Case Studies: Successful AI Implementations in the IT Sector Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a transformative force across multiple industries, and the IT sector is no exception. From automating mundane tasks to enhancing security measures, AI is revolutionizing the way IT companies operate. But don’t just take our word for it—let’s dive into some real-world case studies that highlight the successful implementation of AI in the IT sector. These case studies will give you insights into the practical applications of AI and how it has driven innovation, efficiency, and growth for various organizations. 1. AI in IT Support: IBM’s Watson for IT Service Management IBM’s Watson, a leader in AI technology, is a prime example of how AI can streamline IT support. Watson for IT Service Management is an AI-driven solution that enables IT teams to optimize their support operations, enhance user experience, and reduce costs. By leveraging machine learning and natural language processing, Watson can understand and resolve incidents and requests automatically, all while ensuring seamless integration with existing ITSM (IT Service Management) tools. Key Benefits: Faster Response Times: Watson’s AI-powered chatbots handle routine service requests instantly, reducing the time it takes to resolve issues. Improved Decision-Making: Watson analyzes historical data and recommends best practices, helping IT teams make data-driven decisions quickly. Cost Savings: By automating routine tasks, organizations can reduce reliance on human agents, resulting in significant cost savings. Real-World Impact: A global telecommunications company, using Watson for IT Service Management, saw a 50% reduction in support ticket resolution times. The AI system handled over 70% of support requests without human intervention, allowing IT staff to focus on more complex issues. 2. AI for Cybersecurity: Darktrace’s Autonomous Threat Detection Cybersecurity is one of the most critical concerns in the IT industry today, and AI has proven to be an invaluable tool in protecting organizations from cyber threats. Darktrace, a leading cybersecurity company, has implemented AI-powered threat detection systems that use machine learning to identify potential threats in real time. Key Benefits: Autonomous Threat Detection: Darktrace’s AI analyzes network traffic to detect anomalies and predict potential breaches before they occur. Continuous Monitoring: The AI system provides 24/7 surveillance, ensuring that threats are detected and addressed even during off-hours. Scalability: Darktrace’s AI is highly scalable, capable of monitoring large enterprise networks without compromising performance. Real-World Impact: A major financial institution using Darktrace’s AI system detected a sophisticated cyber-attack in its early stages, preventing data theft and financial loss. The AI system flagged unusual activity in real time and alerted the security team, who took swift action to mitigate the risk. 3. AI in Cloud Computing: Microsoft Azure AI Microsoft Azure AI is another significant AI solution that’s transforming the IT industry. Azure AI provides businesses with the tools to build, deploy, and manage AI applications. From cloud-based AI models to cognitive services, Azure enables IT companies to leverage AI for various functions such as predictive analytics, customer service automation, and more. Key Benefits: Predictive Analytics: Azure AI helps organizations predict future trends, such as customer behavior, server load, or system performance, using historical data. Natural Language Processing: Azure’s cognitive services enable applications to understand and respond to human language, improving customer interactions. Scalability: As a cloud platform, Azure AI is highly scalable, allowing businesses to quickly adjust their resources based on demand. Real-World Impact: A global e-commerce giant used Azure AI to enhance its inventory management system. By analyzing purchase patterns and seasonal trends, the AI system was able to predict which products would be in high demand, allowing the company to optimize its stock levels and avoid overstocking or stockouts. This led to a 30% improvement in operational efficiency. 4. AI in IT Operations: ServiceNow’s Virtual Agent ServiceNow is a popular IT service management platform that has integrated AI to enhance its IT operations. The company’s Virtual Agent uses natural language processing and machine learning to handle customer inquiries, automate tasks, and resolve incidents without the need for human intervention. The AI-powered virtual agent is capable of understanding a wide range of requests and can seamlessly hand off more complex issues to human agents. Key Benefits: Automation of Repetitive Tasks: ServiceNow’s Virtual Agent automates common IT service management tasks, such as password resets and access requests, reducing the workload of IT teams. Increased Efficiency: The virtual agent resolves issues faster by using AI to process requests and provide real-time assistance. Improved User Experience: Users benefit from faster resolutions and consistent service, leading to higher satisfaction levels. Real-World Impact: A multinational technology corporation implemented ServiceNow’s Virtual Agent to streamline their IT support operations. As a result, the company saw a 40% reduction in human intervention for routine tasks and improved customer satisfaction by 25%. The Virtual Agent also helped the company manage a 50% increase in service requests without additional staff. 5. AI in IT Helpdesks: Freshdesk’s AI-Powered Support Freshdesk, a popular customer support software, has incorporated AI to enhance the efficiency of IT helpdesks. Freshdesk’s AI assistant, Freddy, automates the resolution of common IT-related issues, such as software installation, error troubleshooting, and configuration queries. Freddy can also prioritize and route tickets to the appropriate human agents based on the complexity of the issue. Key Benefits: Faster Issue Resolution: Freddy uses machine learning to understand issues and resolve them quickly, reducing wait times for users. Ticket Routing and Prioritization: Freddy automatically classifies and prioritizes tickets based on urgency and complexity, ensuring that critical issues are addressed first. Learning from Interactions: Freddy continuously learns from each interaction, improving its accuracy and response quality over time. Real-World Impact: A global technology company adopted Freshdesk’s Freddy to handle its IT helpdesk operations. As a result, the company experienced a 60% reduction in ticket resolution time and a 35% improvement in overall customer satisfaction. Freddy’s AI capabilities also allowed the company to manage an increased volume of support tickets without expanding their team. 6. Challenges and Considerations for Implementing AI in IT While AI offers tremendous benefits to the IT sector, it’s not
Author: Admin
AI Chatbots: Revolutionizing Customer Support in IT
AI Chatbots: Revolutionizing Customer Support in IT In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses are under constant pressure to provide timely, accurate, and efficient customer support. This is particularly true in the IT sector, where customers often face technical challenges that require immediate attention. One solution that has proven to be a game-changer is AI chatbots. AI chatbots are powered by artificial intelligence, allowing them to engage in conversations with users, understand their queries, and provide instant, context-aware responses. For IT companies, AI chatbots are transforming customer support by enhancing efficiency, reducing response times, and improving customer satisfaction. In this blog, we will explore how AI chatbots are revolutionizing customer support in IT and how businesses can implement them to stay competitive. 1. What Are AI Chatbots? AI chatbots are software applications that use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to simulate human conversation. They can interact with customers in a way that feels natural, answering queries, providing troubleshooting assistance, and even resolving issues—all without human intervention. Key Features of AI Chatbots: 24/7 Availability: AI chatbots can operate round the clock, providing continuous support. Instant Response: They deliver quick, real-time answers to customer queries. Context Understanding: Using NLP, AI chatbots can interpret and respond to customer inquiries based on context. 2. How AI Chatbots Are Enhancing IT Customer Support AI chatbots are not just answering basic questions—they are actively improving IT customer support across several key areas. A. Reducing Response Times One of the most immediate benefits of AI chatbots is their ability to handle inquiries instantly. Customers no longer have to wait in long queues or for hours to receive support. AI chatbots can immediately engage with users, process their requests, and offer solutions. This reduces response times and helps IT companies serve a larger volume of customers efficiently. Instant Answers: AI chatbots provide immediate responses to frequently asked questions (FAQs), allowing customers to access support quickly. Efficient Query Resolution: For more complex issues, chatbots can guide customers through step-by-step troubleshooting processes. B. Handling Repetitive Tasks IT support teams often deal with repetitive tasks, such as password resets, software installation instructions, and system status checks. AI chatbots can take over these tasks, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex, high-level queries. Task Automation: Chatbots can handle routine inquiries, thereby automating time-consuming tasks and boosting the overall productivity of support teams. Error Reduction: Automation reduces human error, ensuring that customers receive accurate and consistent responses. C. Personalized Customer Experience AI chatbots can analyze customer data, providing personalized responses based on the user’s past interactions, preferences, and system configuration. This personalization enhances the customer experience by offering more relevant and timely solutions. Customer Data Integration: Chatbots can pull information from customer profiles or CRM systems, allowing them to deliver tailored support and offer customized solutions. Proactive Engagement: AI chatbots can also reach out to customers with proactive messages, such as reminders for system updates or alerting them to potential issues before they escalate. 3. Improving IT Security with AI Chatbots Security is a top priority in the IT industry, and AI chatbots can enhance security by automating monitoring tasks, flagging suspicious activity, and supporting user authentication. A. Instant Security Alerts AI chatbots can integrate with security monitoring systems to alert users of potential security breaches, unusual activity, or system vulnerabilities. By acting as an early-warning system, chatbots can help prevent cyberattacks or mitigate their impact. Real-Time Alerts: When AI detects unusual behavior or a security threat, chatbots can immediately notify the user and provide instructions on how to mitigate the risk. Security Assistance: AI chatbots can guide users through secure login procedures, password updates, and other security measures. B. Ensuring Compliance Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS is crucial for IT businesses. AI chatbots can assist in ensuring compliance by automating tasks such as customer consent management, data handling, and privacy-related requests. Automated Data Protection: Chatbots can automatically request and manage consent from users when handling sensitive data, ensuring that organizations remain compliant with relevant laws. Audit Trails: AI chatbots can maintain logs of customer interactions, providing a transparent audit trail in case of a security review or investigation. 4. Benefits of AI Chatbots for IT Customer Support The adoption of AI chatbots in IT customer support offers numerous benefits for both businesses and customers. Below are some of the most significant advantages: A. Cost Reduction By automating support tasks, AI chatbots reduce the need for a large customer support team, helping businesses save on labor costs. Additionally, chatbots can reduce the number of support tickets, freeing up resources for more critical tasks. Lower Staffing Costs: AI chatbots handle a significant volume of customer queries, reducing the demand for human agents. Operational Efficiency: Automating routine tasks leads to improved operational efficiency, allowing IT teams to allocate resources more effectively. B. Improved Customer Satisfaction The faster, more accurate responses provided by AI chatbots significantly enhance the customer experience. By reducing wait times and offering 24/7 support, businesses can provide an exceptional level of service, which improves customer satisfaction and loyalty. Quick Problem Resolution: AI chatbots can address customers’ issues immediately, reducing frustration and increasing satisfaction. Customer Retention: With personalized experiences and quick resolutions, AI chatbots help improve customer retention rates. C. Scalability As your business grows, scaling customer support can become a challenge. AI chatbots provide a scalable solution, enabling businesses to handle increased demand without needing to hire additional support staff. Handling High Volumes: AI chatbots can manage large volumes of inquiries without compromising quality, making them ideal for businesses with fluctuating support demands. Global Reach: With multilingual capabilities, AI chatbots can serve customers from around the world, providing support in different languages without the need for human agents. 5. How to Implement AI Chatbots in Your IT Support Strategy To successfully integrate AI chatbots into your IT support strategy, follow these steps: A. Choose the Right Chatbot Platform There are numerous chatbot platforms available, each offering different features. When selecting a
Understanding Explainable AI: Importance for IT Security and Compliance
Understanding Explainable AI: Importance for IT Security and Compliance In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone for driving innovation across industries, including IT security and compliance. While AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data and automate processes is undeniably powerful, its decision-making mechanisms can often seem like a “black box.” This lack of transparency has raised significant concerns, especially in critical areas such as cybersecurity and regulatory compliance. This is where Explainable AI (XAI) comes into play, offering transparency into how AI systems make decisions. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of Explainable AI in IT security and compliance, why it’s essential for building trust and meeting regulatory requirements, and how organizations can adopt XAI to enhance their IT security framework. 1. What is Explainable AI (XAI)? Explainable AI refers to AI models and systems that provide clear, understandable explanations for their decisions, predictions, and actions. Unlike traditional “black-box” AI models, which often provide output without offering insight into the decision-making process, Explainable AI aims to demystify the logic behind AI-driven conclusions. Transparency: XAI seeks to provide insights into the internal workings of AI models. Interpretability: The goal is to make AI predictions comprehensible to humans, even to those without deep technical expertise. Trust and Accountability: By making decisions traceable, organizations can better understand AI behavior and improve trust in automated systems. Why is XAI Important? As AI becomes an integral part of IT security and compliance, stakeholders—whether they are security professionals, auditors, or regulatory bodies—demand transparency to verify that AI systems are functioning as intended and in compliance with legal standards. 2. The Role of XAI in IT Security AI is increasingly used in IT security to detect and mitigate threats such as malware, data breaches, and insider attacks. However, without Explainable AI, organizations may struggle to trust the decisions made by these systems. Here’s why XAI is particularly crucial for IT security: A. Enhanced Threat Detection and Response AI-driven security systems can identify abnormal patterns or potential threats much faster than traditional methods. However, it’s essential to understand why a particular action was flagged or a decision was made. XAI allows security teams to trace AI-generated alerts and predictions back to specific data points, making it easier to validate threats. Real-Time Explanations: With XAI, security professionals can understand in real-time why an action (such as blocking a user or alerting about malware) was taken. Reduction of False Positives: By understanding how AI reached its conclusion, security teams can better fine-tune the system to minimize false positives and focus on real threats. B. Compliance and Auditing In industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, strict regulations govern the handling of sensitive data. XAI can play a critical role in ensuring compliance with these regulations by offering a transparent view of AI decision-making. Audit Trails: XAI helps create an audit trail of AI’s actions and decisions, which is essential for meeting regulatory requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA. Regulatory Compliance: AI models that lack transparency may violate compliance standards. XAI helps demonstrate that AI systems comply with industry regulations, thus avoiding penalties or legal issues. C. Accountability in AI Decisions When AI systems make security-related decisions, accountability is paramount. If an AI system wrongly classifies a user as a threat, leading to a wrongful lockdown, XAI allows IT teams to pinpoint why the system made such a decision, making it easier to correct errors. Transparency in AI Actions: With explainability, security teams can provide reasoning for each decision made by the AI, which is crucial for accountability. Human Oversight: While AI can automate responses, XAI ensures that human experts can step in when needed, making informed decisions based on clear explanations. 3. XAI’s Impact on Compliance and Legal Regulations In regulated industries, compliance with data protection and privacy laws is not just important but mandatory. As AI is increasingly integrated into business processes, organizations need to ensure that their AI systems comply with relevant legal frameworks. Explainable AI plays a crucial role in this regard: A. GDPR and Data Privacy The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) places strict requirements on organizations regarding the collection, storage, and use of personal data. Under GDPR, individuals have the right to understand how their data is being processed and how decisions about them are made. Right to Explanation: XAI ensures that organizations can provide users with an explanation of how automated decisions are made, helping to fulfill the “right to explanation” mandated by GDPR. Data Processing Transparency: XAI allows organizations to demonstrate how personal data is used in AI systems, enhancing transparency and trust. B. Fairness and Non-Discrimination AI systems can sometimes produce biased outcomes, especially if they are trained on biased data. This can lead to discriminatory practices, which can be a significant concern in regulated sectors. XAI helps ensure that AI decisions are fair and non-discriminatory. Bias Detection: XAI makes it easier to identify and address bias in AI systems, ensuring that they comply with anti-discrimination laws and ethical standards. Fairness Audits: With explainable AI, organizations can conduct fairness audits to ensure that AI systems do not unintentionally discriminate against certain groups. C. Improved Risk Management XAI also aids in managing risks associated with the implementation of AI in sensitive areas such as IT security and compliance. Understanding AI’s decisions enables teams to make better decisions about managing security risks. Risk Traceability: In the case of a breach or non-compliance event, XAI allows teams to trace back the AI’s actions, making it easier to assess and mitigate risks. Proactive Risk Mitigation: XAI can help organizations proactively identify areas of AI vulnerability, reducing the potential for regulatory fines or security breaches. 4. How to Implement XAI for IT Security and Compliance Integrating Explainable AI into your organization’s IT security and compliance frameworks requires a thoughtful approach. Here are key steps to consider: A. Identify Use Cases for XAI Before implementing XAI, it’s essential to identify the areas within IT security and compliance where explainability can add the
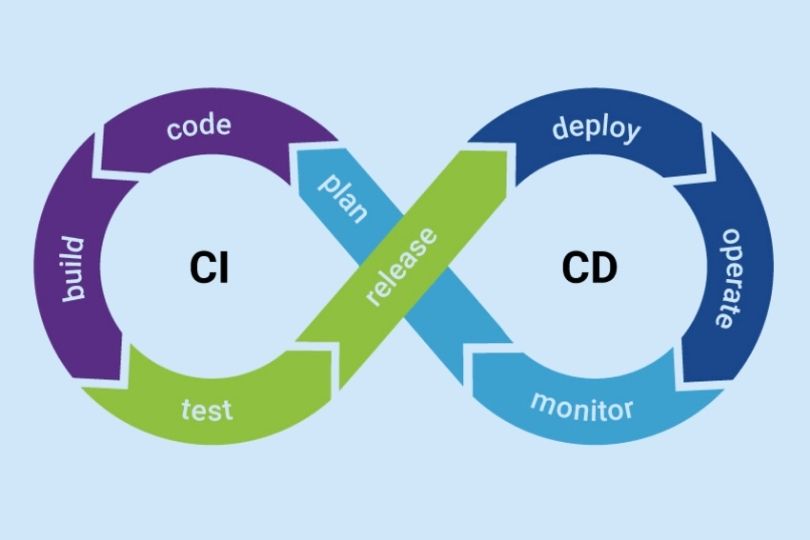
Building Resilient CI/CD Pipelines: Key Practices for Robust Development
Building Resilient CI/CD Pipelines: Key Practices for Robust Development Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) pipelines have become fundamental in modern software development. They help automate and streamline processes, from code commits to deployment. However, building resilient CI/CD pipelines goes beyond simple automation—it’s about ensuring that these pipelines can withstand changes, errors, and scale efficiently. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of building resilient CI/CD pipelines, the best practices to achieve this resilience, and how to maintain these pipelines in the long term. What is a Resilient CI/CD Pipeline? A resilient CI/CD pipeline is one that is robust, reliable, and can gracefully handle failures or changes without disrupting the flow of the development lifecycle. In the context of CI/CD, resilience involves making sure that: Pipelines remain functional under load or when changes occur. Failures are detected early and mitigated efficiently. Automations are consistent and repeatable across different environments. Teams can quickly recover from issues, ensuring minimal downtime. Building resilience into your CI/CD pipeline ensures smoother deployments and accelerates the delivery of high-quality software. Key Components of a Resilient CI/CD Pipeline Before diving into the best practices, let’s briefly discuss the core components of a CI/CD pipeline: 1. Continuous Integration (CI) This is the practice of automatically integrating code changes into a shared repository multiple times a day. The goal is to detect errors early by running tests and validating the code continuously. 2. Continuous Delivery (CD) CD automates the delivery of applications to selected environments. It ensures that your software can be deployed to production at any time with confidence, but it doesn’t necessarily mean every change is deployed automatically. 3. Automation Automation in CI/CD is about making the build, test, and deployment processes as hands-off as possible. This includes automation of tasks like building code, running tests, and deploying to various environments. Best Practices for Building Resilient CI/CD Pipelines 1. Version Control for Pipelines The first step in creating a resilient CI/CD pipeline is to treat your pipelines like code. Just as you version your application code, you should version your pipeline definitions (e.g., in YAML or similar formats). Benefits: Ensures consistency across environments. Makes it easier to roll back to previous pipeline versions in case of issues. Enables easy collaboration and change management within teams. Actionable Tip: Use Git or GitHub Actions to manage and version control your pipeline configurations. 2. Automated Testing at Every Stage Automated testing is critical for ensuring that the code being integrated and delivered is of high quality. Implement tests in stages such as unit tests, integration tests, security tests, and acceptance tests. Benefits: Early Bug Detection: Automated tests help identify issues early in the process, saving time and effort. Consistency: Automated tests ensure that tests are run consistently every time the code changes. Actionable Tip: Incorporate Test-Driven Development (TDD) in your CI pipeline to continuously validate code as it’s written. 3. Failure Detection and Fast Feedback Loops A resilient pipeline should provide quick feedback to developers when things go wrong. Implementing failure detection and reporting tools such as Slack notifications, email alerts, or even status pages can speed up the debugging process. Benefits: Faster Response: DevOps teams can respond to failures faster when alerted instantly. Prevents Bottlenecks: Early failure detection prevents issues from propagating through the pipeline. Actionable Tip: Set up automated notifications to alert teams about build failures or integration issues, using services like Slack, PagerDuty, or Opsgenie. 4. Immutable Infrastructure for Scalability In resilient CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure should be immutable—that is, it should be replaced rather than modified over time. Using infrastructure as code (IaC) allows teams to define and provision infrastructure consistently. Benefits: Scalability: Immutable infrastructure scales easily because new environments are spun up with the same configuration as the old ones. Consistency: It eliminates configuration drift between environments, making deployments more predictable. Actionable Tip: Use Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to automate the deployment of immutable infrastructure. 5. Blue-Green and Canary Deployments One effective way to ensure smooth deployments is by using blue-green or canary deployment strategies. These methods allow you to test new code on a small subset of users before full production deployment. Benefits: Reduced Downtime: These deployment strategies reduce downtime and minimize the impact of potential issues. Easy Rollbacks: If something goes wrong, you can quickly roll back to the previous stable version. Actionable Tip: Implement Blue-Green or Canary deployment strategies in tools like Kubernetes or AWS Elastic Beanstalk. 6. Continuous Monitoring and Logging Monitoring and logging are key to ensuring resilience. Continuously monitor the health of your pipeline, infrastructure, and application. By logging all activities, including builds, tests, deployments, and incidents, you ensure that you have enough data to analyze failures and optimize the pipeline. Benefits: Proactive Issue Resolution: Continuous monitoring allows you to spot issues before they escalate. Visibility: Real-time logs provide transparency into the status of deployments, making it easier to troubleshoot. Actionable Tip: Use Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) for comprehensive monitoring and logging. 7. Incremental and Non-Disruptive Changes Instead of making large changes to your pipeline that can break multiple processes, break down changes into smaller, more manageable increments. This approach reduces risk and ensures that each change can be tested and validated quickly. Benefits: Less Disruption: Smaller changes are easier to test and roll back if necessary. Higher Quality: It’s easier to identify and address issues with smaller, incremental changes. Actionable Tip: Implement a feature toggle strategy to release new features incrementally and test them in production before fully enabling them for all users. 8. Implement Rollback Mechanisms Even with all the resilience built into your pipeline, mistakes happen. A resilient CI/CD pipeline should have rollback mechanisms in place that allow you to revert to a previous stable version quickly. Benefits: Reduced Downtime: Quickly roll back to a previous stable state in case of failure. Minimal Impact: Ensures users are not impacted during outages or disruptions. Actionable Tip: Use Kubernetes for deploying and rolling back applications, or configure AWS CodeDeploy for automatic rollback on
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in SRE: Revolutionizing Reliability and Efficiency
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in SRE: Revolutionizing Reliability and Efficiency Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) has long been recognized as a critical discipline in ensuring the availability, performance, and scalability of software systems. Traditionally, SRE practices focused on building reliable systems through proactive monitoring, incident response, and automation. However, with the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), SRE is experiencing a transformation that is taking it to the next level. In this blog, we will explore the growing role of AI and ML in SRE, their benefits, and how you can integrate these technologies to improve your organization’s reliability and efficiency. What is SRE? Before diving into AI and ML in SRE, let’s quickly review what Site Reliability Engineering is. SRE is a discipline that incorporates aspects of software engineering and applies them to infrastructure and operations problems. Its goal is to create scalable and highly reliable software systems by focusing on the following: Availability: Ensuring systems are up and running as expected. Latency: Minimizing delays in response time. Performance: Optimizing systems for fast and efficient operations. Capacity: Managing resources effectively to support growth. Incident Management: Quickly detecting and resolving incidents to maintain service continuity. While the principles of SRE are well established, the integration of AI and ML is ushering in new methods of achieving these goals. How AI and Machine Learning are Impacting SRE 1. Automating Incident Detection and Response Traditionally, incident management involved manually monitoring logs and metrics to identify issues. This process was both time-consuming and prone to human error. AI and ML, however, can significantly improve this aspect by automatically detecting anomalies and triggering responses based on predefined conditions. Benefits: Faster Incident Detection: Machine learning models can analyze large volumes of data in real-time, identifying patterns or anomalies that could signal potential incidents. These systems can even predict outages before they occur by recognizing trends that lead up to service disruptions. Automated Response: Once an anomaly is detected, AI systems can trigger automatic remediation actions, such as scaling infrastructure, restarting services, or adjusting configurations, all without human intervention. Actionable Tip: Implement AI-powered monitoring tools like Datadog or New Relic that use machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and trigger automated responses in your systems. 2. Optimizing Resource Management and Scaling Managing resources efficiently is key to maintaining reliable systems, particularly in cloud environments where resource demands can fluctuate. AI and ML help SRE teams manage resource scaling by predicting workload spikes and adjusting resource allocation in real time. Benefits: Predictive Scaling: By analyzing historical data and identifying usage patterns, AI can predict periods of high demand and scale resources in advance, preventing overloading of systems and ensuring optimal performance. Cost Efficiency: Machine learning can also help optimize the allocation of resources, ensuring that systems use only the necessary amount of resources, thus reducing costs. Actionable Tip: Use machine learning models to predict traffic spikes and automatically scale your infrastructure using cloud-native tools like AWS Auto Scaling or Google Cloud AutoML. 3. Improving Service Reliability with Predictive Analytics AI and ML can enhance the reliability of services by predicting failures or disruptions before they occur. By analyzing vast amounts of data from system logs, performance metrics, and even external factors like weather or traffic, AI can forecast potential issues with greater accuracy. Benefits: Proactive Issue Resolution: Predictive analytics allows SRE teams to take preventative actions, such as applying patches, increasing resource allocation, or optimizing configurations, before problems impact end-users. Enhanced SLAs: AI-driven predictions enable better forecasting and SLA management by ensuring that service levels are maintained at all times. Actionable Tip: Implement predictive analytics tools like Google AI Platform or Splunk to anticipate system failures and take proactive measures to avoid service disruptions. 4. Enhanced Root Cause Analysis When incidents occur, root cause analysis (RCA) is critical to understanding the underlying issues and preventing recurrence. AI and ML can automate the RCA process by correlating vast amounts of data from multiple sources and identifying the cause of the problem. Benefits: Faster Resolution: AI can quickly sift through logs, metrics, and historical incident data to pinpoint the exact cause of an issue, saving valuable time during critical incidents. Improved Insights: By automating the RCA process, SRE teams can gain more detailed insights into system behavior, enabling them to fine-tune configurations and reduce future issues. Actionable Tip: Leverage machine learning-powered RCA tools like Moogsoft or BigPanda to streamline your troubleshooting process and enhance post-incident analysis. 5. Enhancing Monitoring with AI-Powered Insights Traditional monitoring systems often require manual configuration and tuning. AI and ML can enhance monitoring by providing deeper insights into system performance, helping SRE teams detect anomalies, optimize configurations, and better understand user behavior. Benefits: Intelligent Alerting: AI systems can prioritize alerts based on severity, reducing alert fatigue and ensuring that SRE teams focus on critical issues. Contextual Insights: AI-powered monitoring tools can correlate events across multiple systems, providing context around the root cause of an issue, which aids in faster decision-making. Actionable Tip: Adopt AI-enhanced monitoring platforms such as Prometheus with Kubernetes, Dynatrace, or PagerDuty, which provide contextual, machine-driven insights into your system’s performance. Best Practices for Integrating AI and Machine Learning in SRE 1. Start Small and Scale Gradually AI and ML can seem overwhelming, especially for organizations that are just beginning to explore their potential in SRE. Start by integrating simple AI/ML models to automate repetitive tasks, such as anomaly detection, and gradually expand as you become more comfortable with the technology. 2. Focus on Data Quality Machine learning models rely heavily on data quality. Ensure that your data is clean, accurate, and representative of real-world conditions to achieve the best results with AI-driven solutions. 3. Collaborate with Data Science Teams SRE teams should work closely with data scientists to develop and train machine learning models tailored to their specific systems and environments. Collaborative efforts ensure the models are built with the right data inputs and can address real-world SRE challenges. 4. Continuously Monitor AI Performance AI and
Tutorial on Creating Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide
Tutorial on Creating Effective Dashboards: A Comprehensive Guide Dashboards are essential tools for visualizing data and making informed decisions. Whether for business analysis, operations monitoring, or performance tracking, an effective dashboard presents key insights in an easy-to-understand format. But creating a dashboard that is both visually appealing and functional requires careful planning and design. In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the process of creating an effective dashboard, from gathering the right data to choosing the best visualization tools. By the end, you’ll have actionable insights that can help you build dashboards that empower your team and drive better decisions. Why Dashboards Matter for Your Business Dashboards provide a centralized view of key metrics, making it easier for teams to monitor performance, identify trends, and respond to issues quickly. In a business setting, dashboards help: Monitor Performance: Track metrics such as sales, customer satisfaction, and production efficiency in real-time. Enable Quick Decision-Making: Visualize data so stakeholders can make informed decisions on the fly. Improve Communication: Share dashboards with team members to ensure alignment on performance and business goals. Identify Areas for Improvement: Spot inefficiencies and opportunities for growth using visualized data. Step-by-Step Guide to Creating an Effective Dashboard Step 1: Define Your Goals and Metrics Before diving into the design process, it’s crucial to clarify what you want to achieve with your dashboard. Ask yourself the following questions: Who is the dashboard for? Different audiences may require different information. A sales team might need sales data, while a marketing team might prioritize web traffic and lead generation. What key performance indicators (KPIs) do you need to track? Select metrics that align with your business objectives. What actionable insights do you want to gain from the dashboard? The goal is to display data that leads to meaningful decisions. Actionable Tip: Focus on the “need-to-know” metrics rather than overwhelming your audience with too much information. Keep it simple and relevant. Step 2: Choose the Right Data Sources Your dashboard will be only as good as the data it pulls from. Common data sources for business dashboards include: CRM Tools: Salesforce, HubSpot, and other CRM platforms can provide data on sales, customer interactions, and marketing performance. Analytics Tools: Google Analytics or Adobe Analytics for website and user behavior data. ERP Systems: For financial and operational data. Social Media Analytics: Platforms like Twitter Analytics or Facebook Insights can provide social media performance data. Internal Databases: Pull from company-specific data stores like SQL databases, Google Sheets, or cloud storage. Ensure that the data is accurate, up-to-date, and consistent. Integrating data from multiple sources can offer a more comprehensive view of your business. Actionable Tip: Use automated data integration tools (e.g., Zapier or Integromat) to streamline the data import process and minimize manual updates. Step 3: Choose the Right Visualization Tools The visualization tools you use can significantly impact how well your dashboard communicates insights. Some common tools for creating dashboards include: Tableau: Known for its powerful data visualization capabilities and interactive dashboards. Power BI: A Microsoft product that offers strong integration with other Microsoft tools and robust data modeling. Google Data Studio: Free tool with flexible data integration options, ideal for smaller businesses or teams. Looker: Used by companies seeking advanced data modeling and visualization, especially for big data. Excel or Google Sheets: For simple, static dashboards or quick prototypes. Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses. Consider your team’s familiarity with these tools, the complexity of your data, and your budget when selecting a dashboard platform. Actionable Tip: Start with a simple tool (like Google Data Studio or Power BI) if you’re new to dashboard design. You can always migrate to more sophisticated platforms as your needs grow. Step 4: Design for Usability and Simplicity A good dashboard presents data clearly, without overwhelming the user. Focus on these design principles: 1. Clean Layout Use grids to organize your dashboard and maintain a consistent structure. Place the most important metrics in the center or at the top, as users tend to focus on these areas first. 2. Limit the Number of Metrics Avoid clutter by limiting the number of metrics on your dashboard. A good rule of thumb is to display no more than five to seven key metrics at a time. 3. Use the Right Chart Types Line charts for trends over time. Bar charts for comparisons between categories. Pie charts for proportions (but use sparingly). Heat maps for identifying areas of high or low activity. 4. Interactive Elements Add filters or drill-down capabilities to allow users to explore the data further. For example, users should be able to click on a bar in a bar chart to see more details for that category. 5. Color and Contrast Use color to highlight important data points, but avoid overwhelming the user with too many colors. Stick to a simple color palette and use contrasting colors for high-priority metrics. Actionable Tip: Keep your dashboard as simple as possible—think of it as a quick overview rather than a deep dive into every detail. Step 5: Ensure Real-Time Data and Accessibility An effective dashboard is one that stays up-to-date with real-time data. Depending on your business’s needs, this may require setting up automatic updates for your data sources or integrating with APIs. Additionally, ensure your dashboard is accessible to all stakeholders: Mobile Compatibility: Many users need access to dashboards on-the-go, so make sure it’s optimized for mobile. Permissions: Provide different levels of access depending on the user’s role. For example, some people may only need read-only access, while others may need editing privileges. Actionable Tip: Set up regular checks to ensure your data integrations are working properly, and monitor for any disruptions in data flow. Step 6: Continuously Improve and Update the Dashboard Once your dashboard is live, it’s essential to monitor its performance and gather feedback from users. Some ways to gather feedback include: User Testing: Regularly test the dashboard with actual users to identify pain points or areas for improvement. Engagement Metrics: Track which sections
Integrating APM Tools into Your SRE Workflow: A Comprehensive Guide
Integrating APM Tools into Your SRE Workflow: A Comprehensive Guide As businesses scale their applications and adopt complex architectures, maintaining system reliability becomes increasingly challenging. Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) plays a pivotal role in ensuring systems remain robust, scalable, and performant. A crucial aspect of modern SRE practices is the integration of Application Performance Management (APM) tools into the workflow. In this blog, we will explore why integrating APM tools is essential for your SRE team, how to implement them effectively, and the best practices to get the most out of these tools. What is APM, and Why Does it Matter for SRE? Application Performance Management (APM) refers to the monitoring and managing of performance and availability of software applications. APM tools allow teams to monitor application health, detect issues, and gain deeper visibility into system performance. For SRE teams, APM tools are critical for optimizing reliability, reducing downtime, and enhancing user experience. Integrating APM tools into your SRE workflow provides several benefits: Faster Issue Detection: APM tools provide real-time monitoring and alerts, enabling SRE teams to detect and address performance bottlenecks quickly. Proactive Problem Resolution: By offering insights into application behavior, APM tools help SREs identify problems before they impact end users. Enhanced Collaboration: APM data promotes better collaboration between SREs, developers, and other stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aligned on the root cause of issues. Improved Reliability: Continuous performance monitoring allows SRE teams to optimize systems for better uptime and resilience. Key Considerations When Integrating APM Tools into Your SRE Workflow 1. Choose the Right APM Tool for Your Needs There is a wide range of APM tools available today, each with its unique features. The first step in integration is selecting the tool that best fits your organization’s requirements. Some of the top APM tools for SRE teams include: New Relic: Offers end-to-end monitoring, detailed application performance metrics, and an intuitive dashboard for quick insights. Datadog: Provides cloud-based APM with deep visibility into distributed systems and infrastructure monitoring. AppDynamics: Known for its real-time performance monitoring and ability to trace transactions across microservices architectures. Dynatrace: Offers full-stack monitoring, AI-powered insights, and automated root cause analysis. Actionable Takeaway: Evaluate your application’s specific needs—whether it’s microservices monitoring, cloud infrastructure integration, or transaction tracing—and choose an APM tool that can scale with your organization’s growth. 2. Integrating APM with Your SRE Tools To ensure smooth and effective integration, your APM tool should seamlessly work with the existing tools in your SRE workflow. Common integrations include: Incident Management Tools: Integrate your APM tool with incident management platforms like PagerDuty or Opsgenie. This ensures alerts are automatically triggered when performance thresholds are crossed. Monitoring & Logging Systems: Combine APM data with your monitoring and logging systems, such as Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack, to gain a holistic view of both application and infrastructure performance. Version Control and CI/CD Pipelines: APM tools can be integrated with version control systems like GitHub or GitLab and CI/CD platforms like Jenkins to track performance across deployments. Actionable Takeaway: Set up these integrations to create a centralized view of your application’s health and streamline the workflow for incident detection and resolution. 3. Define Clear SLOs and SLIs Using APM Data Site Reliability Engineering relies heavily on Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service Level Indicators (SLIs) to measure performance. APM tools provide the data necessary to define and track these metrics effectively. SLIs (Service Level Indicators) are measurable metrics that represent the reliability of your service. Common SLIs include error rates, latency, and throughput. SLOs (Service Level Objectives) are the goals set for these SLIs, e.g., 99.9% of transactions must complete within 200 milliseconds. By integrating APM tools with your SLO framework, you can ensure that the performance metrics you monitor align with the goals of your SRE team. APM tools like Datadog and New Relic provide built-in SLO/SLA (Service Level Agreement) tracking, which can help you measure and meet these objectives. Actionable Takeaway: Use your APM tool’s reporting features to define realistic SLIs and SLOs based on historical performance data. Regularly assess these metrics to ensure your service is meeting reliability goals. 4. Leverage APM for Root Cause Analysis and Incident Response When performance issues occur, APM tools provide valuable insights that help SRE teams pinpoint the root cause of incidents. By tracing requests and transactions across your systems, APM tools enable you to understand where bottlenecks or failures occur. Here’s how APM can help in incident response: Transaction Tracing: APM tools can track user transactions from end to end, identifying where latency or failures occur within microservices or databases. Real-Time Dashboards: Visualize key metrics such as response times, error rates, and system load in real-time, allowing for quicker detection and resolution. Automated Alerts: Set up customized alerts based on thresholds for key performance indicators (KPIs). These alerts can be linked to incident management platforms, ensuring that the appropriate teams are notified immediately. Actionable Takeaway: Create automated dashboards for your SRE team that display real-time performance metrics. Set alerts for critical thresholds to improve incident response times. 5. Optimizing Cost and Performance with APM Insights While APM tools provide detailed insights into performance, they can also help optimize operational costs. By monitoring resource utilization and application performance, SREs can identify underused or over-provisioned resources, enabling cost optimization. APM tools allow you to: Monitor Resource Usage: Track resource consumption (CPU, memory, bandwidth) to identify inefficiencies. Analyze Performance Bottlenecks: Identify inefficient code paths, misconfigured servers, or underperforming databases that are contributing to high costs. Actionable Takeaway: Use your APM tool’s analytics capabilities to identify areas where your system’s performance can be improved or optimized for cost efficiency. This proactive approach can help you avoid unnecessary overhead and improve system scalability. Best Practices for Integrating APM into Your SRE Workflow 1. Start with a Clear Plan Before implementing APM tools, it’s crucial to define your monitoring goals. What are you trying to achieve with APM integration? Whether it’s incident resolution, system optimization, or cost management, a clear plan will ensure your
The Future of SRE: Trends and Predictions
The Future of SRE: Trends and Predictions Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) has become an essential discipline for many organizations, particularly those running large-scale, distributed systems. As businesses continue to rely on technology to scale and innovate, SRE teams are tasked with maintaining uptime, improving system reliability, and delivering seamless user experiences. However, the landscape of SRE is constantly evolving. In this blog, we’ll dive into the future of SRE, highlighting emerging trends, predictions, and actionable insights for SRE professionals. What is Site Reliability Engineering? Before exploring the future, let’s first define what SRE is. Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) is a set of practices and principles that combine software engineering and operations to ensure high availability, scalability, and reliability of services. SREs are responsible for monitoring system health, automating processes, responding to incidents, and making data-driven decisions to improve the system’s reliability over time. The ultimate goal of SRE is to create highly reliable systems while enabling continuous innovation, all while keeping operational costs in check. Trends Shaping the Future of SRE As we move into 2025 and beyond, the role of SRE is expected to evolve in several key areas. Here are some of the most significant trends to watch: 1. Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI) One of the most significant trends in SRE is the continued push toward automation. Automation not only reduces the time spent on manual tasks but also improves system reliability by minimizing human error. As machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) tools become more sophisticated, SRE teams will increasingly rely on these technologies to automate monitoring, incident detection, and resolution. Why It Matters: Predictive analytics: AI can help predict incidents before they occur, allowing SRE teams to proactively mitigate issues. Self-healing systems: Automation can enable systems to detect problems and self-correct without human intervention. Improved incident response: AI-powered chatbots and automated runbooks will allow teams to respond faster during incidents, reducing downtime. Actionable Takeaway: SRE teams should start integrating AI and automation tools now to prepare for the future. Tools like Ansible, Terraform, and PagerDuty are great starting points. 2. Focus on Developer Collaboration In the past, SRE teams were often siloed from development teams, with clear boundaries between who was responsible for writing code and who managed infrastructure. Today, that’s changing. As SREs take on more of a DevOps approach, there is a growing emphasis on collaboration between developers and operations teams. Why It Matters: Faster incident resolution: Direct communication between developers and SREs leads to quicker identification of the root cause of issues. Improved system design: Collaboration fosters shared responsibility for both development and reliability, ensuring that systems are designed with resilience in mind from the start. Actionable Takeaway: Encourage regular collaboration between your development and SRE teams. Consider adopting tools like Jira and Slack to facilitate seamless communication. 3. Shift to Cloud-Native Technologies As cloud adoption continues to grow, more companies are shifting to cloud-native architectures, including microservices, Kubernetes, and serverless computing. These technologies promise better scalability, flexibility, and efficiency but introduce new challenges for SRE teams, particularly in managing distributed systems. Why It Matters: Scalability: Cloud-native technologies allow for better horizontal scaling, but SREs need to adapt their monitoring and incident response practices accordingly. Complexity: Distributed systems introduce additional complexity in tracking performance, monitoring services, and resolving incidents, making observability tools essential. Cost efficiency: Proper configuration of cloud resources and scalability ensures that the systems remain cost-effective. Actionable Takeaway: Invest in cloud-native monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana to improve observability and incident management in a distributed environment. 4. Enhanced Focus on Security (SecOps) As the threat landscape continues to evolve, SREs are increasingly expected to work alongside security teams to ensure that systems are not only reliable but also secure. This shift towards SecOps—integrating security into operations—will become even more critical as cyberattacks grow in complexity. Why It Matters: Proactive security measures: By working closely with security teams, SREs can implement best practices like zero-trust architectures, encryption, and automated security checks. Incident detection: Security incidents often overlap with reliability issues, making it essential for SREs to have a close working relationship with security teams to detect and mitigate threats quickly. Actionable Takeaway: Integrate security practices into your incident management process. Tools like HashiCorp Vault, Kubernetes Secrets, and Terraform can help automate security configurations. 5. Site Reliability Engineering as a Service In the future, more organizations will likely adopt SRE as a Service models. This approach allows companies to leverage third-party SRE teams to handle specific aspects of system reliability, reducing the internal burden and allowing teams to focus on core competencies. Why It Matters: Cost-effectiveness: Smaller organizations or startups can access top-tier SRE expertise without the cost of building an in-house team. Specialization: Managed SRE services can offer specialized expertise in areas like cloud migration, Kubernetes management, or disaster recovery. Actionable Takeaway: Evaluate whether an SRE-as-a-service model could benefit your organization. Services like Google Cloud Operations Suite and AWS CloudWatch provide robust monitoring and incident response capabilities. Predictions for the Future of SRE Looking ahead, there are several key predictions for the SRE field: 1. Increased Demand for SRE Professionals As more companies adopt complex architectures and rely on distributed systems, the demand for skilled SRE professionals will continue to grow. There will be a strong need for people who can design, manage, and optimize resilient systems in cloud environments. 2. Greater Emphasis on Observability Tools for observability (gathering, analyzing, and using data to monitor system health) will become even more sophisticated. SREs will have access to richer, more real-time insights into their systems, allowing them to anticipate issues and mitigate downtime more effectively. 3. Proactive Incident Prevention Future SRE teams will shift from reactive incident management to more proactive strategies, using predictive analytics and advanced monitoring tools to prevent incidents before they happen. 4. Integration of AI and ML into Decision-Making Artificial intelligence and machine learning will not just help automate incident response but will also be integral in decision-making. Machine learning algorithms will help predict system
Incident Management Tools and Platforms: Streamlining Your IT Response
Incident Management Tools and Platforms: Streamlining Your IT Response Incident management is a critical aspect of maintaining smooth operations in any organization, particularly in IT. The ability to quickly detect, respond to, and resolve incidents can have a direct impact on system availability, user satisfaction, and the bottom line. Effective incident management requires the right tools and platforms to support real-time communication, tracking, and resolution. In this blog, we’ll explore some of the best incident management tools and platforms that can help organizations streamline their response process, minimize downtime, and enhance their overall service reliability. Why Incident Management Matters Incident management refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving incidents (such as service outages, security breaches, or system failures) that disrupt normal operations. An incident management strategy helps organizations: Minimize downtime by quickly addressing service disruptions. Ensure business continuity through proactive monitoring and rapid issue resolution. Improve communication among stakeholders during incident response. Enhance user satisfaction by reducing the impact of incidents on customers. Having the right incident management tools in place ensures that teams can collaborate effectively, manage incidents efficiently, and restore services promptly. With the right platform, teams can improve response times, track incident status, and continuously improve their processes. Key Features of Effective Incident Management Tools Before diving into specific tools, let’s first examine the essential features that an effective incident management tool should offer: 1. Incident Detection and Monitoring Tools should integrate with monitoring systems to automatically detect incidents and notify the team as soon as they occur. 2. Incident Tracking A centralized system for tracking the progress of incidents from detection to resolution ensures that no issues are overlooked and everything is documented. 3. Real-Time Communication The ability to collaborate in real-time with incident response teams is essential for fast resolution. This can include chat, notifications, and alerts. 4. Root Cause Analysis Tools should help teams investigate and identify the root cause of incidents, so they can take preventive measures to avoid future occurrences. 5. Reporting and Analytics Comprehensive reporting tools help in analyzing incident trends, response times, and root causes. This data can be used to improve incident management processes over time. 6. Integration with Other IT Systems To streamline workflows, incident management tools should integrate with other IT management platforms such as monitoring, configuration management, and service desks. Top Incident Management Tools and Platforms 1. PagerDuty PagerDuty is one of the most well-known incident management platforms, offering robust features to help IT teams respond to incidents quickly. It provides an integrated approach to incident detection, escalation, and resolution, ensuring that no incident goes unnoticed. Key Features: Real-time alerts: Get immediate notifications about incidents via email, SMS, or phone calls. Incident routing: Automatically route incidents to the appropriate responder based on predefined rules. On-call scheduling: Easily manage on-call schedules to ensure there’s always someone available to respond to incidents. Post-incident reporting: Analyze incidents after resolution to identify root causes and prevent recurrence. Why It’s Great: PagerDuty is ideal for organizations with large-scale infrastructure that need a centralized platform for incident management and collaboration. 2. Opsgenie Opsgenie by Atlassian is a comprehensive incident management platform that offers advanced notification and alerting systems for IT operations teams. It integrates with many third-party monitoring tools and streamlines the incident response process. Key Features: Alerts and notifications: Receive customizable alerts that are sent via email, SMS, or mobile push notifications. Escalation policies: Set up escalation policies to ensure that incidents are addressed promptly by the right people. Integration with monitoring tools: Sync with tools like Nagios, New Relic, and Datadog to receive incident alerts directly. Incident timeline: View a complete history of incidents and their resolution to track trends and improve future responses. Why It’s Great: Opsgenie is an excellent choice for organizations already using Atlassian products (like Jira) and those looking for a seamless integration experience. 3. ServiceNow IT Service Management (ITSM) ServiceNow ITSM is an enterprise-grade service management solution that includes robust incident management features. It’s widely used by larger organizations due to its scalability and integration capabilities. Key Features: Incident lifecycle management: From detection to resolution, manage all stages of the incident lifecycle. Collaboration tools: Integrated communication tools for cross-functional teams to collaborate and resolve issues. Knowledge base: Access a knowledge base for troubleshooting and resolving common incidents more efficiently. Automated workflows: Streamline incident handling by automating ticket creation, notifications, and routing. Why It’s Great: ServiceNow is particularly beneficial for large organizations or those with complex IT environments, offering extensive customization and integration capabilities. 4. xMatters xMatters is an incident management and communications platform that ensures rapid, coordinated responses to IT incidents. It’s designed for large enterprises and integrates with numerous third-party tools for comprehensive incident management. Key Features: Alerting and notifications: Real-time alerts through multiple channels such as email, SMS, and voice messages. Incident tracking and escalation: Incident progress is tracked and escalated automatically based on the urgency. On-call management: Manage on-call schedules and rotations to ensure timely response. Reporting and analytics: Post-incident reports and performance analytics to improve incident management strategies. Why It’s Great: xMatters excels at large-scale operations, providing detailed analytics and communication tools that help IT teams handle incidents more effectively. 5. Freshservice Freshservice is a cloud-based IT service management platform designed for businesses of all sizes. It includes a comprehensive incident management module that helps IT teams efficiently manage and resolve service disruptions. Key Features: Incident ticketing: Automatically generate incident tickets when issues are detected and route them to the appropriate team members. Collaboration tools: Share incident details with team members to troubleshoot and resolve issues faster. Self-service portal: Let users report issues via a self-service portal to reduce the burden on support teams. Analytics and reporting: Gain insights into incident trends and team performance with built-in reporting tools. Why It’s Great: Freshservice is great for small to medium-sized organizations looking for an easy-to-use, affordable incident management solution. Best Practices for Incident Management Establish Clear Incident Response Plans: Ensure that all team members understand their roles in the
Security Considerations in Site Reliability Engineering
Security Considerations in Site Reliability Engineering Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) has become a cornerstone of modern IT practices, emphasizing the need to ensure that systems are highly available, resilient, and scalable. While much of the focus in SRE has been on performance, uptime, and system reliability, security is just as crucial for maintaining trustworthy and secure operations. In an era where cyber threats are evolving rapidly, security considerations are integral to an SRE’s role. In this blog, we’ll discuss essential security practices that should be part of your Site Reliability Engineering strategy, including preventive measures, tools, and tactics to secure your infrastructure and applications effectively. Why Security is Critical in Site Reliability Engineering Site Reliability Engineers are responsible for ensuring that systems remain available, scalable, and resilient to failures. However, securing these systems is equally vital. Security vulnerabilities can undermine the reliability and performance of services, leading to downtime, data breaches, or performance degradation. By embedding security practices into your SRE culture, you can: Enhance system reliability by reducing the risk of security incidents. Improve trust with customers, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies. Mitigate risks of data loss or exposure through secure coding and network practices. SREs must adopt a security-first mindset, integrating security controls throughout the software development lifecycle and infrastructure management processes. 1. Shift Security Left in the SDLC Shifting security left means integrating security measures early in the software development lifecycle (SDLC). Rather than waiting until the final stages of development or deployment to address security, SREs can work with developers to identify vulnerabilities during the coding phase. Actionable Tips: Incorporate security checks into CI/CD pipelines: Automate security scanning for vulnerabilities and code weaknesses early in the development cycle. Use static code analysis tools: Implement tools that automatically detect vulnerabilities in code as it is written, such as SonarQube or Checkmarx. Educate developers on secure coding practices: Collaborate with development teams to promote awareness around security, focusing on threat modeling, input validation, and proper error handling. 2. Adopt Zero Trust Security Models The Zero Trust security model assumes that threats could exist both outside and inside the network, and therefore, no one should be trusted by default, even if they are within the corporate network. This model enforces strict identity verification and continuous validation for all users, devices, and applications, irrespective of their location. Actionable Tips: Enforce strict identity and access management (IAM): Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), least-privilege access, and role-based access controls (RBAC) for all users and systems. Implement network segmentation: Isolate critical systems and services from non-essential components to minimize the impact of a breach. Monitor and log all access requests: Continuously audit access patterns and behaviors, using tools like AWS CloudTrail or Google Cloud Audit Logs. 3. Secure Your Infrastructure and Network SREs should ensure that infrastructure and network configurations are secure by default. Proper network architecture, access controls, and segmentation can drastically reduce the attack surface and improve overall system security. Actionable Tips: Use encryption at rest and in transit: Encrypt sensitive data across all stages, whether it’s stored in databases, transmitted over the network, or while in use. Implement firewalls and network access controls: Use firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic and ensure that access is limited to only trusted IP addresses. Deploy DDoS protection: Use services like AWS Shield or Azure DDoS Protection to safeguard applications from Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks that can disrupt availability. 4. Automate Incident Detection and Response Security incidents are inevitable, but how quickly your organization can detect, respond, and recover from these incidents will determine the overall impact on system reliability. Automation can help accelerate detection and response times, allowing SREs to focus on recovery and system resilience. Actionable Tips: Deploy security monitoring tools: Use intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms, and log aggregation tools to continuously monitor for suspicious activities. Automate incident response workflows: Implement automated responses to common security incidents, such as blocking malicious IPs, shutting down compromised services, or isolating vulnerable instances. Regularly test response plans: Simulate security incidents and run tabletop exercises to ensure the team is prepared to handle breaches effectively. 5. Focus on Supply Chain Security Modern software relies heavily on third-party libraries, dependencies, and services. However, these external components can introduce vulnerabilities into your systems if they are not properly managed. Supply chain security is about ensuring that all third-party software components are secure and trusted. Actionable Tips: Audit third-party libraries: Use tools like OWASP Dependency-Check or Snyk to scan for vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and dependencies. Use trusted sources for third-party services: Ensure that external services or APIs are from reliable sources, and validate the security posture of those providers. Monitor for vulnerabilities in open-source components: Stay up to date with known vulnerabilities in open-source software by monitoring databases like the National Vulnerability Database (NVD). 6. Implement Continuous Security Monitoring Security is not a one-time effort—it needs to be continuous. Constantly monitoring the system’s health, security logs, and potential vulnerabilities is essential for maintaining a high level of security and reliability. Actionable Tips: Set up security dashboards: Use platforms like Splunk or Datadog to provide real-time visibility into security events and performance metrics. Conduct regular vulnerability scans: Schedule regular security scans to identify new vulnerabilities and weaknesses within your infrastructure and applications. Implement anomaly detection: Use machine learning-based tools to detect unusual activities that may signal potential security threats, such as unauthorized access or system misconfigurations. 7. Establish Strong Authentication and Authorization Practices Ensuring that only authorized individuals or systems can access sensitive data and resources is crucial. SREs must ensure that the appropriate access controls are in place to protect against unauthorized access. Actionable Tips: Use Identity Federation: Enable federated identity management systems to allow seamless, secure user authentication across different platforms. Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for accessing production systems and critical infrastructure to prevent unauthorized access. Enforce Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define and assign roles based on the principle of least privilege, ensuring