Best Practices for Monitoring and Logging in AWS Introduction Monitoring and logging are crucial elements in managing the health and performance of cloud-based systems. AWS (Amazon Web Services) offers a wide range of tools and services to ensure that your applications are running smoothly and securely. Proper monitoring and logging help to detect potential issues, improve operational efficiency, and ensure system reliability. In this blog, we will explore the best practices for monitoring and logging in AWS, focusing on how to leverage AWS services like CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and others to maximize the effectiveness of your cloud infrastructure. Why Monitoring and Logging Matter in AWS Monitoring and logging provide visibility into the performance, security, and reliability of your infrastructure. Without these processes in place, diagnosing issues, identifying security threats, and optimizing performance become difficult and time-consuming. Key Benefits of Monitoring and Logging: Issue Detection: Identifying and resolving issues quickly before they affect your customers. Performance Optimization: Monitoring helps ensure that your resources are optimized, preventing over-provisioning or under-provisioning. Security and Compliance: Proper logging is essential for auditing and meeting regulatory requirements. Cost Management: Monitoring usage and performance helps manage costs by identifying underutilized resources. AWS Monitoring and Logging Services Overview AWS provides several services to help you monitor and log your infrastructure: Amazon CloudWatch: Monitors AWS resources and applications in real-time. AWS CloudTrail: Records API calls and activity in your AWS account for security and compliance. Amazon CloudWatch Logs: Collects and monitors logs from your AWS resources. AWS X-Ray: Helps debug and analyze the performance of applications, especially distributed ones. AWS Config: Tracks configuration changes in your AWS resources. AWS Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) Logs: Provides logs for load balancing, which is crucial for monitoring application traffic. Let’s dive deeper into the best practices for monitoring and logging in AWS. Best Practices for Monitoring in AWS 1. Leverage CloudWatch Alarms CloudWatch Alarms allow you to monitor AWS resources such as EC2 instances, RDS databases, and Lambda functions. These alarms trigger notifications based on specific thresholds, enabling you to act proactively. Best Practices: Set Thresholds Based on Application Needs: Customize your thresholds according to application requirements, such as CPU utilization, memory, or disk I/O. Create Multiple Alarms: Create alarms for different metrics like error rates, request latency, and service availability to track both infrastructure health and application performance. Use SNS for Notifications: Use Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) to notify stakeholders when alarms are triggered. This ensures immediate action is taken. 2. Use CloudWatch Dashboards CloudWatch Dashboards provide a real-time, visual representation of key metrics. You can create custom dashboards to monitor your application’s health and performance. Best Practices: Visualize Key Metrics: Display metrics like CPU usage, memory usage, disk read/write operations, and network traffic in a central dashboard. Custom Dashboards for Teams: Create separate dashboards for different teams. For example, the development team may focus on application-level metrics, while the operations team monitors infrastructure health. Share Dashboards: CloudWatch allows you to share dashboards with team members for collaborative troubleshooting and monitoring. 3. Monitor Log Data with CloudWatch Logs CloudWatch Logs helps you collect, monitor, and store logs from AWS services, EC2 instances, and custom applications. Best Practices: Centralized Logging: Aggregate logs from all services and applications into a single CloudWatch Logs group. This simplifies management and analysis. Log Retention Policies: Set up log retention policies to automatically delete logs after a certain period, optimizing storage costs. Use Metric Filters: CloudWatch allows you to create custom metrics from log data using metric filters. This is especially useful for monitoring application-specific events (e.g., errors or specific API calls). Best Practices for Logging in AWS 1. Enable CloudTrail for Comprehensive Logging AWS CloudTrail records all API calls and activities across your AWS environment, providing an audit trail for security and compliance purposes. CloudTrail is essential for tracking changes to your AWS resources, ensuring accountability, and detecting malicious activity. Best Practices: Enable CloudTrail Across All Regions: By default, CloudTrail records activities in the region where it is enabled. Ensure that CloudTrail is enabled for all AWS regions to capture activities globally. Store CloudTrail Logs in S3: Set up CloudTrail to deliver logs to an Amazon S3 bucket for long-term storage and analysis. S3 offers durability and scalability for large log data. Integrate with CloudWatch: CloudTrail logs can be integrated with CloudWatch for real-time monitoring. Set up CloudWatch Alarms to notify you about suspicious activities or resource changes. 2. Capture Application Logs Using Amazon CloudWatch Logs While CloudTrail provides visibility into AWS API calls, application logs give insight into how your code is performing. You can configure your EC2 instances, Lambda functions, or containers to send logs to CloudWatch Logs. Best Practices: Use Structured Logging: Instead of logging free-form text, use structured logs (e.g., JSON format) to make it easier to search, filter, and analyze log entries. Log Error and Performance Data: Ensure that your application logs contain useful information such as error codes, stack traces, response times, and other performance metrics. Monitor and Search Logs: Utilize CloudWatch Logs Insights for real-time search and analysis of log data. Create queries to identify trends, pinpoint errors, and track system performance. 3. Use AWS X-Ray for Distributed Tracing AWS X-Ray allows you to analyze and debug distributed applications, helping you identify bottlenecks and troubleshoot issues in real-time. X-Ray is especially valuable for microservices architectures where requests pass through multiple services. Best Practices: Enable X-Ray for Microservices: Integrate X-Ray with your microservices to trace requests as they pass through different components. Visualize Latency and Errors: Use X-Ray’s service map to visualize the interactions between services and pinpoint latency issues or errors in your application. Analyze Request Traces: X-Ray lets you drill down into individual request traces to identify slowdowns, database queries, or failing components. 4. Enable ELB Access Logs for Traffic Monitoring Elastic Load Balancers (ELB) distribute traffic across your resources. Enabling access logging for your ELB provides detailed records of incoming requests and helps with traffic analysis. Best Practices: Enable Logging for All Load Balancers: ELB access
Month: December 2025
Deploying Applications with AWS Elastic Beanstalk: A Complete Guide
Deploying Applications with AWS Elastic Beanstalk: A Complete Guide Introduction In today’s fast-paced development environment, time is of the essence. Developers often face the challenge of managing infrastructure, configuring servers, and ensuring smooth application deployment. AWS Elastic Beanstalk provides an easy-to-use platform for deploying and scaling web applications and services. With Elastic Beanstalk, you can focus on your code while AWS handles the underlying infrastructure. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of deploying an application using AWS Elastic Beanstalk. Whether you’re new to the service or looking for best practices, this step-by-step approach will help you get started quickly. What is AWS Elastic Beanstalk? AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering that allows developers to deploy, manage, and scale web applications and services. It supports a variety of programming languages, such as Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker. Key Features: Easy Deployment: Upload your code, and Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the deployment. Automatic Scaling: Elastic Beanstalk automatically adjusts your application’s capacity based on incoming traffic. Managed Environment: Elastic Beanstalk automatically manages infrastructure tasks, including load balancing, auto-scaling, and monitoring. Integration with AWS Services: It seamlessly integrates with other AWS services like RDS, S3, and CloudWatch. Why Use AWS Elastic Beanstalk? Before we jump into the deployment process, let’s highlight the benefits of using AWS Elastic Beanstalk: Simplifies Application Deployment: Elastic Beanstalk handles all aspects of deployment, reducing manual intervention and configuration. Supports Multiple Languages: Whether you’re using Java, Python, Node.js, or Docker, Elastic Beanstalk supports a wide array of programming languages. Automatic Scaling: Your application can scale automatically in response to traffic changes. Cost-Efficient: You only pay for the resources you use, and it is easy to scale up or down based on your needs. Focus on Code: Developers can focus on writing code without worrying about managing infrastructure or handling operational tasks. Step-by-Step Guide to Deploy an Application with AWS Elastic Beanstalk Step 1: Prepare Your Application Before deploying, ensure your application is ready for Elastic Beanstalk. Here are some general guidelines: Application Code: Ensure your code is packaged correctly for deployment. For example, if you’re deploying a Node.js app, ensure that all dependencies are listed in your package.json file. Environment Variables: If your application requires environment variables, make sure they are set in your configuration files. Configuration Files: For specific configurations (e.g., web server settings), include configuration files such as .ebextensions (for advanced configuration). Step 2: Set Up AWS Elastic Beanstalk 1. Sign In to AWS Management Console: Log in to your AWS account and navigate to the Elastic Beanstalk service. 2. Create a New Elastic Beanstalk Environment: Choose Application: Start by selecting “Create New Application” if you’re deploying an app for the first time. Select Environment: Choose the platform that suits your application (e.g., Node.js, Python, Java). Elastic Beanstalk will create the necessary environment for your selected platform. Choose Environment Tier: Web Server Environment: For applications that handle HTTP requests, like web apps. Worker Environment: For background processing tasks, such as jobs in a queue. 3. Configure the Environment: Set the environment name and description. Configure the environment’s instance type, scaling options, and network settings. Review and modify other settings like health checks and database connections if necessary. Step 3: Upload Your Application After setting up your environment, you need to upload your application code to Elastic Beanstalk: 1. Package the Application: For most environments, you need to package your application into a ZIP file (including all necessary dependencies and configuration files). 2. Upload the Application: Go to the Elastic Beanstalk dashboard and select your environment. Click on Upload and Deploy. Select your ZIP file and click Deploy. Elastic Beanstalk will begin processing the deployment. It will automatically create an EC2 instance, set up an environment, and deploy your application. Step 4: Monitor the Deployment As your application is being deployed, Elastic Beanstalk provides real-time logs and status updates: Health Monitoring: You can monitor the health of your application via the Elastic Beanstalk console. This will show whether your application is running smoothly or encountering issues. Logs: AWS Elastic Beanstalk allows you to access logs directly from the console. These logs can help you debug and troubleshoot issues with your deployment. Elastic Beanstalk also offers CloudWatch integration, allowing you to set up alerts and monitor metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and response times. Step 5: Scale and Manage Your Application Once your application is deployed, AWS Elastic Beanstalk makes it easy to scale and manage: 1. Scaling: Auto Scaling: Elastic Beanstalk can automatically scale your application by adding or removing EC2 instances based on traffic demand. Manual Scaling: You can manually adjust the number of instances if necessary. 2. Load Balancing: Elastic Beanstalk automatically configures load balancing, ensuring that traffic is evenly distributed across multiple EC2 instances. 3. Updates and Rollbacks: Application Versioning: Elastic Beanstalk supports application versioning, so you can easily deploy new versions of your app. Rolling Back: If an issue arises, you can roll back to a previous version of your application. 4. Environment Configuration: Elastic Beanstalk allows you to modify environment settings (e.g., environment variables, scaling options) without needing to redeploy the entire application. Best Practices for Working with AWS Elastic Beanstalk Use Environment Variables: Store configuration settings and secrets like API keys in environment variables to keep them secure. Automate Deployment: Integrate AWS Elastic Beanstalk with your CI/CD pipeline (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab, AWS CodePipeline) to automate deployments. Backup Data: If your application uses a database, make sure to implement regular backups. You can integrate Amazon RDS with Elastic Beanstalk to manage your database. Monitor Performance: Leverage AWS CloudWatch and Elastic Beanstalk’s health monitoring to track performance metrics and ensure that your application is running optimally. Implement Version Control: Always keep track of application versions in Elastic Beanstalk to ensure you can roll back to a stable version if needed. Conclusion AWS Elastic Beanstalk provides a powerful and efficient way to deploy and manage web applications. By abstracting much of the infrastructure management,
AWS Database Services: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
AWS Database Services: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs Introduction Choosing the right database service for your application is crucial to ensuring scalability, reliability, and performance. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a broad range of database solutions to meet various use cases, from relational databases to NoSQL and in-memory data stores. Understanding the unique features and benefits of each AWS database service will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs. In this blog, we will explore AWS’s diverse database offerings, including Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, Aurora, Redshift, and more. We will also provide insights into how to choose the right database solution for your specific requirements. AWS Database Services Overview AWS provides several fully managed database services that cater to different application needs. Here’s a quick breakdown of some of the most popular AWS database services: Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL Database) Amazon Aurora (MySQL and PostgreSQL-Compatible) Amazon Redshift (Data Warehouse) Amazon ElastiCache (In-Memory Data Store) Let’s dive deeper into each of these services and explore their use cases. 1. Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) Amazon RDS is a managed service that simplifies setting up, operating, and scaling a relational database in the cloud. It supports popular relational database engines such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server. Key Features: Automated Backups: RDS provides automated backups and snapshot management. Multi-AZ Deployment: For high availability, RDS can be configured to replicate data across multiple Availability Zones. Scalability: Easily scale your database’s compute and storage resources. Best For: Applications requiring SQL-based relational databases. Use cases involving complex queries, ACID transactions, and relational data models (e.g., financial apps, CRM systems, and enterprise applications). Pricing: Pricing is based on instance size, database engine, storage, and backup options. 2. Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL Database) Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed, serverless, NoSQL database designed for high performance and scalability. It’s a key-value and document database that automatically scales to handle virtually any level of request traffic. Key Features: Serverless: No server management is required; DynamoDB automatically adjusts capacity. High Performance: Single-digit millisecond response times even at scale. Built-in Security: Features encryption at rest and fine-grained access control. Best For: Applications that require low-latency data access, such as mobile apps, gaming platforms, and IoT applications. Use cases where you need to handle large amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data. Pricing: Pricing is based on the read and write throughput, data storage, and optional features such as backups. 3. Amazon Aurora (MySQL and PostgreSQL-Compatible) Amazon Aurora is a relational database engine that is compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL but offers improved performance and availability. It’s designed for enterprise applications with high throughput and low-latency needs. Key Features: Performance: Aurora provides up to five times the performance of standard MySQL and twice the performance of standard PostgreSQL. Scalability: Aurora automatically scales storage up to 64TB per database instance. Fault-Tolerant: Data is automatically replicated across multiple Availability Zones for durability. Best For: Use cases requiring high-performance relational databases with MySQL or PostgreSQL compatibility. Applications that need both performance and high availability, such as SaaS platforms, online transaction processing (OLTP), and content management systems. Pricing: Pricing is based on the instance type, storage used, and data transfer. 4. Amazon Redshift (Data Warehouse) Amazon Redshift is a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service designed for fast querying and analytics. It is ideal for running complex queries on large volumes of structured data, enabling business intelligence and analytics. Key Features: Massively Parallel Processing (MPP): Redshift distributes workloads across multiple nodes for faster query performance. Data Compression: Automatically compresses data to reduce storage requirements. Integration with BI Tools: Redshift integrates with a variety of business intelligence (BI) tools like Tableau, Looker, and QuickSight. Best For: Data analysis, business intelligence, and running complex analytics on large datasets. Use cases like customer analytics, data lakes, and log analytics. Pricing: Pricing is based on the number of nodes in your Redshift cluster, storage, and data transfer. 5. Amazon ElastiCache (In-Memory Data Store) Amazon ElastiCache is a fully managed in-memory data store that supports Redis and Memcached. It’s ideal for caching frequently accessed data to reduce database load and improve application performance. Key Features: High-Speed Performance: ElastiCache provides sub-millisecond response times, enabling fast data retrieval. Fully Managed: AWS handles scaling, patching, and maintenance. Data Persistence: ElastiCache supports data persistence for Redis, enabling recovery of cached data in case of a restart. Best For: Caching frequently accessed data to reduce latency. Applications that require high-speed data storage such as session management, real-time analytics, and leaderboards. Pricing: Pricing is based on the type of cache node and the amount of data stored. How to Choose the Right AWS Database Service Selecting the right AWS database service depends on the specific needs of your application. Here are some factors to consider: 1. Data Structure and Type Relational Data: Use Amazon RDS or Aurora for SQL-based applications with structured, relational data. NoSQL Data: For unstructured or semi-structured data, Amazon DynamoDB is a great choice. Data Warehousing: If you need to analyze large volumes of structured data, consider Amazon Redshift. 2. Scalability Automatic Scaling: If your application requires auto-scaling based on traffic, DynamoDB or Aurora Serverless could be ideal. High Performance and Storage: Aurora and Redshift provide robust scalability for high-throughput applications and large datasets. 3. Latency and Performance Low Latency: If you need fast access to frequently used data, Amazon ElastiCache is designed for high-speed performance. Analytics and Complex Queries: For applications with heavy analytical workloads, Amazon Redshift offers high performance for complex queries. 4. Cost Considerations On-Demand and Pay-As-You-Go: AWS offers flexible pricing models for each database service. Evaluate the cost based on the expected traffic and storage requirements. Serverless: DynamoDB and Aurora Serverless are cost-effective for variable workloads where you only pay for what you use. Use Case Examples E-Commerce Application: Database: Amazon RDS or Aurora. Reason: Supports transactional operations, product catalogs, and customer data. Mobile Game Backend: Database: Amazon DynamoDB. Reason: High scalability and low-latency reads/writes for player
Understanding AWS Machine Learning Services and Their Applications
Understanding AWS Machine Learning Services and Their Applications Introduction Amazon Web Services (AWS) has revolutionized the way businesses utilize cloud technologies, and its machine learning (ML) services are no exception. AWS provides a powerful suite of ML services that allow companies of all sizes to harness the power of AI and data analytics. Whether you’re an experienced data scientist or a business owner looking to integrate AI into your operations, AWS’s machine learning tools offer something for everyone. In this blog, we will dive deep into AWS’s Machine Learning services, their features, use cases, and how they can benefit various industries. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how AWS is enabling businesses to innovate with AI and machine learning. What Is Machine Learning? Machine learning refers to the use of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to improve their performance on tasks through experience without being explicitly programmed. In the context of AWS, machine learning can be used to analyze large datasets, predict trends, automate processes, and much more. AWS offers a variety of machine learning services to support everything from data preprocessing and model training to deployment and inference. Overview of AWS Machine Learning Services AWS provides a wide range of machine learning services that cater to different levels of expertise and business needs. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most popular AWS ML services: 1. Amazon SageMaker Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that allows developers, data scientists, and businesses to quickly build, train, and deploy machine learning models. With SageMaker, users can streamline the entire ML workflow, from data labeling to model optimization and deployment. Key Features: Built-in Algorithms: SageMaker comes with pre-built algorithms for common ML tasks, such as image classification and time-series forecasting. Model Training and Tuning: SageMaker provides distributed training, automated hyperparameter optimization, and model tuning. Deployment and Monitoring: Once trained, models can be deployed to real-time endpoints, with built-in monitoring capabilities. Applications: SageMaker is ideal for companies looking to develop custom ML models for a variety of use cases, including fraud detection, recommendation engines, and predictive maintenance. 2. AWS Lambda for Serverless Machine Learning AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that can be used to run code in response to events, without provisioning or managing servers. Lambda supports machine learning workloads by enabling the execution of models and predictions at scale. Key Features: Automatic Scaling: AWS Lambda can automatically scale based on demand. Integration with SageMaker: Lambda can be easily integrated with SageMaker models to trigger inference requests. Cost Efficiency: With pay-as-you-go pricing, Lambda offers a cost-effective solution for running ML models on demand. Applications: Lambda is used for scenarios where you need to trigger machine learning models in response to real-time events, such as processing transactional data or analyzing customer behavior. 3. Amazon Rekognition Amazon Rekognition is a deep learning-based service that provides image and video analysis. This service can be used for object and scene detection, facial analysis, text recognition, and much more. Key Features: Object and Scene Detection: Rekognition can detect and identify objects, scenes, and activities in images and videos. Facial Analysis: Rekognition provides facial recognition and analysis, including age estimation, emotion detection, and gender classification. Text in Images: It can also extract text from images using optical character recognition (OCR). Applications: Rekognition is widely used for security and surveillance, content moderation, retail, and personalized customer experiences. 4. Amazon Comprehend Amazon Comprehend is a natural language processing (NLP) service that uses machine learning to analyze and understand text. It can be used for sentiment analysis, entity recognition, language detection, and more. Key Features: Sentiment Analysis: Comprehend can identify sentiment in text, whether positive, negative, or neutral. Entity Recognition: It can extract key phrases, places, people, and other entities from unstructured text. Custom Classifier: Users can train a custom classifier to detect specific types of entities or sentiments based on their data. Applications: Comprehend is particularly useful in analyzing customer feedback, reviews, social media posts, and other unstructured text data to gain insights into public opinion and sentiment. 5. Amazon Polly Amazon Polly is a text-to-speech service that uses deep learning to synthesize speech from text. It supports multiple languages and voices, providing businesses with a way to create more natural-sounding interactions. Key Features: Multilingual Support: Polly offers a wide range of languages and voices, enabling businesses to reach a global audience. Neural TTS: The neural text-to-speech (NTTS) capability generates high-quality, human-like speech. Custom Voice Models: Polly allows businesses to create custom voice models tailored to their brand. Applications: Polly is used for creating interactive voice applications, accessibility features, automated voice responses, and enhancing multimedia content. Applications of AWS Machine Learning Across Industries Now that we’ve covered some of the key AWS machine learning services, let’s look at how they’re being applied across various industries to drive innovation and efficiency. 1. Healthcare In healthcare, machine learning is used for predictive analytics, patient care optimization, and drug discovery. AWS provides solutions like SageMaker and Comprehend Medical to assist in data analysis, clinical research, and medical imaging. Predictive Analytics: ML models can predict patient outcomes, reduce readmissions, and optimize treatment plans. Medical Imaging: Tools like Rekognition and SageMaker are used to analyze medical images such as X-rays and MRIs, helping doctors make faster, more accurate diagnoses. 2. Retail Retailers are using AWS ML services to personalize customer experiences, forecast demand, and optimize inventory. Services like SageMaker, Rekognition, and Polly are integrated into customer-facing applications to deliver tailored recommendations and better service. Personalization: Using data from customer interactions, ML algorithms suggest personalized products, discounts, and marketing messages. Inventory Management: Predictive models help retailers forecast demand and optimize supply chains. 3. Finance In finance, machine learning is utilized for fraud detection, risk analysis, and algorithmic trading. AWS services such as SageMaker and Lambda are used to build custom models that monitor transaction patterns and detect anomalies. Fraud Detection: ML models can flag suspicious activities and transactions in real-time, helping prevent financial fraud.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of AWS in Various Industries
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of AWS in Various Industries Introduction Amazon Web Services (AWS) has transformed the way businesses manage and scale their IT infrastructure. From startups to large enterprises, organizations across industries are leveraging AWS to drive innovation, streamline operations, and reduce costs. In this blog, we’ll explore several case studies that showcase how AWS has been successfully implemented across various sectors. By examining these real-world examples, we’ll highlight the power of AWS in transforming operations, increasing efficiency, and driving business growth. Whether you’re in retail, healthcare, or finance, these case studies will provide actionable insights on how AWS can be integrated into your organization. AWS in Retail: Netflix’s Global Streaming Platform Background Netflix, a leader in online streaming, faced significant challenges in scaling its infrastructure to meet the demands of millions of global users. As the company grew, so did the complexity of managing its on-premises data centers. To enhance scalability and agility, Netflix turned to AWS for cloud-based solutions that could handle the global demand for its streaming service. The AWS Solution Netflix’s decision to migrate to AWS was driven by the need for a more flexible and scalable infrastructure. The company moved its entire application stack to AWS, including content delivery, video streaming, and customer management. Key AWS services used include: Amazon EC2 for compute power Amazon S3 for storing large volumes of video content Amazon CloudFront for content delivery AWS Lambda for serverless computing Results Scalability: Netflix’s use of AWS enabled it to handle surges in user demand seamlessly, especially during high-traffic events like new show releases. Cost Efficiency: By moving to the cloud, Netflix reduced its dependency on physical data centers, resulting in significant cost savings. Global Reach: AWS helped Netflix expand its streaming services to over 190 countries with minimal latency. AWS in Healthcare: Philips Healthcare’s Cloud-Based Solutions Background Philips Healthcare, a global leader in health technology, faced challenges in managing and analyzing massive amounts of medical data. They needed a secure and scalable cloud infrastructure to support innovations in telemedicine, diagnostics, and patient care. The company chose AWS to develop its cloud-based healthcare solutions. The AWS Solution Philips Healthcare utilizes a variety of AWS services to power its digital health solutions, including: Amazon EC2 for computing power Amazon S3 for scalable storage AWS IoT to collect data from connected medical devices Amazon Redshift for data analytics Philips also used Amazon SageMaker for developing machine learning models that help improve diagnostics and predict patient outcomes. Results Improved Data Security: By using AWS’s HIPAA-eligible services, Philips ensured the secure storage and processing of patient data. Enhanced Analytics: With AWS, Philips can analyze patient data in real time, leading to faster and more accurate diagnostics. Faster Innovation: The scalability of AWS enabled Philips to quickly deploy new healthcare applications and services. AWS in Finance: Capital One’s Digital Transformation Background Capital One, a major player in the banking industry, has been undergoing a digital transformation to improve customer experience and streamline its internal operations. As part of this transformation, Capital One sought a cloud provider that could deliver security, scalability, and agility. The company turned to AWS to migrate its infrastructure to the cloud. The AWS Solution Capital One migrated several key components of its infrastructure to AWS, including: Amazon EC2 and Amazon RDS for running applications and databases Amazon S3 for secure and scalable data storage Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring applications and infrastructure AWS Lambda for serverless computing and automation By using AWS, Capital One moved away from traditional on-premises data centers to a fully cloud-based infrastructure that could easily scale to meet the demands of its millions of customers. Results Faster Product Development: AWS’s agile environment allowed Capital One to innovate and roll out new products more quickly. Increased Security: Capital One benefited from AWS’s robust security features, such as encryption and compliance with industry standards like PCI-DSS. Cost Reduction: Moving to the cloud eliminated the need for costly data centers and allowed for a pay-as-you-go pricing model. AWS in Manufacturing: Siemens’ Industrial IoT Platform Background Siemens, a global leader in manufacturing and automation, wanted to build an Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platform that would enable businesses to monitor and optimize their manufacturing operations. The company needed a scalable and secure cloud infrastructure to support the platform and handle vast amounts of data from industrial equipment. The AWS Solution Siemens turned to AWS to develop its MindSphere IIoT platform, which connects machines, sensors, and other industrial equipment to the cloud. The solution uses several AWS services: Amazon S3 for storing large amounts of sensor data Amazon EC2 for computing and processing data Amazon Kinesis for real-time data streaming AWS IoT Core for managing IoT devices AWS Lambda for serverless computing By leveraging AWS, Siemens was able to provide real-time insights into manufacturing processes, enabling businesses to optimize operations and reduce downtime. Results Operational Efficiency: The MindSphere platform provided businesses with real-time data and insights, leading to improved manufacturing efficiency and reduced costs. Scalability: Siemens was able to scale its IIoT platform to handle data from millions of devices across multiple industries. Predictive Maintenance: Using AWS services like Amazon SageMaker, Siemens developed machine learning models that help predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime. AWS in Media and Entertainment: The New York Times’ Content Delivery Background The New York Times (NYT) needed a cloud infrastructure that could handle massive amounts of content delivery while ensuring fast, reliable, and secure access to users. The company turned to AWS to modernize its infrastructure and provide a better digital experience for readers around the world. The AWS Solution NYT uses several AWS services to support its content delivery: Amazon S3 for storing articles, videos, and images Amazon CloudFront for fast content delivery to users globally AWS Lambda for running code in response to events Amazon RDS for managing database workloads Additionally, NYT leverages AWS Media Services to stream videos and deliver rich multimedia content to readers. Results Improved Performance: AWS helped NYT reduce content load
Building a Secure Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) in AWS: A Step-by-Step Guide
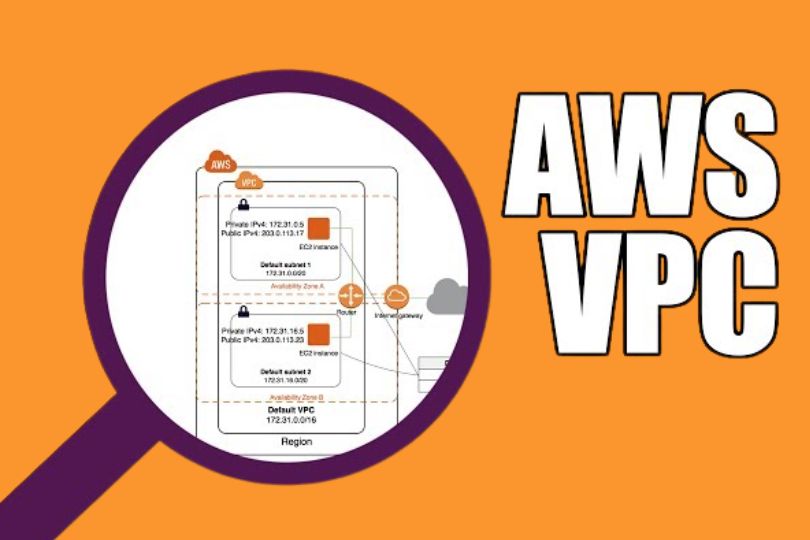
Building a Secure Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) in AWS: A Step-by-Step Guide Introduction As businesses increasingly move to the cloud, security remains a top priority. One of the most effective ways to ensure your AWS infrastructure is secure is by setting up a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). A VPC provides a private, isolated network within AWS, allowing you to control your cloud resources and safeguard your applications. In this blog, we will walk you through the process of building a secure VPC in AWS, including best practices, common pitfalls to avoid, and tips for ensuring robust security. What is a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)? A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a virtual network that you define in AWS. It resembles a traditional on-premises network, but it exists in the cloud. Within a VPC, you can create subnets, configure route tables, manage IP addressing, and set up firewalls. A secure VPC is essential for ensuring that only authorized users and systems can access your cloud resources, while protecting sensitive data from external threats. Key Components of a Secure VPC Before diving into the setup process, let’s review the critical components that make up a VPC: Subnets: Logical divisions of your VPC’s IP address range, where you can deploy AWS resources (like EC2 instances). Subnets can be public (accessible from the internet) or private (isolated from the internet). Internet Gateway (IGW): A gateway that allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet. A secure VPC typically uses an internet gateway for public subnets and restricts private subnets from direct internet access. Route Tables: These determine the traffic flow between subnets and other resources in your VPC. Properly configured route tables are crucial for security and ensuring network traffic follows the correct path. Security Groups: Virtual firewalls that control inbound and outbound traffic to your instances. Security groups are stateful, meaning that if you allow inbound traffic, the response is automatically allowed. Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): These are stateless firewalls that provide an additional layer of security at the subnet level. VPC Peering: Allows two VPCs to communicate with each other privately. This is important for cross-region or cross-account communication. VPN and Direct Connect: These services allow you to securely connect your on-premises network to your AWS VPC using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or dedicated network link. Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Secure VPC in AWS Now that you understand the key components, let’s walk through the steps to set up a secure VPC. Step 1: Define Your Network Architecture Before you create your VPC, it’s important to plan your network architecture. Consider the following: IP Address Range: Choose an appropriate IP range for your VPC (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16). Make sure the range is large enough to accommodate all the resources you plan to deploy. Subnets: Break down your VPC’s IP range into smaller subnets. Typically, you’ll create multiple subnets for different purposes: Public Subnets: For resources that need direct internet access (e.g., load balancers, bastion hosts). Private Subnets: For resources that should not have direct internet access (e.g., databases, application servers). Availability Zones (AZs): AWS VPCs span multiple AZs to provide high availability. Deploy your subnets across at least two AZs for redundancy and fault tolerance. Step 2: Create the VPC Login to the AWS Console: Go to the VPC Dashboard under the Networking & Content Delivery section. Create a New VPC: Select Create VPC and enter the CIDR block (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16). Choose IPv4 CIDR and decide if you need an IPv6 CIDR block. Set Up Subnets: Create subnets for each AZ in your region. For example, create public subnets for load balancers and private subnets for databases. You’ll need to assign a CIDR block for each subnet (e.g., 10.0.1.0/24 for the first subnet, 10.0.2.0/24 for the second). Configure Route Tables: Set up a route table for public subnets that includes a route to the Internet Gateway. For private subnets, you can configure a route table that sends outbound traffic to a NAT Gateway for internet access, or use VPC Peering for communication with other VPCs. Step 3: Attach an Internet Gateway Create an Internet Gateway (IGW): From the VPC Dashboard, go to Internet Gateways, and select Create Internet Gateway. Attach the IGW to Your VPC: Once the IGW is created, attach it to your VPC to allow communication between instances in your public subnet and the internet. Step 4: Set Up Security Groups and NACLs Security Groups: Security groups act as virtual firewalls for your instances. Create security groups with appropriate rules for each type of resource. For public-facing resources (e.g., a web server), allow HTTP/HTTPS traffic from any IP. For private resources (e.g., a database), restrict access to only specific security groups or IP addresses. Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): While security groups are stateful, NACLs are stateless. Apply NACLs at the subnet level to add an extra layer of security. For example, block inbound traffic from all sources to private subnets but allow outbound traffic to the internet through a NAT Gateway. Step 5: Set Up a Bastion Host (Optional) A bastion host is a secure server that you can use to connect to instances in your private subnets. It acts as a jump server, allowing SSH or RDP access to instances in the private subnet without exposing them to the internet directly. Launch an EC2 instance in the public subnet. Configure the security group of the bastion host to allow inbound SSH access from your IP address. Set up the private instances to allow inbound SSH from the bastion host’s security group. Step 6: Enable Monitoring and Logging Once your VPC is set up, it’s essential to monitor and log traffic to ensure security and compliance: AWS CloudWatch: Set up CloudWatch to monitor resource utilization and performance within your VPC. Configure alarms for high CPU usage, low memory, or unusual traffic patterns. VPC Flow Logs: Enable VPC Flow Logs to capture information about IP traffic to and from network interfaces in your VPC. This
How to Migrate Your On-Premises Applications to AWS: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Migrate Your On-Premises Applications to AWS: A Step-by-Step Guide Introduction Cloud computing has become an essential part of modern business strategies. AWS (Amazon Web Services) is one of the most popular cloud platforms, offering a vast array of services to support businesses in their cloud journey. Migrating on-premises applications to AWS allows organizations to benefit from scalability, cost-efficiency, and improved performance. However, a successful migration requires careful planning and execution. In this blog, we will guide you through the entire process of migrating your on-premises applications to AWS, including common challenges, best practices, and tools to make the transition smooth and efficient. Why Migrate to AWS? Migrating your on-premises applications to AWS offers a variety of benefits: Scalability: AWS provides the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring that your applications are always performing optimally. Cost Savings: With AWS, you pay only for what you use, making it a cost-effective solution, especially compared to maintaining expensive on-premises infrastructure. Flexibility: AWS offers a wide range of services, such as compute, storage, and networking, to support different types of workloads. Security: AWS provides robust security features, including data encryption, identity management, and compliance certifications, to protect your applications and data. By migrating to AWS, you not only future-proof your infrastructure but also enhance the overall efficiency and agility of your organization. How to Plan a Successful Migration to AWS Migrating applications to AWS requires careful planning. Here’s a breakdown of the steps involved in the migration process: 1. Assess Your Current Infrastructure Before starting the migration process, assess your existing on-premises environment. Understand the architecture, applications, and workloads that need to be migrated. This includes: Inventory of Applications: Create a list of all applications running on your on-premises servers. Identify critical applications and services that need to be migrated first. Resource Requirements: Determine the compute, storage, and networking resources your applications currently use. This will help you map these resources to the appropriate AWS services. Performance Metrics: Collect performance data such as CPU, memory, and storage usage to ensure that you choose the right AWS resources that meet your application’s needs. Dependencies: Identify interdependencies between applications and databases. Understanding these relationships will help you plan the migration without causing disruptions. 2. Define Your Migration Strategy There are different strategies for migrating to the cloud, and your choice depends on the complexity of the migration and your business needs. AWS provides a framework called the 6 Rs of Cloud Migration to help guide your decision-making: Rehost (Lift and Shift): Move your applications as-is to AWS without making significant changes. This is the quickest migration method and is suitable for applications that require minimal adjustments. Replatform: Make some optimizations or changes to your applications to take advantage of AWS services (e.g., upgrading databases to Amazon RDS). This is often called a “lift-tinker-and-shift” approach. Repurchase: Replace legacy applications with cloud-native applications or services, such as moving to Software as a Service (SaaS). Refactor/Re-architect: Redesign applications to take full advantage of AWS services. This might involve breaking down monolithic applications into microservices. Retire: Decommission outdated applications that are no longer needed or no longer have value for the business. Retain: Keep some applications on-premises while migrating others to the cloud. By choosing the right strategy, you can ensure that your migration is optimized for both cost and performance. 3. Choose the Right AWS Services AWS offers a wide range of services to support your migration. Some of the key services to consider include: Amazon EC2: Virtual servers for running your applications. Amazon RDS: Managed relational databases for SQL workloads. Amazon S3: Scalable object storage for backups and static data. AWS Lambda: Serverless computing for event-driven architectures. Amazon VPC: Virtual private cloud for network isolation and security. Evaluate your application requirements and match them to the appropriate AWS services to ensure efficient resource allocation. 4. Migrate Data and Applications Data migration is a critical part of any cloud migration. Depending on your data size and the amount of downtime allowed, you can choose from several AWS tools: AWS Migration Hub: A centralized place to track the progress of your migration across AWS services. It provides a comprehensive view of your migration journey and helps identify any bottlenecks. AWS Database Migration Service (DMS): This tool helps you migrate databases to AWS with minimal downtime. It supports most major database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle. AWS Snowball: For large-scale data migrations, Snowball is a physical device that securely transfers data to AWS. It’s ideal when transferring terabytes or petabytes of data. AWS DataSync: A managed service that simplifies and accelerates data transfer between on-premises storage and AWS. 5. Test and Validate Your Migration Once your data and applications are moved to AWS, it’s crucial to test and validate the migration. This step ensures that everything is working as expected before going live: Functionality Testing: Ensure that all applications and services are functioning correctly in the AWS environment. Performance Testing: Compare the performance of applications before and after migration to ensure they meet the required standards. Security and Compliance: Check that security configurations, such as encryption and access control, are properly implemented and compliant with industry standards. Post-Migration Best Practices Once your applications are successfully migrated to AWS, there are a few post-migration activities that will help optimize your environment: 1. Optimize for Cost and Performance AWS provides a pay-as-you-go model, but it’s important to optimize your resources to avoid unnecessary costs. Some tips include: Right-sizing: Ensure that the instance types and sizes match your application’s requirements to avoid over-provisioning. Auto Scaling: Use Auto Scaling to automatically adjust resources based on demand. This helps optimize cost and performance by scaling up during traffic spikes and down during periods of low usage. AWS Trusted Advisor: Use AWS Trusted Advisor to identify cost optimization opportunities and other areas for improvement in your AWS environment. 2. Implement Monitoring and Logging Use AWS monitoring and logging tools to ensure the health and performance of your migrated
Maximizing Performance with AWS Elastic Load Balancing: A Guide for Seamless Scalability
Maximizing Performance with AWS Elastic Load Balancing: A Guide for Seamless Scalability Introduction In today’s world of cloud computing, ensuring that your applications remain available, scalable, and resilient is paramount. One of the key services offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) to achieve this is Elastic Load Balancing (ELB). ELB plays a crucial role in distributing incoming traffic across multiple resources, like EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, thereby optimizing application performance and availability. Whether you’re running a small startup’s website or an enterprise-grade application, AWS ELB can help ensure that your traffic is efficiently distributed, providing high availability and fault tolerance. This blog will explore the ins and outs of AWS Elastic Load Balancing, its different types, how it works, and the best practices for maximizing performance using ELB. What is AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)? AWS Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses. ELB ensures that no single resource becomes overwhelmed by traffic, thereby improving both the scalability and availability of applications. There are three main types of load balancers provided by AWS ELB: Application Load Balancer (ALB): Best suited for HTTP/HTTPS traffic, providing advanced routing capabilities for microservices and container-based applications. Network Load Balancer (NLB): Designed for high-performance applications that require low latency, capable of handling millions of requests per second. Classic Load Balancer (CLB): The original AWS load balancer, designed for simple applications but with limited features compared to the newer ALB and NLB. By utilizing these different load balancing options, businesses can enhance their application’s fault tolerance, improve user experience, and scale effortlessly. Benefits of AWS Elastic Load Balancing Here’s how AWS ELB can help maximize performance for your application: 1. High Availability and Fault Tolerance One of the primary benefits of using ELB is the high availability it provides. By automatically distributing traffic to healthy instances across multiple availability zones, ELB ensures that your application remains available even in case of instance failures or traffic spikes. This minimizes downtime and ensures business continuity. Cross-zone Load Balancing: ELB can route traffic to instances in different availability zones within a region. This prevents a single point of failure and enhances availability. Automatic Health Checks: ELB continuously monitors the health of your instances. If an instance becomes unhealthy, traffic is rerouted to healthy instances, ensuring minimal disruption. 2. Scalability AWS ELB integrates seamlessly with Auto Scaling, enabling applications to automatically scale up or down based on demand. Whether it’s a sudden surge in traffic or a drop in user activity, ELB can adapt to these changes by adding or removing instances without manual intervention. Elastic Scaling: When traffic spikes, ELB distributes it across additional instances. Conversely, as demand decreases, instances are removed from the load balancing pool, optimizing resource usage. 3. Security AWS ELB provides several security features that help secure your applications and protect sensitive data: SSL/TLS Termination: With ALB and NLB, you can configure SSL/TLS termination at the load balancer level, offloading the encryption work from your backend instances, thereby improving performance. Integration with AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF): ELB integrates with AWS WAF, which provides an additional layer of protection against common web exploits. Security Groups and Network ACLs: You can configure security groups and network access control lists (ACLs) for fine-grained control over inbound and outbound traffic. 4. Improved User Experience By optimizing traffic distribution, ELB can reduce latency and ensure consistent performance for end users. When combined with other AWS services like Amazon CloudFront for content delivery, users can experience faster load times regardless of their location. Global Load Balancing: With Amazon Route 53 and ELB, you can implement global load balancing to direct users to the closest available region, further improving latency. How Does AWS Elastic Load Balancing Work? AWS Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes incoming traffic to targets such as EC2 instances, containers, or even on-premises servers. Here’s a closer look at how ELB works: Traffic Distribution: When users make a request to your application, the load balancer evaluates the incoming traffic and routes it to the appropriate backend resources based on the configured rules and routing algorithms. Health Monitoring: ELB continuously checks the health of registered targets. If a target is unhealthy, traffic is routed away from that target to ensure availability and performance. Routing Algorithms: ELB uses different routing algorithms based on the type of load balancer: ALB: Routes requests based on URL paths, HTTP methods, or host headers. NLB: Routes traffic based on IP addresses and TCP/UDP protocols. CLB: Uses round-robin or least-connections routing methods, depending on configuration. Types of AWS Elastic Load Balancers As mentioned, AWS offers three types of load balancers, each serving a different use case: 1. Application Load Balancer (ALB) The Application Load Balancer is best for routing HTTP/HTTPS traffic and is highly suitable for applications built using microservices and container-based architectures. Key features of ALB include: Content-based routing: ALB can route traffic based on request URL, headers, or even HTTP methods. Host-based routing: Route traffic based on the domain name or hostname. WebSocket support: ALB supports WebSocket connections, making it ideal for real-time applications. 2. Network Load Balancer (NLB) The Network Load Balancer is designed to handle large volumes of traffic with very low latency. It works at the transport layer (Layer 4) and can handle millions of requests per second. Key features include: Low latency: Ideal for performance-critical applications where every millisecond counts. TCP/UDP support: NLB can handle both TCP and UDP traffic, making it suitable for applications like gaming, VoIP, and real-time communication. Static IP support: NLB provides a static IP for your load balancer, which can simplify firewall management. 3. Classic Load Balancer (CLB) The Classic Load Balancer is the original AWS ELB option and works at both the transport and application layers. While AWS now recommends using ALB or NLB, CLB can still be useful for legacy applications that require simpler configurations. Basic routing: CLB uses simple round-robin or least-connections algorithms to route traffic.
The Role of AWS in Modern DevOps Practices: Enhancing Efficiency and Collaboration
The Role of AWS in Modern DevOps Practices: Enhancing Efficiency and Collaboration Introduction In today’s fast-paced tech landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to accelerate software development, improve quality, and ensure continuous delivery. This is where DevOps comes in. DevOps is a set of practices aimed at bridging the gap between development and operations, focusing on automation, collaboration, and faster delivery cycles. One of the major enablers of DevOps success is cloud computing, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) has proven to be one of the most powerful platforms in facilitating modern DevOps practices. With its wide range of services, AWS provides tools that automate processes, enhance collaboration, and allow teams to focus on delivering value rather than managing infrastructure. In this blog, we’ll explore the role of AWS in DevOps, how it supports automation, scalability, and monitoring, and how organizations can leverage AWS to implement effective DevOps strategies. What is DevOps? Before diving into the AWS-specific tools, let’s clarify what DevOps is and why it’s essential. At its core, DevOps is about fostering a culture of collaboration between development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams. The goal is to streamline the development pipeline, from code creation to production deployment, enabling continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD). Key components of DevOps include: Automation: Automating repetitive tasks such as testing, deployments, and infrastructure provisioning. Collaboration: Enhancing communication between development and operations teams. Monitoring: Tracking the performance of applications in real-time to identify issues early. Speed: Reducing the time it takes to develop, test, and deploy new features. Now, let’s look at how AWS provides the tools and services that help achieve these goals. How AWS Supports DevOps AWS offers a wide range of cloud services that align perfectly with the needs of a modern DevOps pipeline. From automating infrastructure provisioning to facilitating continuous integration, AWS provides the necessary building blocks to implement DevOps practices efficiently. 1. Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Automating Infrastructure with AWS One of the pillars of DevOps is Infrastructure as Code (IaC). With IaC, developers can automate the provisioning and management of infrastructure, ensuring that environments are consistent, repeatable, and scalable. AWS CloudFormation is a key service for IaC. It allows you to define your entire AWS infrastructure using code (in YAML or JSON). CloudFormation templates enable you to version control infrastructure, test changes, and deploy resources at scale. Key benefits of AWS CloudFormation for DevOps: Consistent environments: Create identical environments for development, testing, and production. Version-controlled infrastructure: Maintain history and easily roll back to previous configurations. Automation: Automate provisioning, scaling, and management of resources, reducing human errors. 2. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are essential practices for ensuring quick and reliable software delivery. AWS offers several services to implement CI/CD pipelines effectively: AWS CodePipeline: Automates the workflow for building, testing, and deploying applications. With CodePipeline, you can define the stages of your software release process, such as source, build, test, and deploy, and then automate the transitions between these stages. AWS CodeBuild: A fully managed build service that compiles code, runs tests, and produces software packages. CodeBuild integrates with CodePipeline to automatically trigger builds as part of your deployment process. AWS CodeDeploy: Automates code deployment to various environments, such as EC2 instances, Lambda functions, and on-premises servers. CodeDeploy ensures that updates happen without downtime and with minimal manual intervention. By integrating CodePipeline, CodeBuild, and CodeDeploy, AWS provides an end-to-end solution for implementing CI/CD pipelines that help teams deliver software faster and more reliably. 3. Monitoring and Logging: Ensuring Continuous Feedback Continuous monitoring is a critical component of DevOps, as it ensures teams have real-time visibility into the performance of their applications and infrastructure. AWS offers several services to help monitor applications and resources: Amazon CloudWatch: Provides real-time monitoring of AWS resources and applications. CloudWatch allows you to set up custom alarms for critical metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and error rates. These alarms can trigger automated responses, such as scaling instances or notifying teams of issues. AWS X-Ray: A tool that helps developers analyze and debug distributed applications. X-Ray helps identify performance bottlenecks, errors, and latencies in microservices architectures, making it easier for DevOps teams to resolve issues faster. AWS CloudTrail: Logs all API calls made within your AWS environment, enabling visibility into changes to your resources. This is essential for auditing and ensuring security compliance. Having a robust monitoring setup with CloudWatch, X-Ray, and CloudTrail enables teams to receive continuous feedback, detect issues early, and improve the reliability of their systems. 4. Containerization and Orchestration: Simplifying Deployment with AWS As DevOps evolves, containerization has become a key practice for achieving portability and scalability in applications. AWS provides several services to support container-based deployments: Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS): A fully managed container orchestration service that allows you to run and scale Docker containers easily. ECS integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, enabling automated deployments in a secure environment. Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS): A managed service for running Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration platform. EKS automates many aspects of Kubernetes management, making it easier to deploy and scale containerized applications. AWS Fargate: A serverless compute engine for containers. Fargate allows you to run containers without managing the underlying EC2 instances. This is ideal for DevOps teams looking to simplify infrastructure management while maintaining scalability. By leveraging AWS containerization services, DevOps teams can deploy applications consistently, scale them as needed, and automate many aspects of the deployment pipeline. Best Practices for Implementing DevOps with AWS While AWS provides all the tools needed for DevOps success, it’s important to follow best practices to ensure that your processes are efficient, scalable, and secure. 1. Adopt a Microservices Architecture Microservices architecture aligns well with DevOps principles by breaking down applications into smaller, more manageable services. This allows for easier deployment, scaling, and independent service updates. With AWS, you can leverage services like ECS, EKS, and Lambda (for serverless computing) to manage microservices more efficiently. 2. Automate Everything DevOps is all about
Using AWS CloudFormation for Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
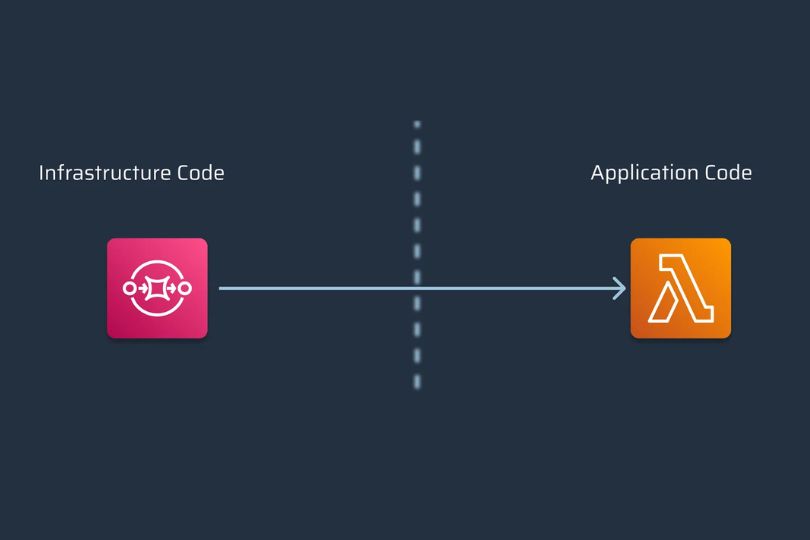
Using AWS CloudFormation for Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Introduction In today’s rapidly evolving cloud landscape, automation is key to scaling and managing infrastructure efficiently. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) has revolutionized how organizations deploy, manage, and scale resources, enabling consistency, speed, and improved collaboration. Among the various IaC tools available, AWS CloudFormation stands out as one of the most powerful and popular solutions. It allows you to define your AWS resources in a declarative way, reducing the complexity of managing cloud infrastructure. But what exactly is CloudFormation, and how can you leverage it for your infrastructure needs? In this blog, we’ll explore AWS CloudFormation, how it works, its key features, and provide actionable tips on how to use it effectively for automating your infrastructure deployment on AWS. What is AWS CloudFormation? AWS CloudFormation is a service that helps you define and provision AWS infrastructure resources using code, or more specifically, through JSON or YAML templates. These templates describe the AWS resources needed for your application, such as EC2 instances, S3 buckets, RDS databases, and more. With CloudFormation, you can: Automate the provisioning and management of AWS resources. Ensure consistency and repeatability in your infrastructure setup. Maintain version control for your infrastructure templates, just like you do with application code. Easily deploy complex environments with a single command. CloudFormation helps reduce the manual effort needed for managing cloud resources, allowing you to focus on building and running your application rather than configuring the infrastructure manually. Key Benefits of Using AWS CloudFormation for IaC 1. Simplified Infrastructure Management CloudFormation simplifies infrastructure management by enabling you to declare the desired state of your infrastructure. Instead of logging into the AWS console and manually configuring resources, you define your setup in a template and let CloudFormation handle the rest. 2. Version Control and Collaboration With CloudFormation, your infrastructure configuration is stored as code. This makes it possible to track changes, revert to previous versions, and collaborate effectively with team members. By using a source control system (like Git), you can manage the lifecycle of your infrastructure similarly to application code. 3. Consistency and Reliability By using CloudFormation templates, you ensure that your infrastructure is always deployed in a consistent manner, whether you are deploying to a test, staging, or production environment. Templates help reduce the risk of human error in manual configurations. 4. Scalable Infrastructure CloudFormation integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, enabling you to scale your infrastructure as your application grows. Whether you’re provisioning a single EC2 instance or an entire architecture, CloudFormation makes it easy to scale resources up or down in a repeatable manner. 5. Cost Efficiency CloudFormation automates the creation and deletion of AWS resources. This helps you to provision only the resources you need, minimizing unnecessary costs. Additionally, it allows for stack deletion, which automatically removes all associated resources when no longer needed, further reducing wastage. How AWS CloudFormation Works At its core, CloudFormation works by using templates that define the AWS resources needed for your application. These templates are in either JSON or YAML format and can be created manually or generated using the AWS Management Console or AWS CLI. When you run a CloudFormation template, AWS automatically provisions the necessary resources in the correct order, taking care of dependencies and making sure that everything is configured as per the template. The infrastructure is referred to as a stack, and you can easily create, update, and delete stacks. Basic CloudFormation Workflow: Create Template: Write a CloudFormation template describing your desired infrastructure. Launch Stack: Use the AWS Console, AWS CLI, or AWS SDKs to create a stack based on the template. Resource Creation: CloudFormation provisions resources such as EC2 instances, load balancers, databases, etc. Monitor and Manage: Use the AWS Console or CLI to track the status and events of your stack. Updates or deletions can be performed as needed. Stack Deletion: When the infrastructure is no longer needed, you can delete the stack, which also removes all associated resources. CloudFormation Template Structure CloudFormation templates follow a defined structure that consists of several sections. Below is an overview of the primary components: Resources: The main section of the template, where the actual AWS resources (e.g., EC2 instances, VPCs, S3 buckets) are defined. Parameters: Allows users to specify values when creating a stack. For instance, you can define parameters for EC2 instance types or Amazon Machine Images (AMIs). Outputs: Defines the output values that CloudFormation returns after the stack is created, such as the public IP address of an EC2 instance. Mappings: Define custom values to be used for lookups in the template, such as mapping region names to specific AMI IDs. Conditions: Define conditions that control whether certain resources are created or certain properties are applied. Metadata: Can be used to include additional information about the resources defined in the template. How to Create a CloudFormation Template Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a simple CloudFormation template to deploy an EC2 instance: Step 1: Write the Template For this example, we’ll use YAML format. AWSTemplateFormatVersion: ‘2010-09-09’ Resources: MyEC2Instance: Type: ‘AWS::EC2::Instance’ Properties: InstanceType: t2.micro ImageId: ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0 # Replace with your desired AMI ID KeyName: MyKeyPair Step 2: Validate the Template Before launching the template, it’s important to validate it to ensure there are no syntax errors. You can do this in the AWS Console or through the CLI using: aws cloudformation validate-template –template-body file://template.yaml Step 3: Launch the Stack Once your template is validated, you can launch a stack using the AWS Management Console, CLI, or AWS SDKs. For the CLI, use: aws cloudformation create-stack –stack-name MyStack –template-body file://template.yaml Step 4: Monitor and Manage the Stack After launching the stack, you can monitor its progress in the AWS Console or by using the CLI: aws cloudformation describe-stacks –stack-name MyStack Advanced CloudFormation Features 1. Change Sets Change Sets allow you to preview changes before applying them to a stack. This is useful for understanding how modifications will affect your infrastructure. 2. StackSets StackSets allow you to manage CloudFormation stacks across multiple