that need to be addressed in future sprints. Product Backlog: The backlog represents the “to-do list” for the product, containing user stories and tasks to be completed in upcoming sprints. Prioritization: PMs are responsible for prioritizing items in the backlog based on customer needs, business goals, and technical feasibility. Stakeholder Alignment: Product managers must also ensure that the backlog aligns with stakeholder expectations and business objectives. 2. Serving as the Voice of the Customer In an agile environment, the product manager is the key advocate for the customer. They must ensure that the development team is working on features that provide value to users. Customer Insights: PMs gather customer feedback through surveys, interviews, and user testing to create a clear picture of user needs. Customer Journey Mapping: PMs work on mapping out the customer journey and ensuring that the product meets customer pain points at every touchpoint. 3. Facilitating Communication Across Teams Agile development emphasizes close collaboration between cross-functional teams, including designers, developers, and marketing. The product manager plays a central role in facilitating this communication. Collaboration: PMs ensure that all team members understand the product vision and are aligned on the project’s objectives. Transparency: They provide clarity and updates about the product’s goals, progress, and any challenges that arise. Stakeholder Communication: PMs also communicate with business stakeholders to keep them informed about progress, roadblocks, and customer feedback. 4. Iterative Planning and Release Management In agile, the focus is on delivering small, incremental updates. Product managers are responsible for ensuring that these updates align with the overall product strategy. Sprint Planning: PMs collaborate with the development team during sprint planning meetings to define what features will be worked on during the sprint. Releases: PMs help define release schedules and ensure that the product is ready for deployment, coordinating efforts across teams to meet deadlines. 5. Monitoring Product Performance and KPIs Once features are launched, product managers are responsible for tracking their success and iterating on them based on performance. Analytics: PMs monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) like user engagement, retention rates, and conversion metrics to assess product success. Continuous Improvement: Using data, PMs work with the development team to refine the product and make necessary changes to improve performance. Challenges Product Managers Face in Agile Environments While the role of a product manager in an agile environment is highly rewarding, it comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges can help PMs navigate their responsibilities more effectively. 1. Balancing Stakeholder Expectations In agile environments, PMs must juggle competing demands from various stakeholders, such as business executives, customers, and development teams. Challenge: Aligning stakeholders with realistic timelines and feature expectations can be difficult, especially when requirements change frequently. Solution: Establishing transparent communication channels and clearly defining the product roadmap can help manage expectations. 2. Navigating Constant Change Agile is inherently flexible, which can sometimes lead to frequent shifts in priorities. PMs need to be adaptable in response to changing requirements and scope. Challenge: Changes in priorities can disrupt progress and cause confusion among teams. Solution: Product managers should focus on prioritizing items in the backlog and ensure that teams are aware of any changes in direction. 3. Managing Cross-Functional Collaboration While agile emphasizes collaboration, getting everyone on the same page can be challenging. PMs often find themselves coordinating between product development, design, marketing, and sales teams. Challenge: Cross-functional alignment can be difficult, particularly when different departments have their own goals and timelines. Solution: Regular stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives can help foster better communication and collaboration among teams. Best Practices for Product Managers in Agile Environments To excel in an agile environment, product managers need to adopt a few best practices that align with agile principles. Here are some strategies for success: 1. Embrace Flexibility and Adaptation Agile thrives on adaptability. Product managers should be prepared to pivot and adjust as new information and feedback emerge. Best Practice: Be open to iterating on the product and adjusting priorities as necessary. Agile is about delivering continuous value, not rigidly adhering to a pre-set plan. 2. Prioritize Effective Communication Clear communication is key to successful product development. Product managers must ensure that everyone involved in the product is aligned